****************************************************************************
Android 4.4 init进程分析文章链接
Android 4.4 Init进程分析一 :Android init进程概述
Android 4.4 Init进程分析二 :Android初始化语言
Android 4.4 Init进程分析三:init.rc脚本文件的解析
Android 4.4 Init进程分析四 :init.rc脚本文件的执行
Android 4.4 Init进程分析五 :进程的终止与再启动
***************************************************************************
1 前言
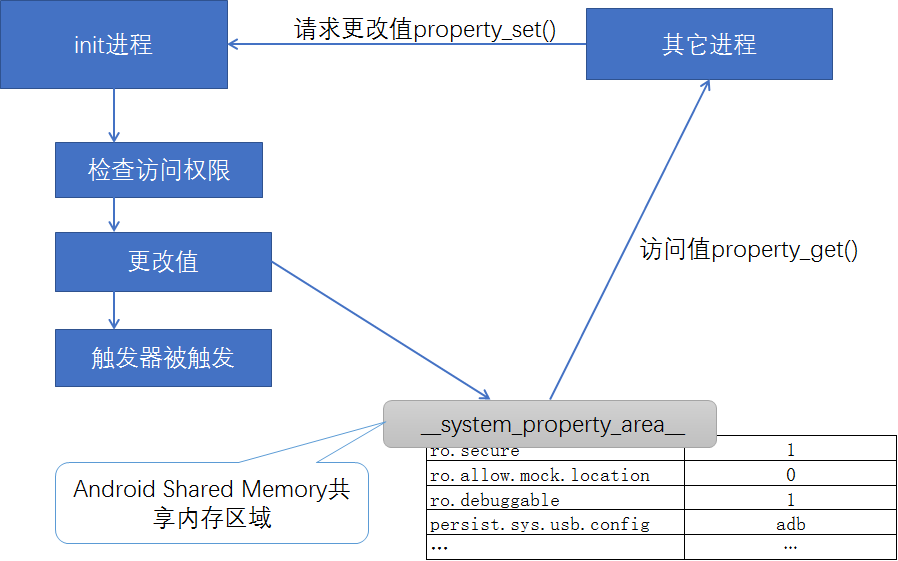
1. 属性变更请求是init事件处理循环处理的另一个事件。
2. 在Android平台中,为了让运行中的所有进程共享系统运行时所需要的各种设置值,系统开辟了属性存储区域,并提供了访问该区域的API。
3. 属性又键(key)和值(value)构成,其表现形式为“键=值”。
4. 系统中所有运行中的进程都可以访问属性值,但仅有init进程才能修改属性值,其他进程修改属性值时,必须向init进程提出请求,最终由init进程负责修改属性值。
5. init进程修改属性值时,首先会先检查各属性的访问权限,而后再修改属性值。当属性值修改后,若定义在init.rc文件中的某个条件得到满足,则与此条件相匹配的动作就会发生。每个动作都有一个触发器(trigger),他决定动作的执行时间,记录在“on property”关键字后的命令即被执行。
如下图,简单描述了init进程与其他进程在访问并修改属性值的大致情形:
2 属性初始化
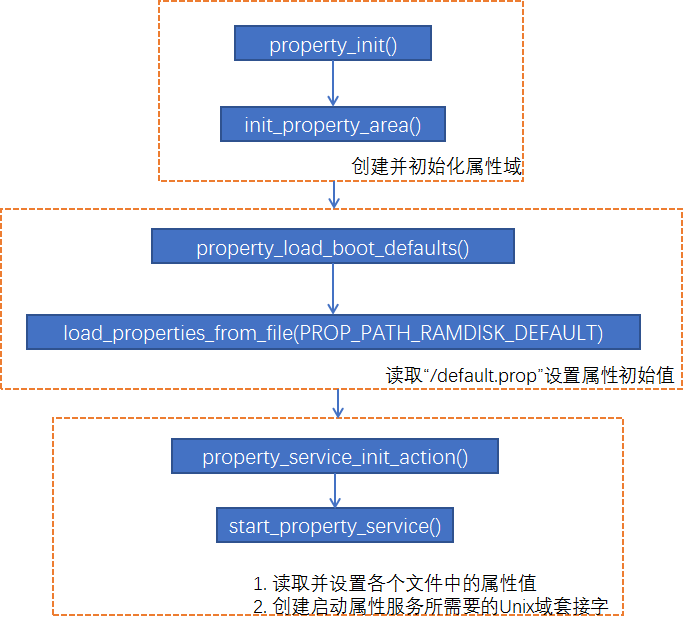
在init进程的main()函数中,调用了property_init()函数,用来初始化属性域,如下代码:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/init.c#1009
1 int main(int argc, char **argv) 2 { 3 .... 4 property_init(); 5 .... 6 }
再看一下property_init()函数的定义:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/property_service.c#541
1 void property_init(void) 2 { 3 init_property_area(); 4 }
可以看到函数内调用了init_property_area()函数,如下定义
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/property_service.c#133

static int init_property_area(void) { if (property_area_inited) return -1; if(__system_property_area_init()) return -1; if(init_workspace(&pa_workspace, 0)) return -1; fcntl(pa_workspace.fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC); property_area_inited = 1; return 0; }
这个函数会在内存中开辟一块共享内存区域,而后将其用作ashmem(Android Shared Memory),并生成属性域。外部进程可以访问这块共享内存区域,获得属性值,但它们不能通过直接访问共享内存区域的方式更改属性值。
init_property_area()函数执行后所创建的属性域被初始化。
在属性域完成初始化之后,就会从指定的文件中读取初始值,并设置为属性值。可以在main()函数中看到:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/init.c#1035
if (!is_charger) property_load_boot_defaults();
property_load_boot_defaults()函数定义:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/property_service.c#546
void property_load_boot_defaults(void) { load_properties_from_file(PROP_PATH_RAMDISK_DEFAULT); }
PROP_PATH_RAMDISK_DEFAULT定义为:
#define PROP_PATH_RAMDISK_DEFAULT "/default.prop"
load_properties_from_file()函数定义为:

1 static void load_properties_from_file(const char *fn) 2 { 3 char *data; 4 unsigned sz; 5 6 data = read_file(fn, &sz); 7 8 if(data != 0) { 9 load_properties(data); 10 free(data); 11 } 12 }
load_properties_from_file()函数读取指定的property file内容到内存,然后调用load_properties():
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/property_service.c#440

1 static void load_properties(char *data) 2 { 3 char *key, *value, *eol, *sol, *tmp; 4 5 sol = data; 6 while((eol = strchr(sol, ' '))) { 7 key = sol; 8 *eol++ = 0; 9 sol = eol; 10 11 value = strchr(key, '='); 12 if(value == 0) continue; 13 *value++ = 0; 14 15 while(isspace(*key)) key++; 16 if(*key == '#') continue; 17 tmp = value - 2; 18 while((tmp > key) && isspace(*tmp)) *tmp-- = 0; 19 20 while(isspace(*value)) value++; 21 tmp = eol - 2; 22 while((tmp > value) && isspace(*tmp)) *tmp-- = 0; 23 24 property_set(key, value); 25 } 26 }
在load_properties()函数中分析得到key and value,并调用property_set(key, value);将属性值写入共享内存。
******************************************
再回到main()函数继续执行,可以看到如下语句:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/init.c#1064
1 queue_builtin_action(property_service_init_action, "property_service_init");
这个动作执行时,会去调用property_service_init_action()函数:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/init.c#789
1 static int property_service_init_action(int nargs, char **args) 2 { 3 /* read any property files on system or data and 4 * fire up the property service. This must happen 5 * after the ro.foo properties are set above so 6 * that /data/local.prop cannot interfere with them. 7 */ 8 start_property_service(); 9 return 0; 10 }
进而调用了start_property_service()函数。用于创建启动属性服务所需要的Unix域套接字,并保存套接字描述符,如下函数定义:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/property_service.c#581

1 void start_property_service(void) 2 { 3 int fd; 4 5 load_properties_from_file(PROP_PATH_SYSTEM_BUILD); 6 load_properties_from_file(PROP_PATH_SYSTEM_DEFAULT); 7 load_override_properties(); 8 /* Read persistent properties after all default values have been loaded. */ 9 load_persistent_properties(); 10 11 fd = create_socket(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, SOCK_STREAM, 0666, 0, 0); 12 if(fd < 0) return; 13 fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC); 14 fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK); 15 16 listen(fd, 8); 17 property_set_fd = fd; 18 }
start_property_service()函数在创建套接字之前,先读取存储在各个文件中的基本设置值,将它们设置为属性值,如上函数定义会读取以下文件:
1 //文件 2 #define PROP_PATH_SYSTEM_BUILD "/system/build.prop" 3 #define PROP_PATH_SYSTEM_DEFAULT "/system/default.prop" 4 #define PROP_PATH_LOCAL_OVERRIDE "/data/local.prop"
当所有系统初始值设置完毕后,开始读取保存在/data/property目录中的属性值:
1 load_persistent_properties(); 2 3 ==>>> 4 5 static void load_persistent_properties() 6 { 7 DIR* dir = opendir(PERSISTENT_PROPERTY_DIR); 8 .... 9 } 10 11 ==>>> 12 13 #define PERSISTENT_PROPERTY_DIR "/data/property"
在/data/property目录中保存着系统运行中其他进程新生成的属性值或更改的属性值,属性的key被用作文件名,value被保存在文件中。
在属性初始值设置完毕后,就会创建名称为 /dev/socket/property_service 的Unix域套接字。
上述过程我们大体可以总结如下图所示:
3 属性变更请求处理
3.1 其他进程请求变更属性值
其他进程设置属性时是调用了libcutils函数库中的property_set()方法,该方法的定义去下:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/libcutils/properties.c#34
1 int property_set(const char *key, const char *value) 2 { 3 return __system_property_set(key, value); 4 }
可以看到,property_set调用了__system_property_set方法,这个方法位于:/bionic/libc/bionic/system_properties.c文件中:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/bionic/libc/bionic/system_properties.c#540

1 int __system_property_set(const char *key, const char *value) 2 { 3 int err; 4 prop_msg msg; 5 6 if(key == 0) return -1; 7 if(value == 0) value = ""; 8 if(strlen(key) >= PROP_NAME_MAX) return -1; 9 if(strlen(value) >= PROP_VALUE_MAX) return -1; 10 11 memset(&msg, 0, sizeof msg); 12 msg.cmd = PROP_MSG_SETPROP; 13 strlcpy(msg.name, key, sizeof msg.name); 14 strlcpy(msg.value, value, sizeof msg.value); 15 16 err = send_prop_msg(&msg); 17 if(err < 0) { 18 return err; 19 } 20 21 return 0; 22 }
上述方法最终调用到send_prop_msg()函数:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/bionic/libc/bionic/system_properties.c#send_prop_msg

1 static int send_prop_msg(prop_msg *msg) 2 { 3 struct pollfd pollfds[1]; 4 struct sockaddr_un addr; 5 socklen_t alen; 6 size_t namelen; 7 int s; 8 int r; 9 int result = -1; 10 11 s = socket(AF_LOCAL, SOCK_STREAM, 0); 12 if(s < 0) { 13 return result; 14 } 15 16 memset(&addr, 0, sizeof(addr)); 17 namelen = strlen(property_service_socket); 18 strlcpy(addr.sun_path, property_service_socket, sizeof addr.sun_path); 19 addr.sun_family = AF_LOCAL; 20 alen = namelen + offsetof(struct sockaddr_un, sun_path) + 1; 21 22 if(TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(connect(s, (struct sockaddr *) &addr, alen)) < 0) { 23 close(s); 24 return result; 25 } 26 27 r = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(send(s, msg, sizeof(prop_msg), 0)); 28 29 if(r == sizeof(prop_msg)) { 30 // We successfully wrote to the property server but now we 31 // wait for the property server to finish its work. It 32 // acknowledges its completion by closing the socket so we 33 // poll here (on nothing), waiting for the socket to close. 34 // If you 'adb shell setprop foo bar' you'll see the POLLHUP 35 // once the socket closes. Out of paranoia we cap our poll 36 // at 250 ms. 37 pollfds[0].fd = s; 38 pollfds[0].events = 0; 39 r = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(poll(pollfds, 1, 250 /* ms */)); 40 if (r == 1 && (pollfds[0].revents & POLLHUP) != 0) { 41 result = 0; 42 } else { 43 // Ignore the timeout and treat it like a success anyway. 44 // The init process is single-threaded and its property 45 // service is sometimes slow to respond (perhaps it's off 46 // starting a child process or something) and thus this 47 // times out and the caller thinks it failed, even though 48 // it's still getting around to it. So we fake it here, 49 // mostly for ctl.* properties, but we do try and wait 250 50 // ms so callers who do read-after-write can reliably see 51 // what they've written. Most of the time. 52 // TODO: fix the system properties design. 53 result = 0; 54 } 55 } 56 57 close(s); 58 return result; 59 }
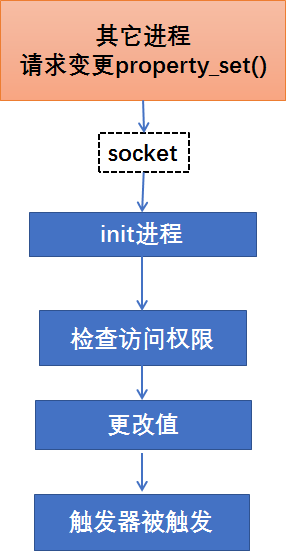
send_prop_msg()函数可以看到:建立与属性服务/dev/socket/property_service 的socket连接,并发送要修改的属性信息。
3.2 init进程处理属性变更
init进程就收到属性变更请求后,init进程就会调用handle_property_set_fd()函数:
1 int main(int argc, char **argv) 2 { 3 .... 4 for (i = 0; i < fd_count; i++) { 5 if (ufds[i].revents == POLLIN) { 6 if (ufds[i].fd == get_property_set_fd()) 7 handle_property_set_fd();// 处理属性变更请求 8 else if (ufds[i].fd == get_keychord_fd()) 9 handle_keychord(); 10 else if (ufds[i].fd == get_signal_fd()) 11 handle_signal(); 12 } 13 } 14 .... 15 }
我们来看一下handle_property_set_fd()函数的定义:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/property_service.c#358

1 void handle_property_set_fd() 2 { 3 .... 4 5 /* Check socket options here */ 6 if (getsockopt(s, SOL_SOCKET, SO_PEERCRED, &cr, &cr_size) < 0) { //分析1 7 close(s); 8 ERROR("Unable to receive socket options "); 9 return; 10 } 11 12 .... 13 switch(msg.cmd) { 14 case PROP_MSG_SETPROP: 15 msg.name[PROP_NAME_MAX-1] = 0; 16 msg.value[PROP_VALUE_MAX-1] = 0; 17 ... 18 if(memcmp(msg.name,"ctl.",4) == 0) { 19 // Keep the old close-socket-early behavior when handling 20 // ctl.* properties. 21 close(s); 22 if (check_control_perms(msg.value, cr.uid, cr.gid, source_ctx)) { //分析2 23 handle_control_message((char*) msg.name + 4, (char*) msg.value); 24 } else { 25 ERROR("sys_prop: Unable to %s service ctl [%s] uid:%d gid:%d pid:%d ", 26 msg.name + 4, msg.value, cr.uid, cr.gid, cr.pid); 27 } 28 } else { 29 if (check_perms(msg.name, cr.uid, cr.gid, source_ctx)) { //分析3 30 property_set((char*) msg.name, (char*) msg.value); //分析4 31 } else { 32 ERROR("sys_prop: permission denied uid:%d name:%s ", 33 cr.uid, msg.name); 34 } 35 36 // Note: bionic's property client code assumes that the 37 // property server will not close the socket until *AFTER* 38 // the property is written to memory. 39 close(s); 40 } 41 ... 42 } 43 }
分析1:执行handle_property_set_fd()函数时,会先从套接字获取SO_PEERCRED值,以便检查传递信息的进程的访问权限。在struct ucred结构体中,存储着传递信息的进程uid、pid和gid值。通过此结构体中的值,以及消息的类型,检查进程的访问权限。
分析2:在属性消息中,以“ctl”开头的消息并非请求更改系统属性值的消息,而是请求进程启动与终止的消息。在代码中调用check_control_perms()函数检查访问权限,仅有system server、root、以及相关进程才能使用ctl消息,终止或启动进程
分析3:其他消息都被用来更改系统属性值,调用check_perms()函数检查访问权限。各属性的访问权限采用Linux的uid进程区分,其定义如下代码所示。若在系统运行中变更属性设置,应充分考虑各属性的访问权限。
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/property_service.c#60

1 struct { 2 const char *prefix; 3 unsigned int uid; 4 unsigned int gid; 5 } property_perms[] = { 6 { "net.rmnet0.", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 7 { "net.gprs.", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 8 { "net.ppp", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 9 { "net.qmi", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 10 { "net.lte", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 11 { "net.cdma", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 12 { "ril.", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 13 { "gsm.", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 14 { "persist.radio", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 15 { "net.dns", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 16 { "sys.usb.config", AID_RADIO, 0 }, 17 { "net.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 18 { "dev.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 19 { "runtime.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 20 { "hw.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 21 { "sys.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 22 { "sys.powerctl", AID_SHELL, 0 }, 23 { "service.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 24 { "wlan.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 25 { "bluetooth.", AID_BLUETOOTH, 0 }, 26 { "dhcp.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 27 { "dhcp.", AID_DHCP, 0 }, 28 { "debug.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 29 { "debug.", AID_SHELL, 0 }, 30 { "log.", AID_SHELL, 0 }, 31 { "service.adb.root", AID_SHELL, 0 }, 32 { "service.adb.tcp.port", AID_SHELL, 0 }, 33 { "persist.sys.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 34 { "persist.service.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 35 { "persist.security.", AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 36 { "persist.service.bdroid.", AID_BLUETOOTH, 0 }, 37 { "selinux." , AID_SYSTEM, 0 }, 38 { NULL, 0, 0 } 39 };
分析4:最后调用property_set()函数更改属性值。若没有问题,接着调用property_changed()函数。
property_changed()函数的定义如下:
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/init.c#412
1 void property_changed(const char *name, const char *value) 2 { 3 if (property_triggers_enabled) 4 queue_property_triggers(name, value); 5 }
http://androidxref.com/4.4_r1/xref/system/core/init/init_parser.c#517

1 void queue_property_triggers(const char *name, const char *value) 2 { 3 struct listnode *node; 4 struct action *act; 5 list_for_each(node, &action_list) { 6 act = node_to_item(node, struct action, alist); 7 if (!strncmp(act->name, "property:", strlen("property:"))) { 8 const char *test = act->name + strlen("property:"); 9 int name_length = strlen(name); 10 11 if (!strncmp(name, test, name_length) && 12 test[name_length] == '=' && 13 (!strcmp(test + name_length + 1, value) || 14 !strcmp(test + name_length + 1, "*"))) { 15 action_add_queue_tail(act); 16 } 17 } 18 } 19 }
queue_property_triggers()函数中,去action_list中检索出与这个属性值相关的action加入到action_queue,等待执行。
在init.rc脚本文件中,记录着某个属性改变后要采取的动作,动作执行的条件以“on property:<key> = <value>”形式给出。当某个条件相关的键值被设定后,与该条件相关的触发器就会被触发。比如:
# adbd on at boot in emulator on property:ro.kernel.qemu=1 start adbd
当ro.kernel.qemu属性值被设置为1时,adbd服务就会启动。
到这里属性变更的处理就分析完了!
大体过程如下:
========
88888888
========
