栈的定义:限定仅在表尾进行删除和插入操作的线性表(即后进先出,Last In First Out)
术语:
- 插入操作:进栈、压栈、入栈
- 删除操作:出栈、弹栈
顺序存储结构
-
两栈共享空间:
-
一个数组,两个栈顶在数组的两端
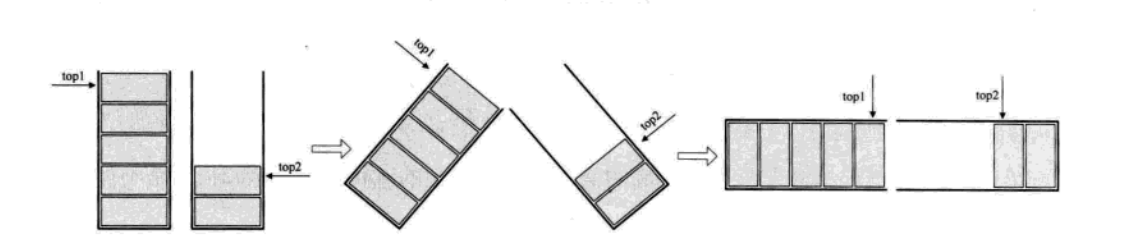
-
下面是一个两栈共享的简单实现:
-
package hdu.test.datastructure;
class ShareTwoStack {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ShareTwoStack sts=new ShareTwoStack(10);
sts.push(1, true);
sts.push(2, true);
sts.push(3, true);
sts.push(10, false);
sts.push(9, false);
sts.push(8, false);
sts.push(7, false);
System.out.print(sts.getSize_0()+" ");
System.out.print(sts.getSize_1()+" ");
System.out.println(sts.getSize_2());
System.out.print(sts.pop(true)+" ");
System.out.println(sts.pop(false));
System.out.print(sts.pop(true)+" ");
System.out.println(sts.pop(false));
System.out.print(sts.getSize_0()+" ");
System.out.print(sts.getSize_1()+" ");
System.out.println(sts.getSize_2());
// 结果
// 10 3 4
// 3 7
// 2 8
// 10 1 2
}
private int[] space;//两个栈共享的空间
private int size_0;//栈空间的大小 默认为20
private int size_1=0;//栈1的大小
private int size_2=0;//栈2的大小
//初始化栈
ShareTwoStack(int size){
this.size_0=size;
this.space=new int[size];
}
ShareTwoStack(){
this(20);
}
//入栈操作 若isFirstStack==true 入第一个栈,否则入第二个栈
public void push(int o,boolean firstStack){
if(firstStack){
if(size_1<(size_0-size_2)){
space[size_1++]=o;
}else{
System.out.println("error");
}
}else{
if((size_0-size_2)>size_1){
space[size_0-1-size_2]=o;
size_2++;
}else{
System.out.println("error");
}
}
}
//出栈操作
public Object pop(boolean firstStack){
Object temp;
if(firstStack){
temp=space[size_1-1];
space[size_1-1]=-1;
size_1--;
}else{
temp=space[size_0-size_2];
space[size_0-size_2]=-1;
size_2--;
}
return temp;
}
public int getSize_0(){
return this.size_0;
}
public int getSize_1(){
return this.size_1;
}
public int getSize_2(){
return this.size_2;
}
}
链式存储结构,简称链栈:
- 链栈也是一种链表,实现方式和第三章的链表相似,只是要以规定的数据结构存取数据(后进先出)
栈的作用:
-
递归
- 斐波那契数列
-
四则运算表达式的求值
队列:
- 定义:队列是只允许在一端进行插入操作,而在另一端进行删除操作的线性表(先进先出,First in First Out)

-
队列的顺序存储结构:
-
循环队列:即头尾相接。
-
下面是循环队列的简单实现:
-
package hdu.test.datastructure;
public class CircleQueue{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
CircleQueue cq=new CircleQueue(10);
cq.printTest();
cq.offer(1);
cq.offer(2);
cq.offer(3);
cq.printTest();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.printTest();
cq.offer(4);
cq.offer(5);
cq.offer(6);
cq.offer(7);
cq.offer(8);
cq.offer(9);
cq.offer(10);
cq.printTest();
cq.offer(1);
cq.printTest();
cq.offer(2);
cq.printTest();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.poll();
cq.printTest();
cq.poll();
}
// Queue
// 队尾进 队头出
private int[] space;//队列空间
private int maxSize;//队列空间的大小
private int size=0;//队列的大小
private int front=-1;//队头下标
private int end=-1;//队尾下标
public void printTest(){
for(int i=0;i<maxSize;i++){
System.out.print(space[i]+ " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
CircleQueue(){
this(20);
}
CircleQueue(int size){
this.maxSize=size;
space=new int[size];
}
//判断是否为空队列
//判断是否为满队列
//0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
//插入操作
public void offer(int e){
int nextEnd=connect(end);
if(nextEnd==front){//队满条件 只剩一个空间
System.out.println("队列已满!");
}else{
space[nextEnd]=e;
end=nextEnd;
size++;
}
}
//删除操作
public void poll(){
int nextFront=connect(front);
if((nextFront-1)==end){
System.out.println("队列为空!");
}else{
space[nextFront]=0;
front=nextFront;
size--;
}
}
//获取队列大小
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
//首尾相接
private int connect(int i){
return i==(maxSize-1)?0:(i+1);
}
}
//结果如下:
//0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
//1 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
//0 0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
//0 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
//1 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
//队列已满!
//1 0 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
//0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
//队列为空!
队列的链式存储结构:
- 链式结构实现方式和链表类似,,只要明白了队列的结构,很容易实现。
最后,栈和队列就学完了,哈哈。