C#中的线程一(委托中的异步)
一、同步委托
我们平时所用的委托以同步居多,我们编写一个方法和相关委托进行演示:
publicdelegatevoid DoSomethingDelegate(string name);
//同步委托
public static void Start1()
{
Console.WriteLine("this is primary thread");
Console.WriteLine("main thread:{0},{1},{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture, Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//DoSomethingDelegate del = new DoSomethingDelegate(Method1);
//注意这里,简单起见还可以把一个方法名直接赋给一个委托类型
DoSomethingDelegate del = Method1;
del("this is delegate method");
}
//委托所关联的方法
public static void Method1(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("sub thread: {0},{1},{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture, Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(name);
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));
Console.WriteLine("sub thread other things...");
}我们分析下这个Start1()方法,首先显示了主线程相关的信息,然后定义了一个委托类型del,利用del("this is delegate method")执行Method1(string name)方法,由于是同步委托,所以主线程在执行到Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));处会暂时挂起,3秒后才继续执行,然后才返回到Start1()方法中继续执行。
我们运行Start1()方法后看看执行顺序
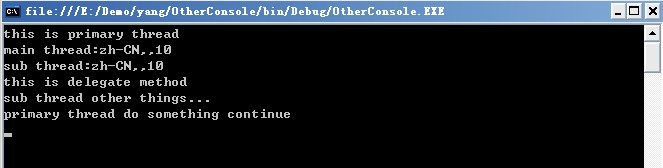
可以看到,运行结果是按主线程的执行顺序依次往下执行。
二、异步委托
//异步委托
public static void Start2()
{
Console.WriteLine("main thread:{0},{1},{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture, Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//DoSomethingDelegate del = new DoSomethingDelegate(Method1);
DoSomethingDelegate del = Method1;
del.BeginInvoke("this is delegate method", null, null);
Console.WriteLine("main thread other things...");
}此次我们利用委托的BeginInvoke方法进行方法调用,BeginInvoke的方法签名如下:
IAsyncResult DoSomethingDelegate.BeginInvoke(string name,AsyncCallBack callback,object @object)
那么利用BeginInvoke进行方法调用的结果如何呢?如结果显示,BeginInvoke调用的方法有一个子线程去调用,主线程没有被执行到,Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));这个方法,也就没有被挂起线程。
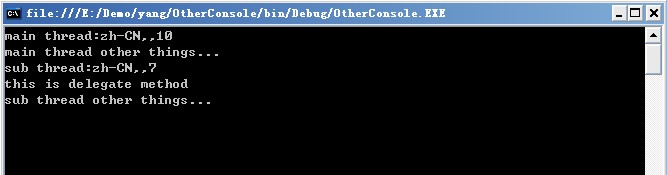
三、异步委托详解
刚才我们通过del.BeginInvoke("this is delegate method", null, null);这样就做到了异步调用,我们在编写代码中还有这样一种需求,如果你要进行异步调用,子线程执行的结果怎么返回给主线程呢?del.EndInvoke上场了!
//异步委托得到返回值,实际上为了得到返回值,阻碍了主线程
public static void Start3()
{
Console.WriteLine("main thread:{0},{1},{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture, Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
//DoSomethingDelegate del = new DoSomethingDelegate(Method1);
DoSomethingDelegate2 del = Method2;
IAsyncResult result=del.BeginInvoke("this is delegate method",null,null);
string s = del.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine("得到返回值:" + s);
Console.WriteLine("main thread other things...");
}//异步委托所调用的方法,注意此方法有返回值
public static string Method2(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("sub thread:{0},{1},{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture, Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(name);
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));
Console.WriteLine("sub thread other things...");
return "返回委托值";
}从实例代码中我们可以看到,我们为了得到异步方法的返回值写了这么两行代码:
IAsyncResult result=del.BeginInvoke("this is delegate method",null,null);
string s = del.EndInvoke(result);
我们查看执行结果:由运行结果可以看到,屏幕输出了返回值,但是Method2(string name)方法并没有被异步执行到!原因在于string s = del.EndInvoke(result);这句阻碍了主线程的继续执行,等子线程返回值后赋给s后,主线程才继续执行。这样写的后果就是:为了得到返回值,阻碍了主线程
我们刚才执行异步委托都是通过下面的代码来完成的
IAsyncResult result=del.BeginInvoke("this is delegate method",null,null);我们将BeginInvoke方法的第二个和第三个参数都设置为了null,我们现在来看看这两个参数的作用!第二个参数AsyncCallBack callback,这个参数实际上是一个回调委托,我们看此委托的定义:
public delegate void AsyncCallback(IAsyncResult ar);
什么是回调方法?就是说委托所调用的方法执行完毕后自动执行的方法,即上面的Method2(string name)方法被异步执行结束后所调用的方法。于是我们在定义一个跟AsyncCallback委托匹配的方法:
public static void CallBack(IAsyncResult result)
{
DoSomethingDelegate2 del = result.AsyncState as DoSomethingDelegate2;
string s = del.EndInvoke(result);
Console.WriteLine("得到返回值:" + s);
}public static void Start4()
{
Console.WriteLine("main thread:{0},{1},{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture, Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
DoSomethingDelegate2 del = Method2;
AsyncCallback callBack = CallBack;
del.BeginInvoke("this is delegate method", callBack, del);
Console.WriteLine("main thread other things...");
}public static string Method2(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("sub thread:{0},{1},{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture, Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
Console.WriteLine(name);
Thread.Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(3));
Console.WriteLine("sub thread other things...");
return "返回委托值";
}从上面的代码可以看出,在CallBack方法中我们得到了Method2(string name)方法的返回值。并且整个过程是异步执行的!请看运行结果:

为了得到异步方法的返回值还可以这么做:
public static void Start4()
{
Console.WriteLine("main thread:{0},{1},{2}", Thread.CurrentThread.CurrentCulture, Thread.CurrentThread.Name, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
DoSomethingDelegate2 del = Method2;
//另一种实现方法
del.BeginInvoke("this is delegate method", CallBack2, null);
Console.WriteLine("main thread other things...");
}public static void CallBack2(IAsyncResult result)
{
AsyncResult ar = result as AsyncResult;
DoSomethingDelegate2 del = ar.AsyncDelegate as DoSomethingDelegate2;
string s=del.EndInvoke(ar);
Console.WriteLine("得到返回值:" + s);
}这段代码的运行效果跟上面是一样的,只不过写法不同而已!