简介
java多线程中可以使用synchronized关键字来实现线程间同步互斥,但在jdk1.5中新增加了ReentrantLock类也能实现同样的效果,并且在扩展功能上也更加强大,比如具有嗅探锁定、多路通知分支等功能,并且使用上比synchronized更加灵活。
如何使用ReentrantLock
主要是lock.lock()和lock.unlock()两个方法
1 public class MyService implements Runnable { 2 3 protected ReentrantLock lock; 4 5 public MyService(ReentrantLock lock){ 6 this.lock = lock; 7 } 8 9 public void run() { 10 lock.lock(); 11 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i); 13 try { 14 Thread.sleep(1000); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 } 19 lock.unlock(); 20 } 21 22 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 10 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 11 new Thread(new MyService(lock)).start(); 12 } 13 } 14 }
Thread-0 0 Thread-0 1 Thread-0 2 Thread-0 3 Thread-0 4 Thread-1 0 Thread-1 1 Thread-1 2 Thread-1 3 Thread-1 4 Thread-2 0 Thread-2 1 Thread-2 2 Thread-2 3 Thread-2 4 Thread-3 0 Thread-3 1 Thread-3 2 Thread-3 3 Thread-3 4
使用Condition类实现wait、notify的功能
Condition类也是jdk1.5里出来的,它能实现synchronized和wait、notify搭配的功能,另外比后者更灵活,Condition可以实现多路通知功能,也就是在一个Lock对象里可以创建多个Condition(即对象监视器)实例,线程对象可以注册在指定的Condition中,从而可以有选择的进行线程通知,在调度线程上更加灵活。
而synchronized就相当于整个Lock对象中只有一个单一的Condition对象,所有的线程都注册在这个对象上。线程开始notifyAll时,需要通知所有的WAITING线程,没有选择权,会有相当大的效率问题。
使用Condition为什么会报java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException异常
还是刚才的代码,稍作改动
1 public class MyService implements Runnable { 2 3 protected ReentrantLock lock; 4 protected Condition condition; 5 6 public MyService(ReentrantLock lock,Condition condition){ 7 this.lock = lock; 8 this.condition = condition; 9 } 10 11 public void run() { 12 // lock.lock(); 13 try { 14 condition.await(); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 17 e1.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i); 21 try { 22 Thread.sleep(1000); 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 // lock.unlock(); 28 } 29 30 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 10 Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 11 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { 12 new Thread(new MyService(lock,condition)).start(); 13 } 14 } 15 }
Exception in thread "Thread-0" Exception in thread "Thread-1" Exception in thread "Thread-2" Exception in thread "Thread-3" java.lang.IllegalMonitorStateException at java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock$Sync.tryRelease(Unknown Source) at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.release(Unknown Source) at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.fullyRelease(Unknown Source) at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer$ConditionObject.await(Unknown Source) at ww.MyService.run(MyService.java:26) at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source)
报错的异常信息是监视器出错,原因是在调用condition.await()之前是要先调用lock.lock()来获得同步监视器。
正确使用Condition类
1 public class MyService implements Runnable { 2 3 protected ReentrantLock lock; 4 protected Condition condition; 5 6 public MyService(ReentrantLock lock,Condition condition){ 7 this.lock = lock; 8 this.condition = condition; 9 } 10 11 public void await(){ 12 try { 13 lock.lock(); 14 System.out.println("await time is "+System.currentTimeMillis()); 15 condition.await(); 16 System.out.println("after await info..."); 17 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 18 e1.printStackTrace(); 19 } finally { 20 lock.unlock(); 21 } 22 } 23 24 public void signal(){ 25 try { 26 lock.lock(); 27 System.out.println("signal time is "+System.currentTimeMillis()); 28 condition.signal(); 29 } finally { 30 lock.unlock(); 31 } 32 } 33 34 public void run() { 35 await(); 36 } 37 38 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 10 Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 11 MyService service = new MyService(lock,condition); 12 new Thread(service).start(); 13 try { 14 Thread.sleep(3000); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 service.signal(); 19 } 20 }
await time is 1501142954379 signal time is 1501142957381 after await info...
成功实现等待通知模式,整理一下,下表的方法功能是对应的
|
Object类 |
Condition类 |
|
Wait() |
Await() |
|
Wait(long timeout) |
Await(long time,TimeUnit unit) |
|
Notify() |
Signal() |
|
notifyAll() |
signalAll() |
使用多个Condition实现通知部分线程
1 public class MyService implements Runnable { 2 3 protected ReentrantLock lock; 4 protected Condition conditionA; 5 protected Condition conditionB; 6 7 public MyService(ReentrantLock lock,Condition conditionA,Condition conditionB){ 8 this.lock = lock; 9 this.conditionA = conditionA; 10 this.conditionB = conditionB; 11 } 12 13 public void await_A(){ 14 try { 15 lock.lock(); 16 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" await_A time is "+System.currentTimeMillis()); 17 conditionA.await(); 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" after await_A info..."); 19 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 20 e1.printStackTrace(); 21 } finally { 22 lock.unlock(); 23 } 24 } 25 26 public void await_B(){ 27 try { 28 lock.lock(); 29 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" await_B time is "+System.currentTimeMillis()); 30 conditionB.await(); 31 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" after_B await info..."); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e1) { 33 e1.printStackTrace(); 34 } finally { 35 lock.unlock(); 36 } 37 } 38 39 public void signal_A(){ 40 try { 41 lock.lock(); 42 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" signal_A time is "+System.currentTimeMillis()); 43 conditionA.signal(); 44 } finally { 45 lock.unlock(); 46 } 47 } 48 49 public void signal_B(){ 50 try { 51 lock.lock(); 52 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" signal_B time is "+System.currentTimeMillis()); 53 conditionB.signal(); 54 } finally { 55 lock.unlock(); 56 } 57 } 58 59 public void run() { 60 String tname = Thread.currentThread().getName(); 61 if (tname.equals("A")) { 62 await_A(); 63 } else if (tname.equals("B")) { 64 await_B(); 65 } 66 } 67 68 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 10 11 Condition conditionA = lock.newCondition(); 12 Condition conditionB = lock.newCondition(); 13 MyService service = new MyService(lock,conditionA,conditionB); 14 15 Thread tA = new Thread(service); 16 tA.setName("A"); 17 tA.start(); 18 19 Thread tB = new Thread(service); 20 tB.setName("B"); 21 tB.start(); 22 23 try { 24 Thread.sleep(3000); 25 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 26 e.printStackTrace(); 27 } 28 29 service.signal_A(); 30 } 31 }
A await_A time is 1501482321344 B await_B time is 1501482321346 main signal_A time is 1501482324344 A after await_A info...
可以看到只唤醒了A线程。。。
一对一的生产者消费者
1 /** 2 * 生产者和消费者一对一 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class MyService { 7 8 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 9 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 10 protected boolean hasValue = false; 11 12 public void set(){ 13 try { 14 lock.lock(); 15 while (hasValue == true) { 16 condition.await(); 17 } 18 System.out.println("★"); 19 hasValue = true; 20 condition.signal(); 21 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 22 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } finally { 25 lock.unlock(); 26 } 27 } 28 29 public void get(){ 30 try { 31 lock.lock(); 32 while (hasValue == false) { 33 condition.await(); 34 } 35 System.out.println("☆"); 36 hasValue = false; 37 condition.signal(); 38 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 39 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 40 e.printStackTrace(); 41 } finally { 42 lock.unlock(); 43 } 44 } 45 46 }
1 /** 2 * 生产者 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Producer implements Runnable { 7 8 protected MyService myService; 9 10 public Producer(MyService myService) { 11 super(); 12 this.myService = myService; 13 } 14 15 public void run() { 16 for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) { 17 myService.set(); 18 } 19 } 20 21 }
1 /** 2 * 消费者 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Customer implements Runnable { 7 8 protected MyService myService; 9 10 public Customer(MyService myService) { 11 super(); 12 this.myService = myService; 13 } 14 15 public void run() { 16 for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE; i++) { 17 myService.get(); 18 } 19 } 20 21 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 MyService myService = new MyService(); 10 Producer p = new Producer(myService); 11 Customer c = new Customer(myService); 12 13 new Thread(p).start(); 14 new Thread(c).start(); 15 16 } 17 }
打印结果

多对多的生产者消费者
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 MyService myService = new MyService(); 10 11 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 12 new Thread(new Producer(myService)).start(); 13 new Thread(new Customer(myService)).start(); 14 } 15 16 } 17 }
1 /** 2 * 生产者和消费者多对多 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class MyService { 7 8 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 9 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 10 protected boolean hasValue = false; 11 12 public void set(){ 13 try { 14 lock.lock(); 15 while (hasValue == true) { 16 System.out.println("有可能★连续打印"); 17 condition.await(); 18 } 19 System.out.println("★"); 20 hasValue = true; 21 condition.signalAll(); 22 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 23 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } finally { 26 lock.unlock(); 27 } 28 } 29 30 public void get(){ 31 try { 32 lock.lock(); 33 while (hasValue == false) { 34 System.out.println("有可能☆连续打印"); 35 condition.await(); 36 } 37 System.out.println("☆"); 38 hasValue = false; 39 condition.signalAll(); 40 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 41 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } finally { 44 lock.unlock(); 45 } 46 } 47 48 }
要注意的是由于现在是多个生产者消费者,所以condition.signal()要改为condition.signalAll(),其它代码不变。

查看打印结果,发现★和☆总是间隔打印,但是 有可能★连续打印 和 有可能☆连续打印 却有可能连续打印,这是因为改为signalAll后唤醒的是所有线程,有可能再次把自己唤醒,所以会出现这种情况。
公平锁与非公平锁
公平锁表示线程获取锁的顺序是按照线程加锁的顺序来分配的,而非公平锁是一种抢占机制,随机的。
还是上面的代码,给ReentrantLock换个有isFair参数的构造方法,new ReentrantLock(isFair) true就是公平锁,false就是非公平锁。再给打印的语句加上线程名,当为true时,线程是按顺序打印,为false时随机打印。


方法getHoldCount()的使用
getHoldCount()表示当前线程获取锁的个数
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); 3 public void method1(){ 4 try { 5 lock.lock(); 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程保持lock锁的个数:"+lock.getHoldCount()+" method1"); 7 method2(); 8 } catch (Exception e) { 9 e.printStackTrace(); 10 } finally { 11 lock.unlock(); 12 } 13 } 14 15 public void method2(){ 16 try { 17 lock.lock(); 18 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程保持lock锁的个数:"+lock.getHoldCount()+" method2"); 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } finally { 22 lock.unlock(); 23 } 24 } 25 }
1 public class ThreadA extends Thread { 2 3 protected MyService myService; 4 5 public ThreadA(MyService myService) { 6 super(); 7 this.myService = myService; 8 } 9 10 public void run() { 11 myService.method1(); 12 } 13 14 }
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyService myService = new MyService(); 4 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 5 } 6 }
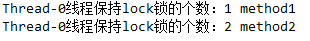
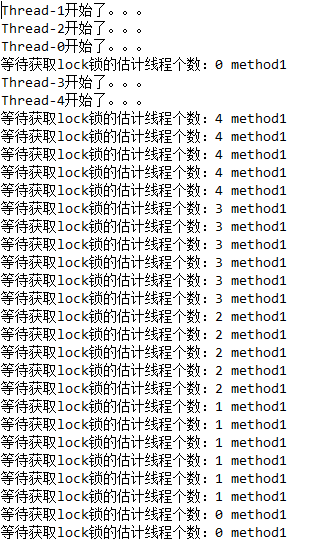
getQueueLength()方法使用
getQueueLength()表示等待获取lock锁的估计线程个数。
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 3 4 public void getql(){ 5 System.out.println("等待获取lock锁的估计线程个数:"+lock.getQueueLength()+" method1"); 6 } 7 8 public void synmethod(){ 9 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始了。。。"); 10 lock.lock(); 11 try { 12 Thread.sleep(5000); 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 lock.unlock(); 17 } 18 }
1 public class ThreadA extends Thread { 2 protected MyService myService; 3 4 public ThreadA(MyService myService) { 5 super(); 6 this.myService = myService; 7 } 8 9 public void run() { 10 myService.synmethod(); 11 } 12 }
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyService myService = new MyService(); 4 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 5 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 6 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 7 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 8 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 9 while (true) { 10 myService.getql(); 11 try { 12 Thread.sleep(900); 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 } 17 } 18 }
getWaitQueueLength(condition)的用法
getWaitQueueLength(condition) 表示返回等待与此锁相关的给定条件condition的线程估计数。比如有3个线程都执行了同一个condition的await方法,那么调用getWaitQueueLength(condition)返回的就是3.
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 3 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 4 protected Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition(); 5 6 7 public void synmethod(){ 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始了。。。"); 9 lock.lock(); 10 System.out.println("进入lock锁与condition关联的的估计线程个数:"+lock.getWaitQueueLength(condition)); 11 System.out.println("进入lock锁与condition1关联的的估计线程个数:"+lock.getWaitQueueLength(condition1)); 12 System.out.println(""); 13 try { 14 if (!Thread.currentThread().getName().contains("2")) { 15 condition.await(); 16 }else{ 17 condition1.await(); 18 } 19 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 lock.unlock(); 23 } 24 }
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyService myService = new MyService(); 4 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 5 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 6 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 7 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 8 new ThreadA(myService).start(); 9 } 10 }

hasQueuedThread(thread)和hasQueuedThreads()的使用
hasQueuedThread(thread)返回的是线程thread是否在等待获取lock锁
hasQueuedThreads()返回的是是否有线程正在等待获取lock锁
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 3 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 4 5 public void hasa(Thread thread){ 6 if (lock.hasQueuedThread(thread)) { 7 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"正在等待获取lock锁。。。"); 8 }else{ 9 System.out.println(thread.getName()+"不在等待获取lock锁。。。"); 10 } 11 System.out.println("是否有线程在等待获取lock锁:"+lock.hasQueuedThreads()); 12 System.out.println(""); 13 } 14 15 public void synmethod(){ 16 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始了。。。"); 17 lock.lock(); 18 19 if (Thread.currentThread().getName().contains("1")) { 20 try { 21 condition.await(); 22 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } 25 } 26 try { 27 Thread.sleep(15000); 28 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 29 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 30 e.printStackTrace(); 31 } 32 lock.unlock(); 33 } 34 }
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyService myService = new MyService(); 4 ThreadA ta = new ThreadA(myService); 5 ta.start(); 6 ThreadA tb = new ThreadA(myService); 7 tb.start(); 8 while (true) { 9 myService.hasa(ta); 10 myService.hasa(tb); 11 System.out.println(""+ta.getName()); 12 try { 13 Thread.sleep(1000); 14 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 15 e.printStackTrace(); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 }

hasWaiters(condition)的用法
hasWaiters(condition)表示是否有线程进入了lock锁与condition相关联的等待中。
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 3 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 4 5 public void synmethod(){ 6 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始了。。。"); 7 lock.lock(); 8 9 System.out.println("是否有线程进入了lock锁与condition相关联的等待中:"+lock.hasWaiters(condition)); 10 if (Thread.currentThread().getName().contains("0")) { 11 try { 12 condition.await(); 13 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 14 e.printStackTrace(); 15 } 16 } 17 try { 18 Thread.sleep(3000); 19 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 lock.unlock(); 23 } 24 }
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyService myService = new MyService(); 4 5 ThreadA ta = new ThreadA(myService); 6 ta.start(); 7 8 try { 9 Thread.sleep(3500); 10 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } 13 14 ThreadA tb = new ThreadA(myService); 15 tb.start(); 16 17 } 18 }

方法isFair()、isHeldByCurrentThread()、isLocked()的使用
isFair()判断线程锁是不是公平锁
isHeldByCurrentThread()查询当前线程是否保持此锁定
isLocked()查询此锁定是否由任意线程保持
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); 3 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 4 5 public void synmethod(){ 6 System.out.println("lock锁是不是公平锁:"+lock.isFair()); 7 System.out.println("lock锁定是否由任意线程保持:"+lock.isLocked()); 8 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"是否保持lock锁定:"+lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()); 9 lock.lock(); 10 System.out.println("lock锁定是否由任意线程保持:"+lock.isLocked()); 11 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"是否保持lock锁定:"+lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()); 12 lock.unlock(); 13 } 14 }
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 MyService myService = new MyService(); 4 5 ThreadA ta = new ThreadA(myService); 6 ta.start(); 7 } 8 }

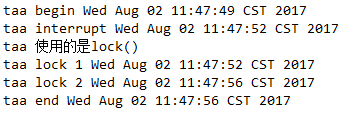
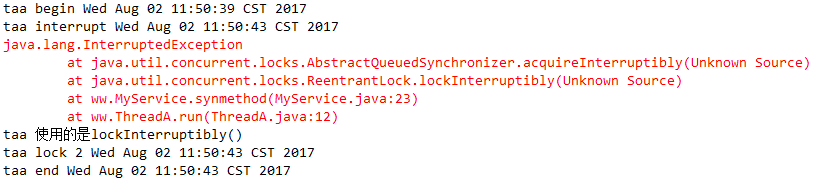
lockInterruptibly()方法的使用
lockInterruptibly()比lock()获取锁之前多了个判断,如果当前线程未被中断,则获取锁定,如果已被中断,则抛出java.lang.InterruptedException异常。
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); 3 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 4 5 public void synmethod(){ 6 try { 7 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" begin "+new Date().toString()); 8 for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE/20; i++) {// 大概会延长7 8s,这里不用sleep延长线程时间,而是这样写,是因为调用线程的interrupt()方法时,如果线程在sleep会报异常 9 Math.random(); 10 } 11 if(new Random().nextInt(5)%2==0){// 随机 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 使用的是lock() "); 13 lock.lock(); 14 }else{ 15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 使用的是lockInterruptibly() "); 16 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 17 } 18 19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" lock 1 "+new Date().toString()); 20 for (int i = 0; i < Integer.MAX_VALUE/20; i++) {// 同上 21 Math.random(); 22 } 23 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 24 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } finally { 27 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" lock 2 "+new Date().toString()); 28 if (lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) { 29 lock.unlock(); 30 } 31 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end "+new Date().toString()); 32 } 33 } 34 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 MyService myService = new MyService(); 9 10 ThreadA taa = new ThreadA(myService); 11 taa.setName("taa"); 12 taa.start(); 13 14 try { 15 Thread.sleep(1500);// 等前面的线程都启动好 16 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 20 System.out.println("taa interrupt "+new Date().toString()); 21 taa.interrupt();// 打标记 这个时候taa还没有进入lock锁里 22 23 } 24 }
代码里采用了随机的处理,有的时候使用的是lock(),有的时候使用的是lockInterruptibly(),多运行几遍就能得到两种结果。
lock.tryLock()、lock.tryLock(timeout, unit)方法使用
lock.tryLock()) 立即返回,获得锁返回true,没获得锁返回false
lock.tryLock(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS) 等待3s,3s后,获得锁返回true,没获得锁返回false
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); 3 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 4 5 public void synmethod(){ 6 try { 7 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进入方法"+new Date().toString()); 8 9 if (lock.tryLock()) {// 立即返回,获得锁返回true,没获得锁返回false 10 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得锁"); 11 } else { 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"没有获得锁"); 13 } 14 15 // if (lock.tryLock(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {// 等待3s,3s后,获得锁返回true,没获得锁返回false 16 // System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获得锁的时间"+new Date().toString()); 17 // Thread.sleep(10000); 18 // } else { 19 // System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"没有获得锁"); 20 // } 21 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"方法结束"+new Date().toString()); 23 } catch (Exception e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 MyService myService = new MyService(); 9 10 ThreadA ta = new ThreadA(myService); 11 ta.setName("ta"); 12 ta.start(); 13 14 ThreadA taa = new ThreadA(myService); 15 taa.setName("taa"); 16 taa.start(); 17 } 18 }
awaitUninterruptibly()方法使用
当在线程等待的时候,如果外部要中断该线程,不会报InterruptedException异常,而await()会报异常
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); 3 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 4 5 public void synmethod(){ 6 try { 7 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进入方法"+new Date().toString()); 8 9 lock.lock(); 10 11 if (new Random().nextInt(5)%2 == 0) { 12 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"走的是await()"); 13 condition.await(); 14 } else { 15 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"走的是awaitUninterruptibly()"); 16 condition.awaitUninterruptibly(); 17 } 18 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } finally { 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"方法结束"+new Date().toString()); 23 lock.unlock(); 24 } 25 } 26 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 MyService myService = new MyService(); 9 10 ThreadA taa = new ThreadA(myService); 11 taa.setName("taa"); 12 taa.start(); 13 14 try { 15 Thread.sleep(1000); 16 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 taa.interrupt();// 打标记 20 } 21 }
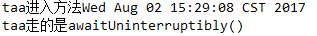
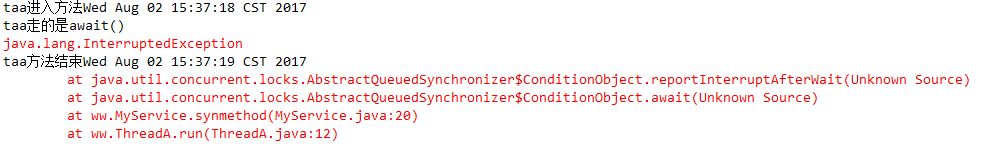
awaitUntil(Time time)方法使用
awaitUntil(Time time)和await()一样会使当前线程进入等待状态,不过它有个截止时间,到了time这个时间,自动唤醒。
1 public class MyService { 2 protected ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); 3 protected Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); 4 5 public void synmethod(){ 6 try { 7 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"进入方法"+new Date().toString()); 8 9 lock.lock(); 10 11 Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); 12 calendar.add(Calendar.SECOND, 10); 13 System.out.println("begin awaitUntil "+new Date().toString()); 14 condition.awaitUntil(calendar.getTime());// 15 System.out.println("after awaitUntil "+new Date().toString()); 16 17 } catch (Exception e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } finally { 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"方法结束"+new Date().toString()); 21 lock.unlock(); 22 } 23 } 24 }
1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 MyService myService = new MyService(); 9 10 ThreadA taa = new ThreadA(myService); 11 taa.setName("taa"); 12 taa.start(); 13 } 14 }

使用Condition实现顺序执行

1 /** 2 * 利用condition实现顺序执行 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class MyService implements Runnable{ 7 protected ReentrantLock lock; 8 protected Condition signalCondition;// 在某个线程里负责等待 9 protected Condition awaitCondition;// 在某个线程里负责唤醒 10 11 public MyService(ReentrantLock lock, Condition signalCondition, Condition awaitCondition) { 12 super(); 13 this.lock = lock; 14 this.signalCondition = signalCondition; 15 this.awaitCondition = awaitCondition; 16 } 17 18 public void print(Condition signalCondition, Condition awaitCondition) throws InterruptedException{ 19 lock.lock(); 20 for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) { 21 for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) { 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i); 23 } 24 System.out.println(""); 25 signalCondition.signal(); 26 awaitCondition.await(); 27 } 28 lock.unlock(); 29 } 30 31 public void run() { 32 try { 33 print(signalCondition, awaitCondition); 34 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 39 }

1 /** 2 * 测试类 3 * @author ko 4 * 5 */ 6 public class Test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); 9 Condition conditionA = lock.newCondition(); 10 Condition conditionB = lock.newCondition(); 11 Condition conditionC = lock.newCondition(); 12 13 MyService myService = new MyService(lock, conditionB, conditionA); 14 15 new Thread(new MyService(lock, conditionB, conditionA),"thread a").start(); 16 new Thread(new MyService(lock, conditionC, conditionB),"thread b").start(); 17 new Thread(new MyService(lock, conditionA, conditionC),"thread c").start(); 18 19 } 20 }

thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
thread a 1
thread a 2
thread a 3
thread b 1
thread b 2
thread b 3
thread c 1
thread c 2
thread c 3
