今日知识点整理
复习内容
* 1. 定位 * 1.为了实现页面中特殊的样式结构或是效果 比如轮播图中的左右按钮 * 2.为了让元素在页面中灵活的进行移动 * * 2. 定位分四种 * static 任何元素都有静态定位 * relative * absolute * fixed * * 3. static的特点 * 1. 任何元素其实都有一个静态定位 * 2. 不脱离标准流,占据原来标准流的位置 * 3. 不能够通过边偏移进行位置的移动 * * 4. relative的特点 * 1. 不脱离标准流的控制,占据原来标准流的位置 * 2. 可以通过边偏移来进行位置的移动 * 3. 是相对于自身原来的位置进行的移动 * * 5. 绝对定位的特点 * 1. 脱离标准流的控制,不占据原来标准流的位置 * 2. 可以通过边偏移进行位置的移动 * 3. 如果只有一个元素,而且是绝对定位,是以页面为参考进行移动 * 4. 如果元素有多层嵌套的话,如果子元素是绝对定位,则参考点是以离自身最近的具有非静态定位的父级元素 * 5. 可以改变元素的显示方式(定位了的行内元素具有行内块的特性,可以设置宽高) * * 6. 固定定位的特点 * 1. 脱离标准流的控制,不占据原来标准流的位置 * 2. 可以通过边偏移进行位置的移动 * 3. 参考浏览器可视区进行的边偏移移动 * 4. 可以改变元素的显示方式(具有固定定位的行内元素,也会有行内块的特性,可以设置宽高) * * 7. 层级z-index * 定位(非静态定位)了的元素都有一个层级的概念,默认的层级是0 * 如果定位了的元素,在页面中的显示有重合的话,后面的元素会盖住前面的元素 * 如果不想被别的后面的元素所盖住,需要设置z-index的值 * 只有非静态定位的元素才会有层级的概念。
今日学习任务
* 能够说出display:none与 visibility:hidden隐藏元素的区别 * 能够说出CSS精灵技术产生的目的(解决什么问题) 减少请求的次数,提高页面渲染的效率 * 能够使用精灵图设置背景图片 * 能够写出滑动门微信案例 * 能够写出3中常见的鼠标样式(cursor) pointer move text help * 能够写出溢出文字显示省略号的代码 * 能够使用字体图标

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>绝对定位</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box { width: 300px; height: 300px; position: absolute; background-color: orange; right: 0; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>绝对定位</title> <style> * { margin:0; padding: 0; } .demo { width: 300px; height: 300px; border: 1px solid blue; margin: 200px 0 0 160px; position: relative; } .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid red; /* position: relative; */ position: absolute; left:60px; top: 70px; } .one { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: orangered; position: absolute; left: 20px; top: 30px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="demo"> <div class="box"> <div class="one"></div> </div> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>z-index</title> <style> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: green; position: absolute; } .box:hover { cursor: pointer; z-index: 1; } .box2 { width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: yellow; position: absolute; left: 150px; top: 150px; /* 默认是.box2覆盖.box1,如果想让box1覆盖box2就需要给box1设置z-index */ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="box2"></div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>定位与浮动</title> <style> * { margin:0; padding: 0; } div { width: 300px; height: 300px; } .demo { background-color: red; position: absolute; top: 100px; left: 100px; } .box { background-color: blue; float: left; /* z-index: 1px; 无效 */ } /* 只有非静态定位的元素才有层级的概念,默认的层级是0,即使层级为0,也会盖住非定位的元素 */ </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="demo"></div> </body> </html>
01-元素的隐藏和溢出
display:none/block
visibility:hidden/visible
两者的区别:
display:none的元素,不占原来标准流的位置了,在页面是也看不到了,但是源码中还有对应的标签。
visibility:hidden的元素,占据原来的标准流位置,在页面中看不到,源码中有对应的标签。

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { width: 600px; height: 600px; border: 1px solid blue; } .one { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 1px solid green; /* display: none; 不占原来的位置 */ background-color: green; visibility: hidden; /* 占原来的位置 */ } .two { width: 100px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid lightgreen; background-color: green; } .box:hover .one { visibility: visible; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <div class="one"></div> <div class="two"></div> </div> </body> </html>
02-元素内容的溢出隐藏

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>元素内容溢出的隐藏</title> <style> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { width: 300px; height: 100px; background-color: lightpink; /* overflow: hidden; 隐藏超出的内容 */ /* overflow: visible; 不隐藏超出的内容,默认属性 */ overflow: auto; /* 超出的内容会隐藏,但通过下拉框的方式查看 */ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> 天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣;天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣 </div> </body> </html>
溢出省略
三个属性:overflow,white-space,text-overflow缺一不可

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box1 { width: 200px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; border: 1px solid pink; overflow: hidden; white-space: nowrap; /* 将文字内容设置为不换行 */ text-overflow: ellipsis; /* ellipsis是省略的意思,也就是省略溢出的文本 */ } .box2 { width: 200px; height: 100px; background-color: orange; border: 1px solid orange; overflow: hidden; white-space: nowrap; /* 将文字内容设置为不换行 */ text-overflow: ellipsis; /* ellipsis是省略的意思,也就是省略溢出的文本 */ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box1"> 天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣;天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣; 天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣;天下事有难易乎,为之,则难者亦易矣,不为,则易者亦难矣; </div> <div class="box2">this is a test...this is a test...this is a test...this is a test...this is a test...this is a test...this is a test...</div> </body> </html>
03-光标的样式
cursor: default 默认 | pointer 小手 | move 移动 | text 文本 | help 帮助
最最常用的是 pointer,move;

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>鼠标光标样式</title> <style> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { width: 300px; height: 300px; margin: 0 auto; background-color: deeppink; } .box:hover { /* cursor: default; 默认鼠标样式 */ /* cursor: pointer; 小手样式 */ /* cursor: move; 光标样式 */ /* cursor: help; 帮助样式 */ /* cursor: text; 文本样式 */ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>
去掉文本框或是文本域的环绕线
outline:none

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> .demo { width: 600px; height: 100px; outline: none; /* 去掉点击时蓝色的环绕线 */ /* outline是个复合属性,和font、background这类属性类似 */ /* outline: 10px solid red; */ /* outline: 10px dotted red; */ /* outline: 10px dashed red; */ } </style> </head> <body> <input type="text" class="demo"> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> <style> textarea { resize: none; /* 禁止拖拽大小,以免造成布局混乱 */ outline: none; /* 取消环绕线 */ } </style> </head> <body> <textarea name="" id="" cols="30" rows="10">说点什么吧...</textarea> </body> </html>
04-图片和文字的对齐方式
vertical-align: baseline | top | middle | bottom
一般用middle让图片和文字在垂直方向都居中。
还可以使用top,middle,bottom将图片与盒子底部的默认间距给清除。
将图片与盒子底部的默认间距清除掉的方式:
vertical-align:top|middle|bottom 还可以将图片设置为块级元素 display:block

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>图片的对齐方式</title> <style> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } .box { border: 1px solid red; } .one { width: 100px; height: 100px; background-color: pink; } .box img { /* display: block; */ /* vertical-align: middle; 中线对齐 */ /* vertical-align: top; 顶线对齐 */ /* vertical-align: bottom; 底线对齐 */ /* 上面的四种方法都可以去除间隙问题 */ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <img src="./images/3.jpg" title="楚乔传">楚乔传 <!-- <div class="one"></div> 注释掉后盒子和文字会以基线(baseline)方式对齐,导致盒子和底边框之间有空隙 1.通过vertical-align的top,middle,bottom其中任意参数就能解决 2.将img转换为块级标签 --> </div> <input type="checkbox" name="hejiu" />喝酒 </body> </html>
05-精灵图
-
为了降低向服务器发送请求的次数
-
提高页面的加载速度
2.什么是精灵图
CSS 精灵其实是将网页中的一些背景图像整合到一张大图中(精灵图),然而,各个网页元素通常只需要精灵图中不同位置的某个小图,要想精确定位到精灵图中的某个小图,就需要使用CSS的background-image、background-repeat和background-position属性进行背景定位,其中最关键的是使用background-position属性精确地定位。
3.精灵图使用本质
利用背景图片的位置属性进行设置

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>精灵图应用</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box a { width: 90px; height: 28px; line-height: 28px; margin: 200px auto; background: url(./img/jd.png) no-repeat 0 -65px; border: 1px solid red; display: block; color: purple; padding-left: 22px; text-decoration: none; } .box a:hover { background: url(./img/jd.png) no-repeat 0 -380px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <a href="#">京东购物车</a> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>精灵图应用2</title> <style> * { margin: 0px; padding: 0px; } i { font-style: none; } .box { width: 248px; height: 208px; border: 1px solid red; margin: 100px auto; overflow: hidden; } ul { list-style: none; /* li不设置宽度的话,默认是和父元素的宽度一样 */ width: 252px; } ul li { float: left; } ul li a { width: 62px; height: 26px; text-align: center; padding-top: 44px; display: block; border-right: 1px solid red; border-bottom: 1px solid red; position: relative; } .box li a i { width: 24px; height: 24px; background-color: blue; position: absolute; left: 17px; top: 13px; background: url(./img/icons.png) no-repeat; } .box li:first-child a i { background-position: -18px -16px; } .box li:nth-child(2) a i { background-position: -80px -16px; } .box li:nth-child(3) a i { background-position: -142px -16px; } .box li:nth-child(4) a i { background-position: -206px -16px; } .box li:nth-child(5) a i { background-position: -18px -88px; } .box li:nth-child(6) a i { background-position: -80px -88px; } .box li:nth-child(7) a i { background-position: -142px -88px; } .box li:nth-child(8) a i { background-position: -206px -88px; } .box li:nth-child(9) a i { background-position: -18px -158px; } .box li:nth-child(10) a i { background-position: -80px -158px; } .box li:nth-child(11) a i { background-position: -142px -158px; } .box li:nth-child(12) a i { background-position: -206px -158px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <ul> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> <li><a href="#">话费<i></i></a></li> </ul> </div> </body> </html>
06-字体图标
1.精灵图的缺点
1.额外的增加总文件的大小,因为精灵图本质上还是图片
2.会额外的增加http请求次数
3.缩放会失真
2.字体图标的优点:
1.可以做出跟图片一样可以做的事情,改变透明度、旋转度,等..
2.但是本质其实是文字,可以很随意的改变颜色、产生阴影、透明效果等等...
3.本身体积更小,但携带的信息并没有削减。
4.几乎支持所有的浏览器
5.移动端设备必备良药...

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>字体图标的使用</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="./font/iconfont.css"> <style> .icon-shengriliwu { font-size: 30px; /* color: red; */ } .icon-bingxiang { font-size: 30px; /* color: cyan; */ /* font-family: "隶书"; */ } </style> </head> <body> <span class="iconfont icon-shengriliwu"></span> <span class="iconfont icon-bingxiang"></span> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>unicode方式的字体图标</title> <style> @font-face { font-family: 'qianduan'; src: url('./font/iconfont.eot'); src: url('./font/iconfont.eot?#iefix') format('embedded-opentype'), url('./font/iconfont.woff2') format('woff2'), url('./font/iconfont.woff') format('woff'), url('./font/iconfont.ttf') format('truetype'), url('./font/iconfont.svg#iconfont') format('svg'); } .iconfont { font-family: "qianduan" !important; font-size: 86px; font-style: normal; -webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased; -moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale; color: gold; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="iconfont">㑎</div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Symbol的做字体图标</title> <script src="./font/iconfont.js"></script> <style> .icon { width: 10em; height: 10em; vertical-align: -0.15em; fill: currentColor; overflow: hidden; color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <svg class="icon" aria-hidden="true"> <use xlink:href="#icon-yiguanzhu"></use> </svg> </body> </html>
07-过渡

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>过渡</title> <style> .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: blue; /* 谁要变化就给谁添加过渡属性 */ /* transition-property: width; transition-property: height; transition-duration: 2s; transition-timing-function:ease-in-out; */ /* 由快到慢 */ transition: all 1s; /* 设置所有的属性,时间为1s */ } .box:hover { width: 1600px; height: 600px; } .demo { width: 450px; height: 300px; background: url(./images/1.jpg) no-repeat; transition: all 4s; } .demo:hover { background-image: url(./images/2.jpg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> <div class="demo"></div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>transform的使用</title> <style> .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: orangered; transition: all 1s; border-radius: 50%; } .box:hover { /* transform: translate(100px,100px); */ /* transform: translateX(300px); */ transform: translateY(600px); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>让盒子垂直水平居中对齐</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: orange; position: absolute; /* 方法1:使用定位,缺点是宽度高度改变了之后marign-top和marig-left的值也必须跟着改 */ /* left: 50%; top: 50%; margin-top: -100px; margin-left: -100px; */ /*方法2:使用transform的translate位置参数设置百分比实现垂直水平居中 */ left: 50%; top: 50%; transform: translate(-50%,-50%); /* 水平,垂直 */ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>变形中的缩放</title> <style> .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; background-color: orange; margin: 100px auto; transition: all 1s; /* 过渡 */ } .box:hover { transform: scale(1.2); transform: scaleX(2); transform: scaleY(2); transform: scale(.5); /* 缩小 */ } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>变形之旋转</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box { width: 300px; height: 300px; background-color: orangered; margin: 100px auto; transition: all 1s; } .box:hover { transform: rotate(360deg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>

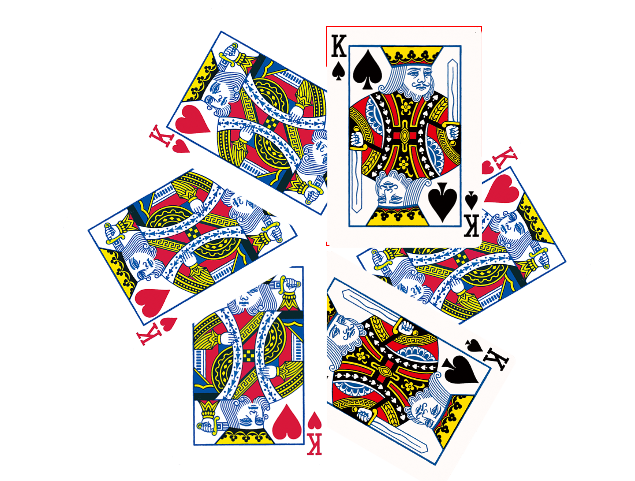
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>旋转的扑克牌</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box { margin: 100px auto; width: 310px; height: 438px; position: relative; /* 设置相对定位 */ border: 1px solid red; } .box img { position: absolute; left: 0; left: 0; transition: all 2s; /* 添加过渡属性 */ transform-origin: left bottom; /* 设置旋转的圆点 */ } .box:hover img:first-child { transform: rotate(60deg); } .box:hover img:nth-child(2) { transform: rotate(120deg); } .box:hover img:nth-child(3) { transform: rotate(180deg); } .box:hover img:nth-child(4) { transform: rotate(240deg); } .box:hover img:nth-child(5) { transform: rotate(300deg); } .box:hover img:nth-child(6) { transform: rotate(360deg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <img src="./images/pk1.png" alt=""> <img src="./images/pk2.png" alt=""> <img src="./images/pk1.png" alt=""> <img src="./images/pk1.png" alt=""> <img src="./images/pk1.png" alt=""> <img src="./images/pk2.png" alt=""> </div> </body> </html>
案例效果:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>倾斜</title> <style> * { margin: 0; padding: 0; } .box img { transition: all 2s; } .box:hover img { transform: skew(45deg,45deg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <img src="./images/s.png" alt=""> </div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>泡泡</title> <style> .box { width: 343px; height: 100px; border: 1px solid blue; margin: 100px auto; background: url(./img/paopao.png) no-repeat left top, url(./img/paopao.png) no-repeat right bottom #02f; transition: all 0.3s; } .box:hover { background: url(./img/paopao.png) no-repeat right bottom, url(./img/paopao.png) no-repeat left top #02f; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"></div> </body> </html>

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>旋转图片</title> <style> .box { width: 767px; height: 620px; margin: 100px auto; } .box img { width: 100%; transition: all 2s; } .box:hover img { transform: rotateY(180deg); } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <img src="./images/s.png" alt=""> </div> </body> </html>
今天学习非常充实,下午上课有点走神了,看来每天睡5个小时并不适合我这种瘦弱的身体,很累,睡了。
