spark 资源调度包 Stage(阶段) 类解析
-
Stage 概念
-
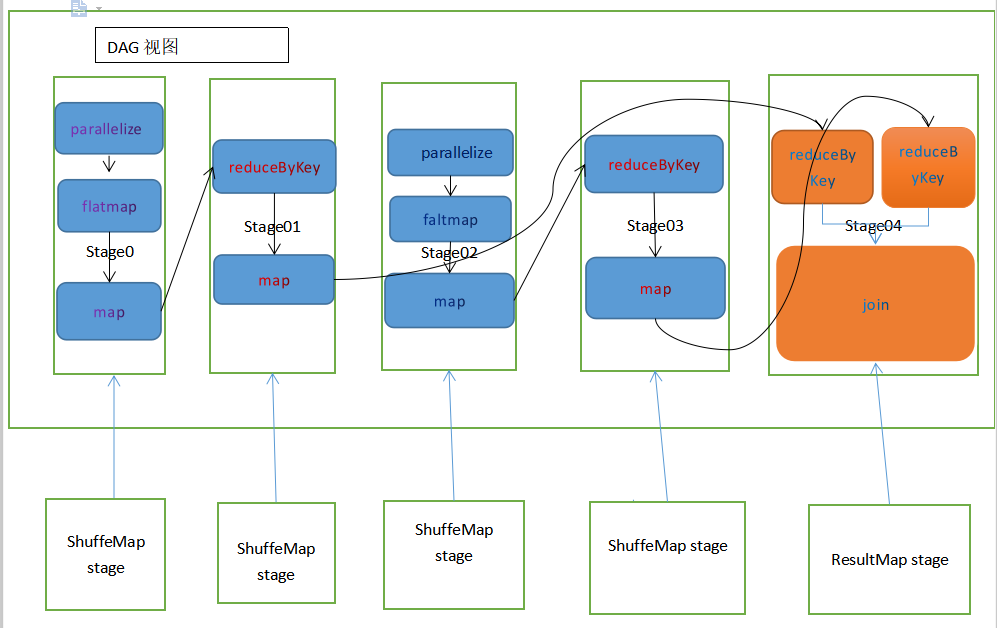
Spark 任务会根据 RDD 之间的依赖关系, 形成一个DAG有向无环图, DAG会被提交给DAGScheduler, DAGSchedular 会把DAG划分为相互依赖的多个stage。
-
而划分stage的依据就是RDD之间的宽窄依赖。
-
每个stage包含一个或多个task任务。而这些task以taskSet的形式提交给TaskScheduler运行。
-
stage是由一组并行的task组成的。
-
stage计算模式
-
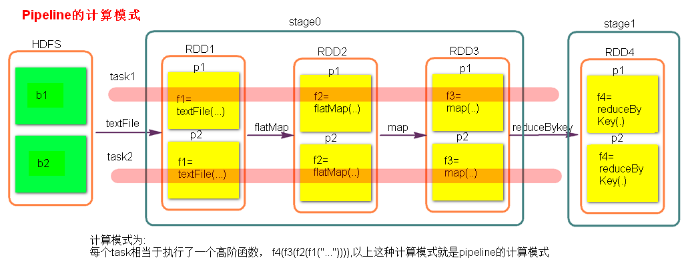
pipeline 管道设计模式(是一种思想)
-
由于 RDD 中记录的是 执行的算子(函数)的记录(业务逻辑), 图中的task可以看作是一系列函数的迭代计算, 比如: f4(f3(f2(f1(" ... ")))) <=> 将f1("...") 的结果作为参数传入f2()进行计算, 再将该次计算的结果作为参数传入f3()进行计算......
-
这种思想其实在线代中很常见, 而scala的高阶函数可以理解为其的一种具体体现。
-
数据在管道里什么时候数据会落地?
-
Stage 的 task 并行度是由stage的最后一个RDD的分区数来决定的。
-
Stage 的 task逻辑不一定都一样
-
什么操作会改变RDD分区(partition)数?
-
除repartition外的大多数宽依赖型算子操作大多会改变RDD的分区数
-
窄依赖算子不会改变RDD的分区数
-
-
以下代码验证了pipeline管道设计模式的存在
package com.ronnie.pipeline import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext} object Pipeline { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val conf = new SparkConf() conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("pipeline") val sc = new SparkContext(conf) val rdd: RDD[Int] = sc.parallelize(Array(1,2,3,4)) val rdd01: RDD[Unit] = rdd.map{ x => {println("map ------" + x)}} val rdd02: RDD[Unit] = rdd01.filter{ x => println("filter ******" + x) // 返回所有, 不过滤 true } rdd02.collect() sc.stop() } }-
输出结果:
map ------1 filter ******() map ------2 filter ******() map ------3 filter ******() map ------4 filter ******()- 可以看到filter总是在map之后执行而不是批量执行map后再批量执行filter
-
-
-
-
类注释:
/** * A stage is a set of parallel tasks all computing the same function that need to run as part * of a Spark job, where all the tasks have the same shuffle dependencies. * 一个阶段是所有计算相同功能的并行任务集合, 作为spark作业的一部分, 这些任务都有相同的 shuffle 依赖 * * Each DAG of tasks run by the scheduler is split up into stages at the boundaries where * shuffle occurs, and then the DAGScheduler runs these stages in topological order. * 每个由调度器运行的任务的有向无环图在shuffle发生的分界处分化成不同的阶段, 并且这些有向无环图的调度器 * 将以拓扑排序来运行这些 不同阶段的任务 * * Each Stage can either be a shuffle map stage, in which case its tasks' results are input for * other stage(s), or a result stage, in which case its tasks directly compute a Spark action * (e.g. count(), save(), etc) by running a function on an RDD. * 每个阶段都可以是一个 shuffle 匹配阶段, 该任务的结果可以被其他阶段作为导入, 也可以是 一个结果阶段, * 它的任务 通过 在RDD上运行 一个公式 来直接计算 一个 spark 行为(计数, 保存等...) * * For shuffle map stages, we also track the nodes that each output partition is on. * 对于 shuffle 匹配阶段, 我们会追踪 每个输出的分区的节点 * * Each Stage also has a firstJobId, identifying the job that first submitted the stage. When * FIFO scheduling is used, this allows Stages from earlier jobs to be computed first or * recovered faster on failure. * 每个阶段都有一个 首任务Id, 用于辨识第一个提交到该阶段的 任务。 当 先进先出 调度策略被使用时, 这会允 * 许 更早 的 作业 的阶段先被计算, 或者 在失败之后更早的恢复。 * * Finally, a single stage can be re-executed in multiple attempts due to fault recovery. In * that case, the Stage object will track multiple StageInfo objects to pass to listeners or * the web UI. * 最终, 由于 容错恢复机制, 单个阶段可以在多次尝试运行中 被重新执行。在这种情况下, 该阶段对象会追踪 许 * 多 阶段信息对象 并 将信息传递给监听者 或者 web UI 界面 * * The latest one will be accessible through latestInfo. * 最新的阶段可以通过 最新的信息获取 * * @param id Unique stage ID id: 唯一的阶段Id * @param rdd RDD that this stage runs on: for a shuffle map stage, it's the RDD we run map * tasks on, while for a result stage, it's the target RDD that we ran an action on * rdd:该 阶段 所运行在的 RDD:对于shuffle匹配阶段, 该RDD是我们 运行匹配任务 所在的RDD, 但对于结果阶 * 段,该RDD是我们运行 行为所在的RDD * @param numTasks Total number of tasks in stage; 当前阶段的任务数量 * result stages in particular may not need to compute all partitions, e.g. for first(), * lookup(), and take(). * 结果阶段 实际上不一定需要计算所有分区, 比如使用 first(), lookup() 和 take() 等算子 * @param parents List of stages that this stage depends on (through shuffle dependencies). * parent: 该阶段 所依赖(shuffle依赖) 的 阶段列表 * @param firstJobId ID of the first job this stage was part of, for FIFO scheduling. * firstJobId: 该阶段的第一个任务Id, 用于先进先出调度 * @param callSite Location in the user program associated with this stage: either where the * target RDD was created, for a shuffle map stage, or where the action for a result stage was * called. * callSite: 与该阶段相关的用户程序的位置: 对于 shuffle 匹配阶段 是 目标 RDD创建的位置, 对于 结果 * 阶段, 是 行为被调用的位置 (调用位点) */ -
代码:
private[scheduler] abstract class Stage( val id: Int, val rdd: RDD[_], val numTasks: Int, val parents: List[Stage], val firstJobId: Int, val callSite: CallSite) extends Logging { // 根据数组长度确定分区数 val numPartitions = rdd.partitions.length /** Set of jobs that this stage belongs to. 该阶段 的任务Id集合*/ val jobIds = new HashSet[Int] /** The ID to use for the next new attempt for this stage. * 该阶段的下一次新尝试的 Id */ private var nextAttemptId: Int = 0 // 短型的调用位点 val name: String = callSite.shortForm // 长型的调用位点 val details: String = callSite.longForm /** * Pointer to the [[StageInfo]] object for the most recent attempt. * 指向阶段信息对象的指针, 用于获取最近最多的尝试 * This needs to be initialized here, before any attempts have actually been created, because * the DAGScheduler uses this StageInfo to tell SparkListeners when a job starts (which * happens before any stage attempts have been created). * 在任何尝试被实际创建之前, 它需要被初始化, 因为 有向无环图的调度器 使用了该阶段信息来告诉spark的监 * 听者有任务启动了(这发生在任何阶段的尝试被发生之前) */ private var _latestInfo: StageInfo = StageInfo.fromStage(this, nextAttemptId) /** * Set of stage attempt IDs that have failed with a FetchFailure. * 拉取失败的的阶段尝试Id集 * We keep track of these failures in order to avoid endless retries if a stage keeps failing * with a FetchFailure. * 我们追踪这些失败时为了防止 一个阶段一直发生拉取失败后 无尽的重试 * We keep track of each attempt ID that has failed to avoid recording duplicate failures if * multiple tasks from the same stage attempt fail (SPARK-5945). * 我们追踪失败的每次尝试的Id以防止 如果许多任务在同一个阶段的尝试中失败 会导致 记录重复的失败 */ val fetchFailedAttemptIds = new HashSet[Int] // 清除失败Id private[scheduler] def clearFailures() : Unit = { fetchFailedAttemptIds.clear() } /** Creates a new attempt for this stage by creating a new StageInfo with a new attempt ID. * 通过创建一个新的附带新的尝试Id的状态信息 来为当前阶段创建一个新的尝试 */ def makeNewStageAttempt( // 需要计算的分区 numPartitionsToCompute: Int, // 本地优先的任务 taskLocalityPreferences: Seq[Seq[TaskLocation]] = Seq.empty): Unit = { // TaskMetrics是内部累加器的一个包装类 val metrics = new TaskMetrics metrics.register(rdd.sparkContext) // 获取最近的阶段信息 _latestInfo = StageInfo.fromStage( this, nextAttemptId, Some(numPartitionsToCompute), metrics, taskLocalityPreferences) nextAttemptId += 1 } /** Returns the StageInfo for the most recent attempt for this stage. * 返回最近最多尝试的 当前阶段的 阶段信息 */ def latestInfo: StageInfo = _latestInfo override final def hashCode(): Int = id override final def equals(other: Any): Boolean = other match { case stage: Stage => stage != null && stage.id == id case _ => false } /** Returns the sequence of partition ids that are missing (i.e. needs to be computed). * 返回缺失的分区 id 的序列 */ def findMissingPartitions(): Seq[Int] }