1,将1-9入队列
2,出队列
3,进栈
4,出栈
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include "stack.h";
#define Capacity 9
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
}node;
//定义一个链队列
typedef struct LinkQueue {
node* front; //队首结点
node* rear; //队尾结点
}LQ;
//初始化空链队列
LQ initLQ(LQ LQ) {
LQ.front = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));
LQ.front->data = -1;
LQ.front->next = NULL;
LQ.rear = LQ.front; //队首结点和队尾结点是同一个结点
return LQ;
}
//遍历打印出栈中的全部元素
void showStack(node* LS) {
printf("链栈中的元素是:
");
node* tmp;
for (tmp = LS; tmp != NULL; tmp = tmp->next) { //遍历时,注意tmp!=NULL,不是 tmp->next!=NULL,前者可以遍历到栈底结点,后者栈底结点遍历不到
printf("%d ", tmp->data);
}
printf("
");
}
//进栈
node* PushStack(node* LS ,int elem) { //LS是栈顶结点
node* new_node = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node)); //创建一个结点
if (new_node == NULL) {
printf("创建链栈结点失败
");
exit(0);
}
else {
new_node->data = elem;
new_node->next = LS; //给新结点的指针域赋值,新结点指向当前栈顶结点
LS = new_node; //新结点成为新的栈顶结点
//printf("将%d压入链栈后,栈顶元素是:%d
", i, LS2->data);
}
return LS;
}
//出栈
void PopStack(node* LS) {
while (LS != NULL) {
node* tmp = LS;
LS = tmp->next;
printf("出栈元素是:%d
", tmp->data);
free(tmp);
printf("栈顶元素是:%d
", LS->data);
}
}
//入队列
LQ pushQueue(LQ LQ) {
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) {
node* new_node = (node*)malloc(sizeof(node));//生成新结点
new_node->data = i;
new_node->next = NULL;
LQ.rear->next = new_node; //在队尾结点处插入新结点
LQ.rear = new_node;//队尾结点后移
}
return LQ;
}
//出队列
node* popQueue(LQ LQ,node* LS) {
while (LQ.front != LQ.rear) {
printf("出队结点是:%d
", LQ.front->next->data); //从入队第一个元素开始打印
LS = PushStack(LS, LQ.front->next->data); //出队元素进栈
showStack(LS);
//PopStack(LS);
node* tmp = LQ.front;
LQ.front = LQ.front->next;
free(tmp);
}
free(LQ.front);
return LS;
}
//打印队列全部元素
void showLQ(LQ LQ) {
node* tmp = LQ.front;
while (tmp != NULL) {
printf("%d ", tmp->data);
tmp = tmp->next;
}
printf("
");
}
void main() {
struct LinkQueue myLQ;
node* mystack = NULL;
myLQ.front = myLQ.rear = NULL;
myLQ = initLQ(myLQ);
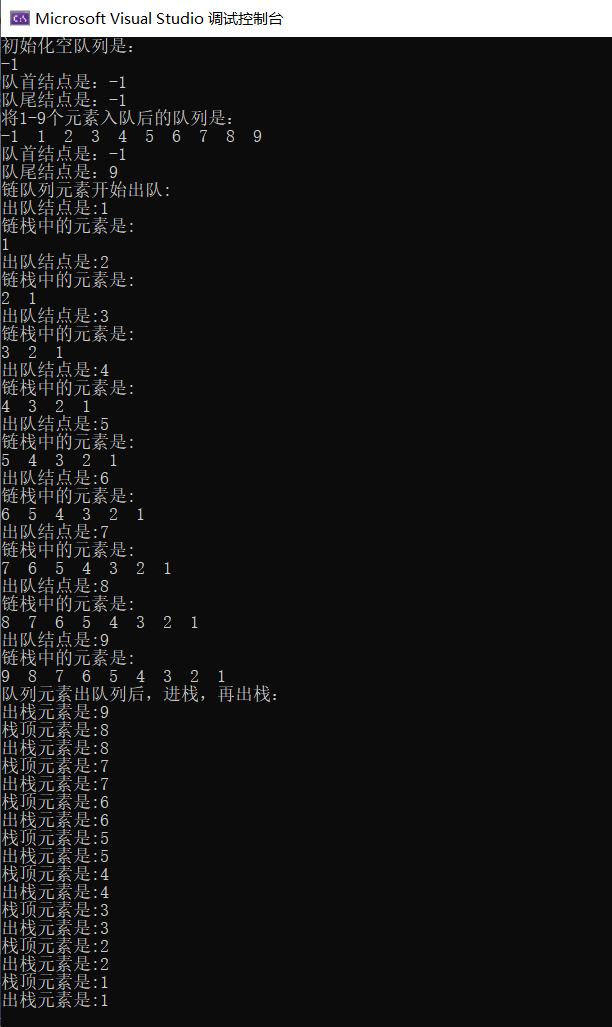
printf("初始化空队列是:
");
printf("%d
", myLQ.front->data);
printf("队首结点是:%d
", myLQ.front->data);
printf("队尾结点是:%d
", myLQ.rear->data);
myLQ = pushQueue(myLQ);
printf("将1-9个元素入队后的队列是:
");
showLQ(myLQ);
printf("队首结点是:%d
", myLQ.front->data);
printf("队尾结点是:%d
", myLQ.rear->data);
printf("链队列元素开始出队:
");
mystack=popQueue(myLQ,mystack);
printf("队列元素出队列后,进栈,再出栈:
");
PopStack(mystack);
}