原文出处
脏数据检查 != 轮询检查更新
谈起angular的脏检查机制(dirty-checking), 常见的误解就是认为: ng是定时轮询去检查model是否变更。
其实,ng只有在指定事件触发后,才进入$digest cycle:
- DOM事件,譬如用户输入文本,点击按钮等。(
ng-click) - XHR响应事件 (
$http) - 浏览器Location变更事件 (
$location) - Timer事件(
$timeout,$interval) - 执行
$digest()或$apply()

参考《mastering web application development with angularjs》 P294
$digest后批量更新UI
传统的JS MVC框架, 数据变更是通过setter去触发事件,然后立即更新UI。
而angular则是进入$digest cycle,等待所有model都稳定后,才批量一次性更新UI。
这种机制能减少浏览器repaint次数,从而提高性能。
参考《mastering web application development with angularjs》 P296
另, 推荐阅读: 构建自己的AngularJS,第一部分:Scope和Digest
提速 $digest cycle
关键点
- 尽少的触发$digest (P310)
- 尽快的执行$digest
优化$watch
$scope.$watch(watchExpression, modelChangeCallback), watchExpression可以是String或Function。- 避免watchExpression中执行耗时操作,因为它在每次$digest都会执行1~2次。
- 避免watchExpression中操作dom,因为它很耗时。
console.log也很耗时,记得发布时干掉它。(用grunt groundskeeper)ng-if vs ng-show, 前者会移除DOM和对应的watch- 及时移除不必要的$watch。(angular自动生成的可以通过下文介绍的
bindonce)参考《mastering web application development with angularjs》 P303~309
var unwatch = $scope.$watch("someKey", function(newValue, oldValue){
//do sth...
if(someCondition){
//当不需要的时候,及时移除watch
unwatch();
}
});
-
避免深度watch, 即第三个参数为true
参考《mastering web application development with angularjs》 P313
-
减少watch的变量长度
如下,angular不会仅对{{variable}}建立watcher,而是对整个p标签。
双括号应该被span包裹,因为watch的是外部element参考《mastering web application development with angularjs》 P314
<p>plain text other {{variable}} plain text other</p>
//改为:
<p>plain text other <span ng-bind='variable'></span> plain text other</p>
//或
<p>plain text other <span>{{variable}}</span> plain text other</p>
$apply vs $digest
- $apply会使ng进入
$digest cycle, 并从$rootScope开始遍历(深度优先)检查数据变更。 - $digest仅会检查该scope和它的子scope,当你确定当前操作仅影响它们时,用$digest可以稍微提升性能。
参考《mastering web application development with angularjs》 P308
延迟执行
- 一些不必要的操作,放到
$timeout里面延迟执行。 - 如果不涉及数据变更,还可以加上第三个参数false,避免调用
$apply。 - 对时间有要求的,第二个参数可以设置为0。
$http.get('http://path/to/url').success(function(data){
$scope.name = data.name;
$timeout(function(){
//do sth later, such as log
}, 0, false);
});
$evalAsyncvs$timeout- http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17301572/angularjs-evalasync-vs-timeout
- directive中执行的
$evalAsync, 会在angular操作DOM之后,浏览器渲染之前执行。 - controller中执行的
$evalAsync, 会在angular操作DOM之前执行,一般不这么用。 - 而使用
$timeout,会在浏览器渲染之后执行。
优化ng-repeat
限制列表个数
- 列表对象的数据转换,在放入scope之前处理。如
$scope.dataList = convert(dataFromServer) - 可以使用ngInfiniteScroll来做无限滚动。
使用 track by
刷新数据时,我们常这么做:$scope.tasks = data || [];,这会导致angular移除掉所有的DOM,重新创建和渲染。
若优化为ng-repeat="task in tasks track by task.id后,angular就能复用task对应的原DOM进行更新,减少不必要渲染。
参见:http://www.codelord.net/2014/04/15/improving-ng-repeat-performance-with-track-by
使用单次绑定
我们都知道angular建议一个页面最多2000个双向绑定,但在列表页面通常很容易超标。
譬如一个滑动到底部加载下页的表格,一行20+个绑定, 展示个100行就超标了。
下图这个只是一个很简单的列表,还不是表格,就已经这么多个了: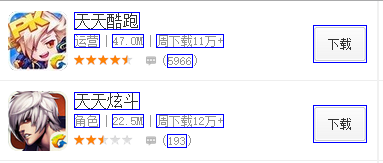
但其实很多属性显示后是几乎不会变更的, 这时候就没必要双向绑定了。(不知道angular为何不考虑此类场景)
如下图,改为bindonce或angular-once后减少了很多: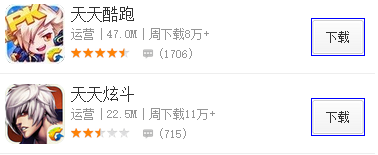
update:
1.3.0b10开始支持内建单次绑定, {{::variable}}
设计文档:http://t.cn/RvIYHp9
commit: http://t.cn/RvIYHpC
目前该特性的性能似乎还有待优化(2x slower)
慎用filter
在$digest过程中,filter会执行很多次,至少两次。
所以要避免在filter中执行耗时操作。
参考《mastering web application development with angularjs》 P136
angular.module('filtersPerf', []).filter('double', function(){
return function(input) {
//至少输出两次
console.log('Calling double on: '+input);
return input + input;
};
});
可以在controller中预先处理
//mainCtrl.js
angular.module('filtersPerf', []).controller('mainCtrl', function($scope, $filter){
$scope.dataList = $filter('double')(dataFromServer);
});
慎用事件
- 减少事件广播,使用双向数据绑定或共享service等方法来代替。
$broadcast会遍历scope和它的子scope,而不是只通知注册了该事件的子scope。- 一个优化方式是使用
$emit, 参见https://github.com/angular/angular.js/issues/4574 - 1.2.7版本对事件做过一个优化,参见https://github.com/angular/angular.js/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md#127-emoji-clairvoyance-2014-01-03
- 对高频的事件做缓冲限速,避免触发太频繁。
directive
- 跟scope数据无关的操作放在compile阶段,它只执行一次。
- 除了directive外其他地方,特别是controller里面不要操作dom, 尤其是绑定到scope后,便是灾难。
- 改变以前使用JQuery那样
以DOM为中心的思维,拥抱以数据为中心的思维。参见
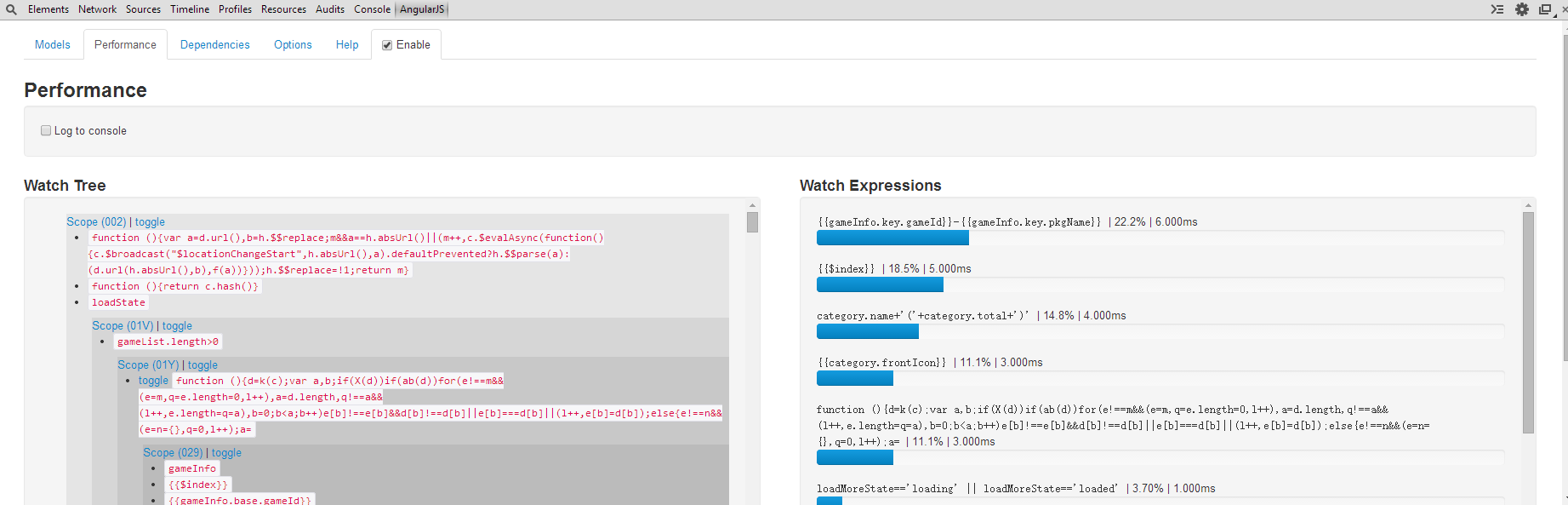
使用Batarang来分析性能
- AngularJS Batarang是官方提供的chrome插件