1. 对象的创建
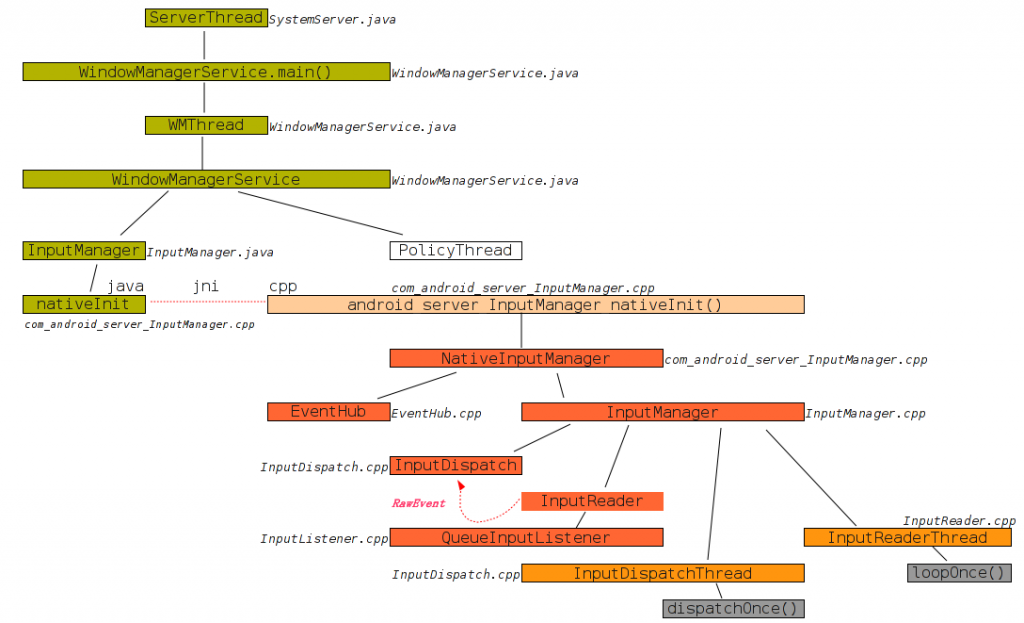
2. 事件的传递
上图中有标示出来,RawEvent是待发出去的事件,InputReader经由QueueInputListener就可以关联到InputDispatch,最后由InputDispatch将事件处理或分发出去。
InputManager::InputManager(
const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,
const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {
mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);
initialize();
}
InputReader::InputReader(const sp<EventHubInterface>& eventHub,
const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,
const sp<InputListenerInterface>& listener) :
mContext(this), mEventHub(eventHub), mPolicy(policy),
mGlobalMetaState(0), mDisableVirtualKeysTimeout(LLONG_MIN), mNextTimeout(LLONG_MAX),
mConfigurationChangesToRefresh(0) {
mQueuedListener = new QueuedInputListener(listener);
...
}
InputManager里创建了InputDispatch和InputReader,就是在此时将这两者关联了起来。以mDispatcher为参数创建了InputReader,mDispatcher就是InputReader的实际监听者,那么InputReader一收到事件就要主动通知监听者mDispatcher把这个事件处理掉。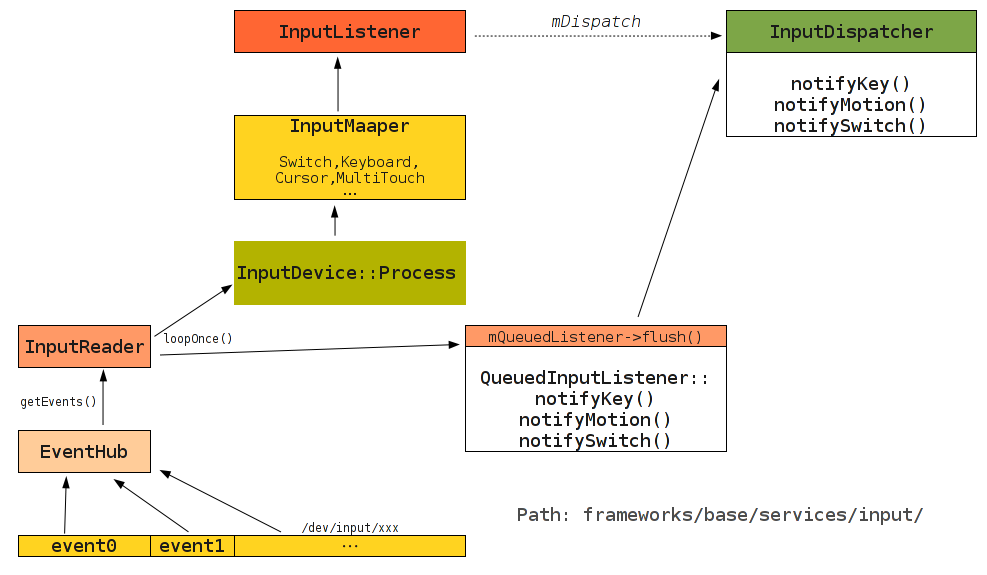
事件的传递过程如图中箭头走向。
2.1. InputReader
InputReader会创建InputReaderThread线程,threadloop()返回true表示该线程会一直执行loopOnce().
bool InputReaderThread::threadLoop() {
mReader->loopOnce();
return true;
}
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
if (count) {
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
} // release lock
// Flush queued events out to the listener.
// This must happen outside of the lock because the listener could potentially call
// back into the InputReader's methods, such as getScanCodeState, or become blocked
// on another thread similarly waiting to acquire the InputReader lock thereby
// resulting in a deadlock. This situation is actually quite plausible because the
// listener is actually the input dispatcher, which calls into the window manager,
// which occasionally calls into the input reader.
mQueuedListener->flush();
}
loopOnce()先用getEvents()从设备文件中读出事件数据,然后进行一些处理。这种处理包括根据事件的类型(EV_KEY, EV_ABS, EV_SW)使用不同的InputMapper来处理事件,最后将事件放到列队中。最后的flush()会调用监听者(实际上是InputDispatch)来处理掉列队中所有的事件。
3. 事件的策略标志policyFlags
Android里事件有许多标志,如flags, policyFlags, metaState等,其中policyFlags用于决定一个事件的策略行为。比如一些特殊按键POWER,VOLUME,HOME等的处理行为在上层策略上不同,就需要对policyFlags设置不同的标志位。
frameworks/base/include/ui/Input.h 文件中定义了policyFlags所有的标志位。
有两个地方会设置policyFlags:
1. EventHub 对每个设备都有一个struct Device结构,每个Device又有自己的KeyMap。EventHub::openDeviceLocked()打开一个设备时会使用loadKeyMapLocked()加载并解析keylayout文件。关于keylayout可以看官方的说明 http://source.android.com/tech/input/key-layout-files.html
比如 frameworks/base/data/keyboards/Generic.kl 这个文件中有:
frameworks/base/include/ui/Input.h 文件中定义了policyFlags所有的标志位。
有两个地方会设置policyFlags:
1. EventHub 对每个设备都有一个struct Device结构,每个Device又有自己的KeyMap。EventHub::openDeviceLocked()打开一个设备时会使用loadKeyMapLocked()加载并解析keylayout文件。关于keylayout可以看官方的说明 http://source.android.com/tech/input/key-layout-files.html
比如 frameworks/base/data/keyboards/Generic.kl 这个文件中有:
key 113 VOLUME_MUTE key 114 VOLUME_DOWN key 115 VOLUME_UP key 116 POWER WAKE
frameworks/base/libs/ui/KeyLayoutMap.cpp
frameworks/base/include/ui/KeycodeLabels.h // NOTE: If you edit these flags, also edit policy flags in Input.h.
static const KeycodeLabel FLAGS[] = {
{ "WAKE", 0x00000001 },
{ "WAKE_DROPPED", 0x00000002 },
{ "SHIFT", 0x00000004 },
{ "CAPS_LOCK", 0x00000008 },
{ "ALT", 0x00000010 },
{ "ALT_GR", 0x00000020 },
{ "MENU", 0x00000040 },
{ "LAUNCHER", 0x00000080 },
{ "VIRTUAL", 0x00000100 },
{ "FUNCTION", 0x00000200 },
{ NULL, 0 }
};需要注意的是,在 frameworks/base/include/ui/Input.h 中定义了所有策略相关的标志,且需要和FLAGS[]里的值保持一致,不然就乱套了。
EventHub::getEvents()读到一个事件之后,会从按照scancode从keylayout中得到相应的策略标志,此时记录于event->flags中。按下POWER键时,getEvents()收到的scanCode是116,再从keyMap中用扫一遍,POWER键有"WAKE"属性,则设置0x00000001标志位。
2. InputDispatcher 中也会再做一些判断来设置policyFlags标志。
EventHub::getEvents()读到一个事件之后,会从按照scancode从keylayout中得到相应的策略标志,此时记录于event->flags中。按下POWER键时,getEvents()收到的scanCode是116,再从keyMap中用扫一遍,POWER键有"WAKE"属性,则设置0x00000001标志位。
if (iev.type == EV_KEY && device->keyMap.haveKeyLayout()) {
status_t err = device->keyMap.keyLayoutMap->mapKey(iev.code,
&event->keyCode, &event->flags);
LOGV("iev.code=%d keyCode=%d flags=0x%08x err=%d\n",
iev.code, event->keyCode, event->flags, err);
}