LINQ,语言集成查询;
LINQ TO SQL,同EF,NHibernate一样,也是一种ORM框架;
1. 入门应用示例:

static public void LinqBasic() { var colors = new[] { "Red", "Orange", "Yellow", "Black", "Purple", "Grenn", "White", "Blue", "Hello World !" }; var query = from color in colors orderby color ascending, color.Length descending where color == "Red" || color.StartsWith("P") && color.Length >= 3 || !color.Any() select color; foreach (var color in query) { Console.WriteLine(color); } }
2. 限定符运算:
Any() //判断是否有元素满足某个条件
All()//判断是否所有的数据都满足某个条件
Contains//判断是否包含某个元素;
3. Set集合的用法:
主要测试了几中常见方法:Distinct(),Except(),Intersect()及Union()

static public void Set() { List<String> htsA = new List<String>() { "Red", "Red", "Black", "White", "White", "Blue" }; List<String> htsB = new List<String>() { "Red", "Red", "Black", "Black" }; IEnumerable<String> htsC = htsA.Distinct(); IEnumerable<String> htsD = htsA.Except(htsB); IEnumerable<String> htsE = htsA.Intersect(htsB); IEnumerable<String> htsF = htsA.Union(htsB); foreach (String ht in htsA) { Console.WriteLine(ht); } }
4. Skip()/SkipWhile() 及 Take()/TakeWhile()
Skip(n):跳过n元素开始读取;
SkipWhile(): 从第一个条件为false的地方开始读取元素,遇到第一个true条件则停止读取;
Take(n): 从第一个元素开始,读取n个元素
TakeWhile(); 从第一个条件为true的地方开始读取元素,遇到第一个false条件则停止读取;

static public void Skip() { var colors = new[] { "Red", "Orange", "Yellow", "Black", "Purple", "Grenn", "White", "Blue", "Hello World !" }; var res = colors.SkipWhile(n => n != "Black"); foreach (var color in res) //foreach (var color in colors.Skip(5)) { Console.WriteLine(color); } } static public void Take() { var colors = new[] { "Red", "Orange", "Yellow", "Black", "Purple", "Grenn", "White", "Blue", "Hello World !" }; var res = colors.TakeWhile(n => n != "Black"); foreach (var color in res) //foreach (var color in colors.Take(5)) { Console.WriteLine(color); } }
5. Select/SelectMany用法:
SelectMany:将嵌套列表合并为一个列表:

static public void Select() { var mat = new[] { new[] {11,12,13,14}, new[] {21,22,23,24}, new[] {31,32,33,34}, new[] {41,42,43,44} }; var query_01 = mat.Select(n => n.ToList()); var query_02 = mat.SelectMany(n => n.ToList()); foreach (var val in query_01) { Console.WriteLine(val); } foreach (var val in query_02) { Console.WriteLine(val); } }
6. Join/GroupJoin用法:
Join(param1,param2,param3,param4): param1:要联接的第一个集合;param2:第一个集合中与第二个集合的关联列;param3:第二个集合中与第一个集合的关联列;param4:返回列的集合(可以对返回列进行重命名)
Group join:适合返回有级别的列表

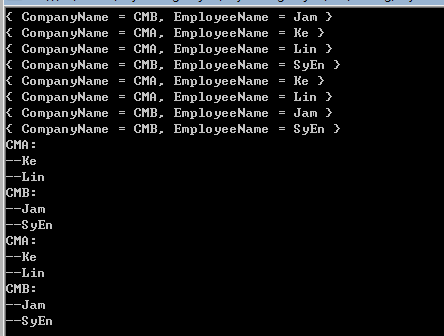
static public void Join() { List<Company> cmyList = new List<Company> { new Company {Id=1,ComName="CMA"}, new Company {Id=2,ComName="CMB"}, }; List<Employee> empList = new List<Employee> { new Employee {CompanyId=2,EmpName="Jam",}, new Employee {CompanyId=1,EmpName="Ke"}, new Employee {CompanyId=1,EmpName="Lin"}, new Employee {CompanyId=2,EmpName="SyEn"}, new Employee {CompanyId=3,EmpName="Kate"} }; var matJoin11 = cmyList.Join(empList, m => m.Id, n => n.CompanyId, (m, n) => new {CompanyName=m.ComName,EmployeeName=n.EmpName}).OrderBy(p => p.EmployeeName); var matJoin12 = from cmy in cmyList join emp in empList on cmy.Id equals emp.CompanyId select new { CompanyName = cmy.ComName, EmployeeName = emp.EmpName }; foreach (var val in matJoin11) { Console.WriteLine(val); } foreach (var val in matJoin12) { Console.WriteLine(val); } var matGJoin21 = cmyList.GroupJoin(empList, m => m.Id, n => n.CompanyId, (m, o) => new { CompanyName = m.ComName,EmployeeName=o.Select(n => n.EmpName)}); var matGJoin22 = (from cmy in cmyList join emp in empList on cmy.Id equals emp.CompanyId into nt select new { CompanyName = cmy.ComName, EmployeeName = nt }).ToList(); foreach (var val in matGJoin21) { Console.WriteLine(val.CompanyName+":"); foreach(var emp in val.EmployeeName) { Console.WriteLine("--"+emp); } } foreach (var val in matGJoin22) { Console.WriteLine(val.CompanyName + ":"); foreach (var emp in val.EmployeeName) { Console.WriteLine("--" + emp.EmpName); } } }
运行结果:
7. Range()/Repeat()/SequenceEqual()
Range(param1,param2) param1:第一个值,默认第二个值为2,依次为3,4,5...; param2:需要生成的元素个数
Repeat()列表复制
SequenceEqual() 列表是否相等(元素个数,每个位置元素内容)的判断

static public void Range() { //Range(param1,param2) param1:第一个值,默认第二个值为2,依次为3,4,5...; param2:需要生成的元素个数 List<int> nl = Enumerable.Range(1, 20).Select(x => x + 2).ToList(); foreach (int i in nl) { Console.WriteLine("{0}",i); } } static public void Repeat() { List<String> hts = new List<String>() { "Red", "Red", "Black", "White", "White", "Blue" }; var nht = Enumerable.Repeat(hts,10).ToList().SelectMany(n => n.ToList()); foreach (var v in nht) { Console.WriteLine(v); } } //Enumerable.Empty:返回具有指定类型参数的空 IEnumerable<T>。 static public void SequenceEqual() { List<String> htA = new List<String>() { "Red", "Red", "Black", "White", "White", "Blue" }; List<String> htB = new List<String>() { "Red", "Red", "Black", "White", "White", "Blue" }; bool b = htA.SequenceEqual(htB); Console.WriteLine(b); }
8. 列表元素操作:First()/FirstOrDefault()/Last()/ElementAt()/Single()

static public void ElementOperation() { List<String> hts = new List<string>() { "Red", "Orange", "Yellow", "Black", "Purple", "Grenn", "White", "Blue"}; Console.WriteLine(hts.First()); Console.WriteLine(hts.FirstOrDefault(color => color.Length>10)); Console.WriteLine(hts.Last()); Console.WriteLine(hts.ElementAt(5)); //Console.WriteLine(hts.Single(color => color.Length>5)); }static public void ElementOperation() { List<String> hts = new List<string>() { "Red", "Orange", "Yellow", "Black", "Purple", "Grenn", "White", "Blue"}; Console.WriteLine(hts.First()); Console.WriteLine(hts.FirstOrDefault(color => color.Length>10)); Console.WriteLine(hts.Last()); Console.WriteLine(hts.ElementAt(5)); //Console.WriteLine(hts.Single(color => color.Length>5)); }
9. GroupBy用法:

static public void GroupBy() { List<String> hts = new List<String>() { "Red", "Red", "Black", "White", "White", "Blue" }; var query = from ht in hts group ht by ht.Substring(0, 1); foreach (var gp in query) { Console.WriteLine("Colors start with "+gp.Key); foreach (var dt in gp) { Console.WriteLine(dt); } } }
10. Union用法:

static public void Union() { var matA = new[] { new[] {11,12,13,14}, new[] {21,22,23,24} }; var matB = new[] { new[] {31,32,33,34}, new[] {41,42,43,44} }; var matJoin = matA.Union(matB); var v = matJoin.SelectMany(n => n.ToList()); foreach (var val in v) { Console.WriteLine(val); } }
11. 类型转换:
Cast():将IEnumerable的元素强制转换为指定的IEnumerable类型;
AsEnumerable():将其他类型转为IEnumerable<T>;
OfType():根据指定类型筛选IEnumerable的元素。

static public void TypeConvert() { var colors = new[] { "Red", "Black", "Green", "Purple", "White", "Blue" }; List<string> hts = colors.AsEnumerable().ToList(); foreach (string s in hts) { Console.WriteLine(s); } Console.WriteLine("The int value in the list is as below:"); ArrayList ays = new ArrayList() { "Red", "Black", "Green", 100, "White", "Blue" }; List<int> sls = ays.OfType<int>().ToList(); foreach (int s in sls) { Console.WriteLine(s); } Console.WriteLine("The new list after convert is as below:"); List<string> sls_new = ays.OfType<string>().ToList(); IEnumerable<string> ays_new = sls_new.Cast<string>(); foreach (string s in ays_new) { Console.WriteLine(s); } }
12.序列合并:
把两个序列合并为一个:

static public void Concat() { List<String> htA = new List<String>() { "Red", "Blue" }; List<String> htB = new List<String>() { "Black", "White" }; List<string> hts = htA.Select(x => x).Concat(htB.Select(y => y)).ToList(); foreach (string ht in hts) { Console.WriteLine(ht); } }
13. 聚合运算:

static public void Aggregate() { List<int> its = new List<int> { 9, 3, 4, 7, 6, 1, 8 }; double avg = its.Average(); int max = its.Max(); int min = its.Min(); int cut = its.Count(); int sum = its.Sum(); Console.WriteLine("Average is {0};", avg); Console.WriteLine("Max is {0};", max); Console.WriteLine("Min is {0};", min); Console.WriteLine("Count is {0};", cut); Console.WriteLine("Sum is {0};", sum); }
至此,关于Linq的基本用法几乎都在这里了,对于更多详细说明,请参见官方文档.
