java的线程池:
1.线程池的作用:
限制程序执行线程的数量
2.为什么要用线程池:
- 避免新开线程带来的开销,可以重复利用线程池里的线程
- 用线程池,还可以降低内存的耗用,可根据服务器硬件情况初始线程池的大小
- 创建线程的时间耗时为t1,执行任务的时间耗时为t2,销毁线程的时间耗时为t3,若t1+t3>t2即适合用线程池,以此来提高服务器性能
3.常用的线程池接口ExecutorService
线程池的顶级接口是Executor,从源码上来看是从jdk1.5开始的

public interface Executor { /** * Executes the given command at some time in the future. The command * may execute in a new thread, in a pooled thread, or in the calling * thread, at the discretion of the {@code Executor} implementation. * * @param command the runnable task * @throws RejectedExecutionException if this task cannot be * accepted for execution * @throws NullPointerException if command is null */ void execute(Runnable command); }
但ExecutorService次接口里面定义了线程池大部分执行的方法,详看此接口的源码。
目前创建线程池由Executors类提供的静态方法提供,目的是减少创建线程池复杂性。涉及到创建线程池分为以下四种:
-
1.newSingleThreadExecutor,详见以下源码:

/** * Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread operating * off an unbounded queue. (Note however that if this single * thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to * shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute * subsequent tasks.) Tasks are guaranteed to execute * sequentially, and no more than one task will be active at any * given time. Unlike the otherwise equivalent * {@code newFixedThreadPool(1)} the returned executor is * guaranteed not to be reconfigurable to use additional threads. * * @return the newly created single-threaded Executor */ public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }
从源码上Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread operating,就是创建一个单线程的线程池,即线程池里只有一个线程在工作;源码注释上还有一段话
* Creates an Executor that uses a single worker thread operating
* off an unbounded queue. (Note however that if this single
* thread terminates due to a failure during execution prior to
* shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to execute
* subsequent tasks.
即这个单线程串行执行任务的时候异常的时候且改线程关闭了,则重新new一个线程来继续执行任务。以下是demo代码:

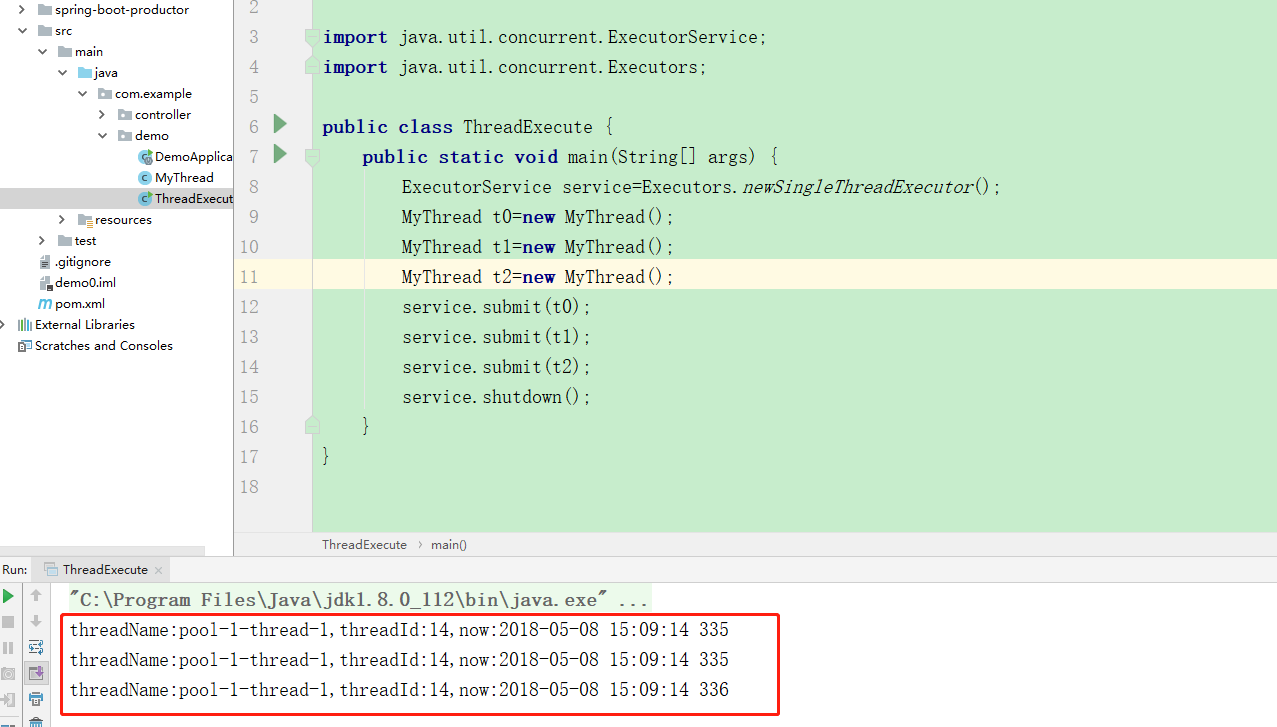
public class MyThread extends Thread { @Override public void run(){ Long threadId= Thread.currentThread().getId(); String threadName=Thread.currentThread().getName(); String now=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS").format(System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("threadName:"+threadName+",threadId:"+threadId+",now:"+now); } } public class ThreadExecute { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService service=Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); MyThread t0=new MyThread(); MyThread t1=new MyThread(); MyThread t2=new MyThread(); service.submit(t0); service.submit(t1); service.submit(t2); service.shutdown(); } }
执行结果如下:
- 2.newFixedThreadPool,详见以下源码:

/** * Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads * operating off a shared unbounded queue. At any point, at most * {@code nThreads} threads will be active processing tasks. * If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active, * they will wait in the queue until a thread is available. * If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution * prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to * execute subsequent tasks. The threads in the pool will exist * until it is explicitly {@link ExecutorService#shutdown shutdown}. * * @param nThreads the number of threads in the pool * @return the newly created thread pool * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code nThreads <= 0} */ public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }
从源码注释来看:
* Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads
* operating off a shared unbounded queue
* If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active,
* they will wait in the queue until a thread is available.
* If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution
* prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to
* execute subsequent tasks.
创建一个固定大小的线程池,每处理一个任务创建一个线程直到达到最大值,若其中有线程因为一场关闭了,则会重新生成一个线程来补上。以下是demo:

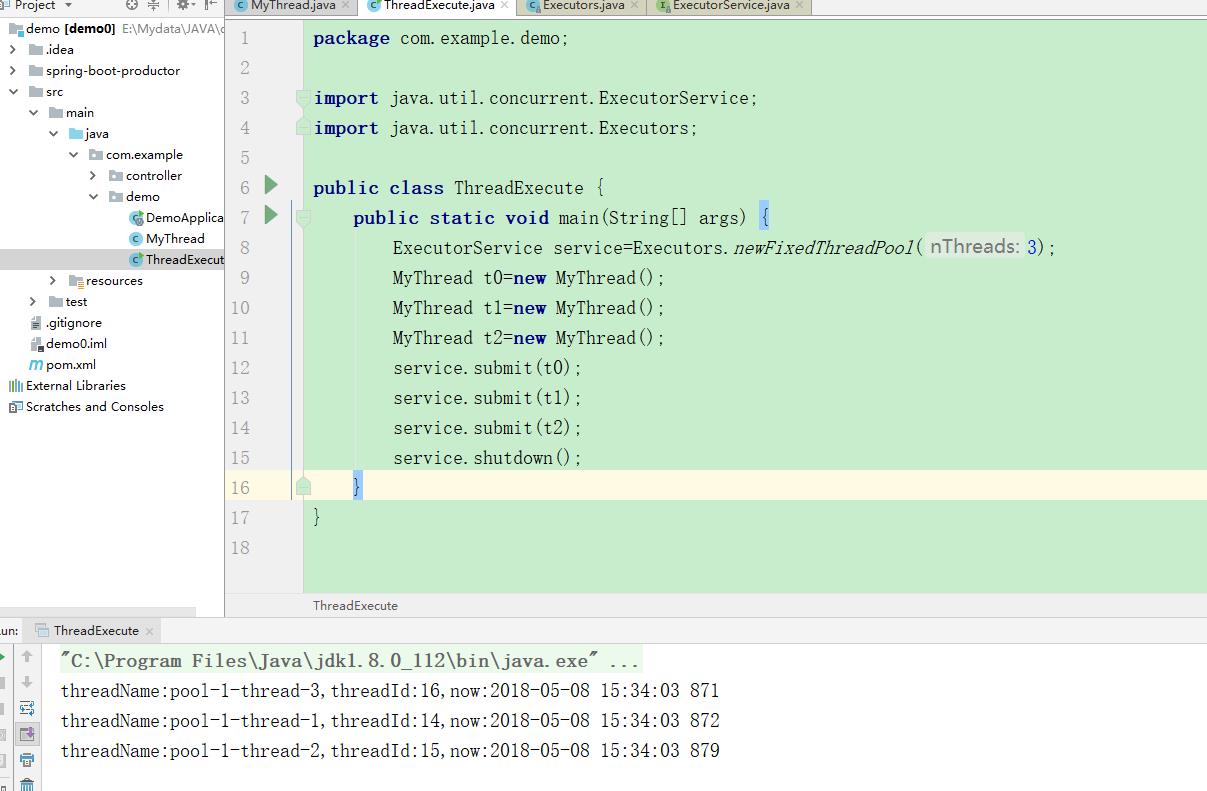
public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService service=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); MyThread t0=new MyThread(); MyThread t1=new MyThread(); MyThread t2=new MyThread(); service.submit(t0); service.submit(t1); service.submit(t2); service.shutdown(); }
执行结果如下:
- 3.newCachedThreadPool,详见如下源码:

/** * Creates a thread pool that creates new threads as needed, but * will reuse previously constructed threads when they are * available. These pools will typically improve the performance * of programs that execute many short-lived asynchronous tasks. * Calls to {@code execute} will reuse previously constructed * threads if available. If no existing thread is available, a new * thread will be created and added to the pool. Threads that have * not been used for sixty seconds are terminated and removed from * the cache. Thus, a pool that remains idle for long enough will * not consume any resources. Note that pools with similar * properties but different details (for example, timeout parameters) * may be created using {@link ThreadPoolExecutor} constructors. * * @return the newly created thread pool */ public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }
/** * Creates a thread pool that creates new threads as needed, but
* will reuse previously constructed threads when they are
* available. These pools will typically improve the performance
* of programs that execute many short-lived asynchronous tasks.
* Calls to {@code execute} will reuse previously constructed
* threads if available. If no existing thread is available, a new
* thread will be created and added to the pool. Threads that have
* not been used for sixty seconds are terminated and removed from
* the cache. Thus, a pool that remains idle for long enough will
* not consume any resources.
创建一个缓存的线程池,当任务增加时,可智能的新增线程,对于60s没有活动的线程将会移除,以下是demo:

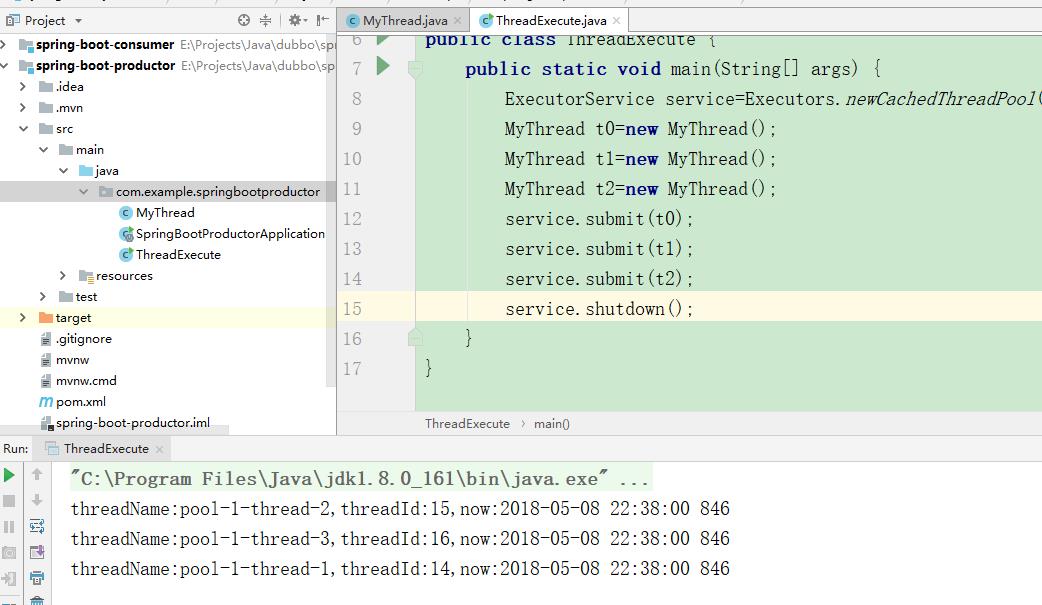
public class ThreadExecute { public static void main(String[] args) { ExecutorService service=Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); MyThread t0=new MyThread(); MyThread t1=new MyThread(); MyThread t2=new MyThread(); service.submit(t0); service.submit(t1); service.submit(t2); service.shutdown(); } }
执行结果如下:
- 4.newScheduledThreadPool,详见如下源码:

/** * Creates a thread pool that can schedule commands to run after a * given delay, or to execute periodically. * @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, * even if they are idle * @return a newly created scheduled thread pool * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code corePoolSize < 0} */ public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize); }
* Creates a thread pool that can schedule commands to run after a
* given delay, or to execute periodically.
* @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool,
* even if they are idle
该返回值是:ScheduledExecutorService.且源码里new的是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor创建初始大小的线程池,即使有线程处于空闲状态也不会移除掉,不像newCachedThreadPool有60s的非活动状态移除。
此线程正如注释一样,在delay(延时)后执行或者间隔性的重复执行。以下是demo:

public static void main(String[] args) { ScheduledExecutorService service=Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3); MyThread t0=new MyThread("t0"); MyThread t1=new MyThread("t1"); MyThread t2=new MyThread("t2"); service.schedule(t0,1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); service.schedule(t1,2000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); service.schedule(t2,3000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); service.shutdown(); } public class MyThread extends Thread { private String name; public MyThread(String name) { this.name=name; } @Override public void run(){ Long threadId= Thread.currentThread().getId(); String threadName=Thread.currentThread().getName(); String now=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS").format(System.currentTimeMillis()); System.out.println("this.name:"+this.name+",threadName:"+threadName+",threadId:"+threadId+",now:"+now); } }
执行结果如下:

备注:此线程池与timer的区别很明显,前者可以多个线程同时处理,但timer是单线程串行处理

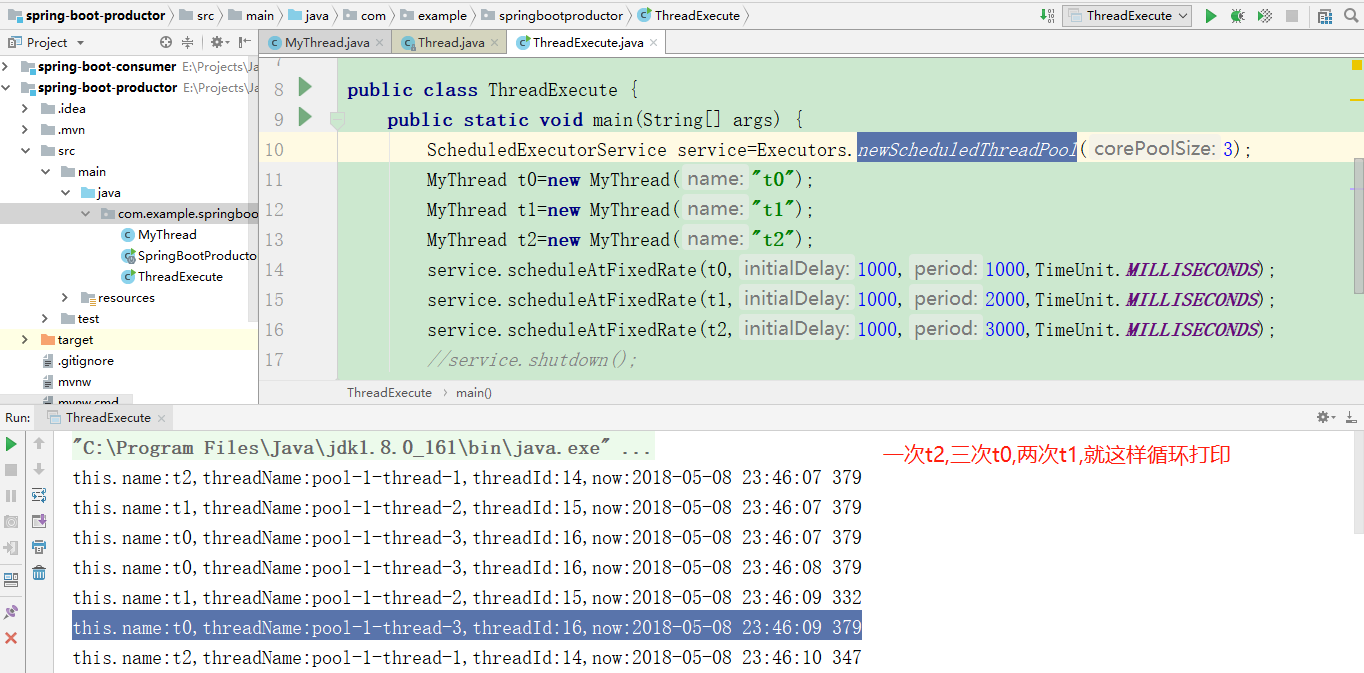
public class ThreadExecute { public static void main(String[] args) { ScheduledExecutorService service=Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(3); MyThread t0=new MyThread("t0"); MyThread t1=new MyThread("t1"); MyThread t2=new MyThread("t2"); service.scheduleAtFixedRate(t0,1000,1000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); service.scheduleAtFixedRate(t1,1000,2000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); service.scheduleAtFixedRate(t2,1000,3000,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); //service.shutdown(); } }
执行结果如下:
- 5.newWorkStealingPool,详见如下源码:

/** * Creates a thread pool that maintains enough threads to support * the given parallelism level, and may use multiple queues to * reduce contention. The parallelism level corresponds to the * maximum number of threads actively engaged in, or available to * engage in, task processing. The actual number of threads may * grow and shrink dynamically. A work-stealing pool makes no * guarantees about the order in which submitted tasks are * executed. * * @param parallelism the targeted parallelism level * @return the newly created thread pool * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code parallelism <= 0} * @since 1.8 */ public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool(int parallelism) { return new ForkJoinPool (parallelism, ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory, null, true); } /** * Creates a work-stealing thread pool using all * {@link Runtime#availableProcessors available processors} * as its target parallelism level. * @return the newly created thread pool * @see #newWorkStealingPool(int) * @since 1.8 */ public static ExecutorService newWorkStealingPool() { return new ForkJoinPool (Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(), ForkJoinPool.defaultForkJoinWorkerThreadFactory, null, true); }
* Creates a thread pool that maintains enough threads to support
* the given parallelism level, and may use multiple queues to
* reduce contention. The parallelism level corresponds to the
* maximum number of threads actively engaged in, or available to
* engage in, task processing. The actual number of threads may
* grow and shrink dynamically. A work-stealing pool makes no
* guarantees about the order in which submitted tasks are
* executed.
* since jdk1.8
创建一个并行大小的线程池,因为并行执行即不能保证每个线程执行的顺序。以下是demo:

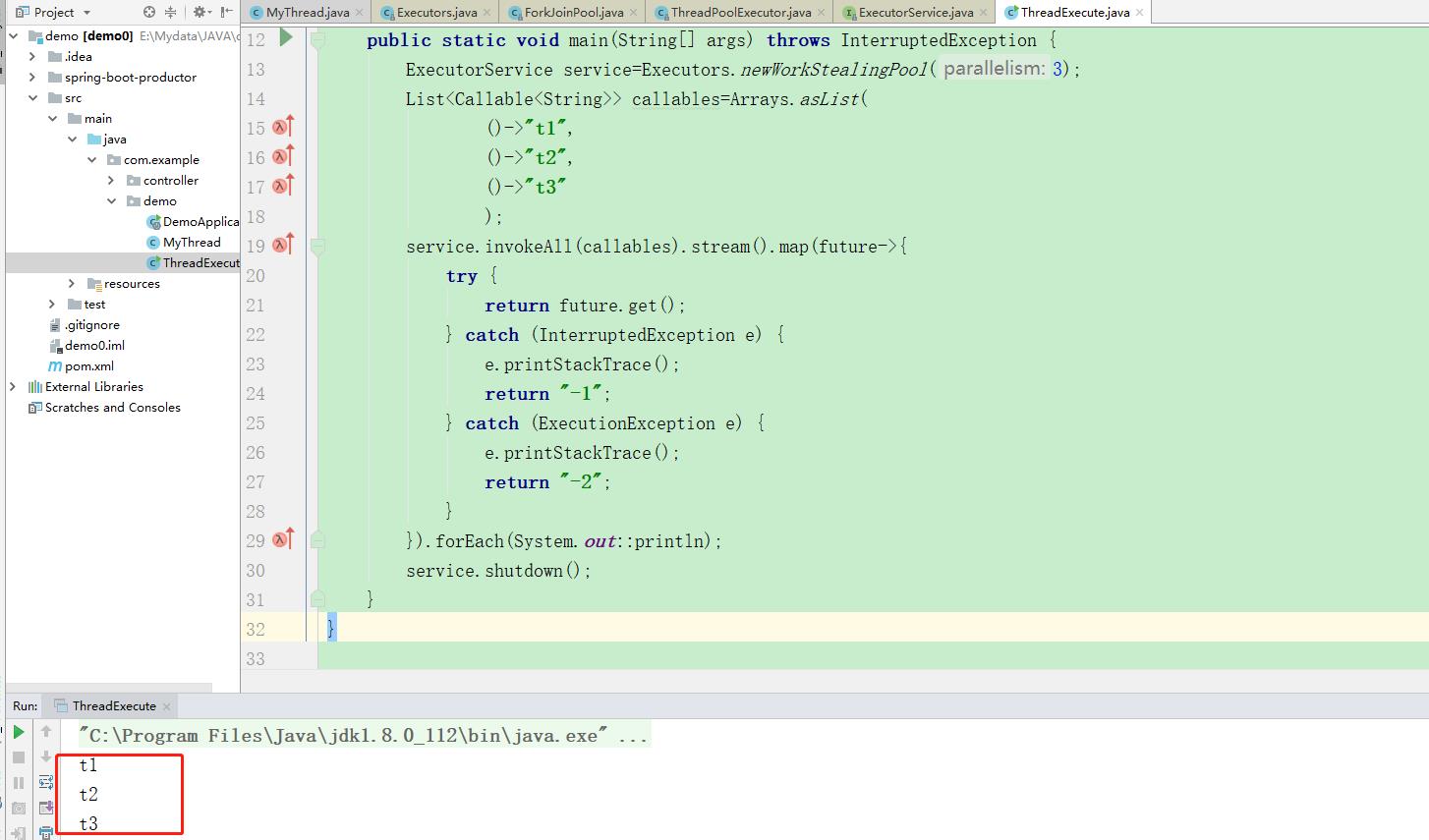
public class ThreadExecute { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { ExecutorService service=Executors.newWorkStealingPool(3); List<Callable<String>> callables=Arrays.asList( ()->"t1", ()->"t2", ()->"t3" ); service.invokeAll(callables).stream().map(future->{ try { return future.get(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return "-1"; } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return "-2"; } }).forEach(System.out::println); service.shutdown(); } }
以下是运行结果:
备注:一般情况下用并行的情况,除非数据源TSource的数据量大,不超过万级别的话,个人觉得并行的意义不大
