题目如下:
Given a m x n
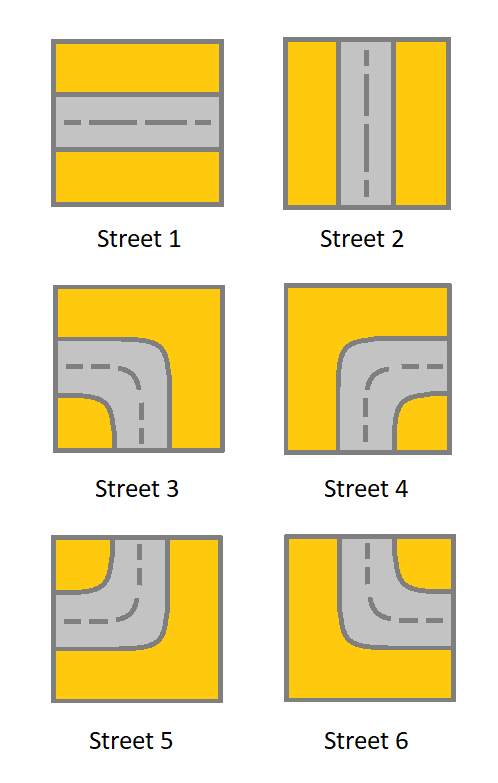
grid. Each cell of thegridrepresents a street. The street ofgrid[i][j]can be:
- 1 which means a street connecting the left cell and the right cell.
- 2 which means a street connecting the upper cell and the lower cell.
- 3 which means a street connecting the left cell and the lower cell.
- 4 which means a street connecting the right cell and the lower cell.
- 5 which means a street connecting the left cell and the upper cell.
- 6 which means a street connecting the right cell and the upper cell.
You will initially start at the street of the upper-left cell
(0,0). A valid path in the grid is a path which starts from the upper left cell(0,0)and ends at the bottom-right cell(m - 1, n - 1). The path should only follow the streets.Notice that you are not allowed to change any street.
Return true if there is a valid path in the grid or false otherwise.
Example 1:
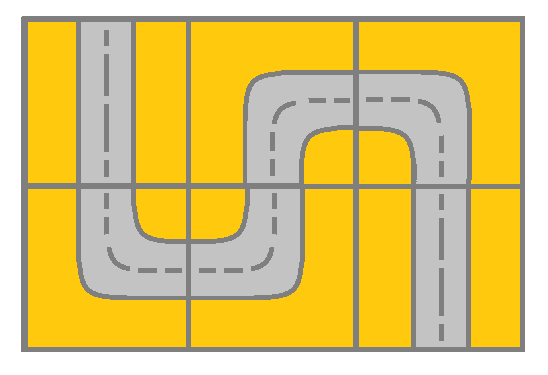
Input: grid = [[2,4,3],[6,5,2]] Output: true Explanation: As shown you can start at cell (0, 0) and visit all the cells of the grid to reach (m - 1, n - 1).Example 2:
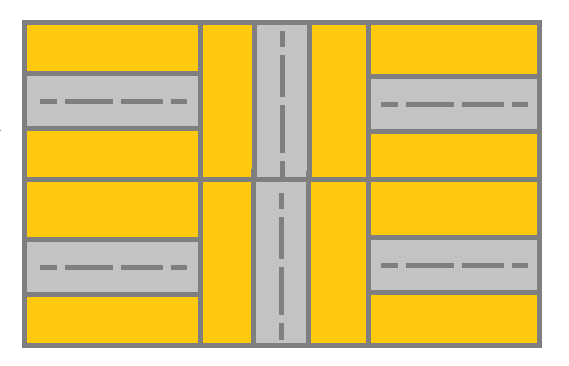
Input: grid = [[1,2,1],[1,2,1]] Output: false Explanation: As shown you the street at cell (0, 0) is not connected with any street of any other cell and you will get stuck at cell (0, 0)Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,1,2]] Output: false Explanation: You will get stuck at cell (0, 1) and you cannot reach cell (0, 2).Example 4:
Input: grid = [[1,1,1,1,1,1,3]] Output: trueExample 5:
Input: grid = [[2],[2],[2],[2],[2],[2],[6]] Output: trueConstraints:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 3001 <= grid[i][j] <= 6
解题思路:本题的关键在于确定移动方向,比如1向左移动可以对接上1,4,6;4向下移动可以对接上2,5,6。另外就是进出的方向,比如从5的左边进去,就只能从上面出去。如果存在符合题目要求的路径,那么这个路径一定是唯一的,确定了这些,只要从起点开始依次尝试即可。
代码如下:
class Solution(object): def hasValidPath(self, grid): """ :type grid: List[List[int]] :rtype: bool """ dic_pair = {} dic_pair[(1,'L')] = [1,4,6] dic_pair[(1, 'R')] = [1,3,5] dic_pair[(2,'D')] = [2,5,6] dic_pair[(2,'U')] = [2,3,4] dic_pair[(3,'L')] = [1,4,6] dic_pair[(3,'D')] = [2,5,6] dic_pair[(4, 'R')] = [1,3,5] dic_pair[(4, 'D')] = [2,5,6] dic_pair[(5, 'U')] = [2,3,4] dic_pair[(5, 'L')] = [1,4, 6] dic_pair[(6, 'U')] = [2,3,4] dic_pair[(6, 'R')] = [1,3,5] dic_dir = {} dic_dir[1] = ['L','R'] dic_dir[2] = ['U', 'D'] dic_dir[3] = ['L', 'D'] dic_dir[4] = ['R', 'D'] dic_dir[5] = ['L', 'U'] dic_dir[6] = ['R', 'U'] queue = [] def verify(): #queue = [] dic_visit = {} dic_visit[(0,0)] = 1 direction = {} direction['R'] = (0,1) direction['L'] = (0, -1) direction['U'] = (-1,0) direction['D'] = (1,0) while len(queue) > 0: x,y,d = queue.pop(0) #print x,y if x == len(grid)-1 and y == len(grid[0]) - 1: return True x1,y1 = direction[d] if x1 + x >= 0 and x1 + x < len(grid) and y + y1 >= 0 and y + y1 < len(grid[0]) and grid[x1 + x][y1 + y] in dic_pair[(grid[x][y], d)] and (x1 + x, y1 + y) not in dic_visit: if d == 'L': reversed_d = 'R' elif d == 'R': reversed_d = 'L' elif d == 'U': reversed_d = 'D' else: reversed_d = 'U' inx = dic_dir[grid[x1 + x][y1 + y]].index(reversed_d) if inx == 0: d1 = dic_dir[grid[x1 + x][y1 + y]][1] else: d1 = dic_dir[grid[x1 + x][y1 + y]][0] queue.append((x1 + x, y1 + y, d1)) dic_visit[(x1 + x, y1 + y)] = 1 return False if grid[0][0] == 1: queue.append((0, 0, 'R')) elif grid[0][0] == 2: queue.append((0, 0, 'D')) elif grid[0][0] == 3: queue.append((0, 0, 'D')) elif grid[0][0] == 4: queue.append((0, 0, 'D')) elif grid[0][0] == 6: queue.append((0, 0, 'R')) return verify()