学习要点
- Servlet生命周期
- Servlet API的常用接口和类
- Servlet的部署和配置
- Servlet处理用户请求
Servlet
JSP回顾
JSP技术开发web应用在服务器端生成网页的过程:
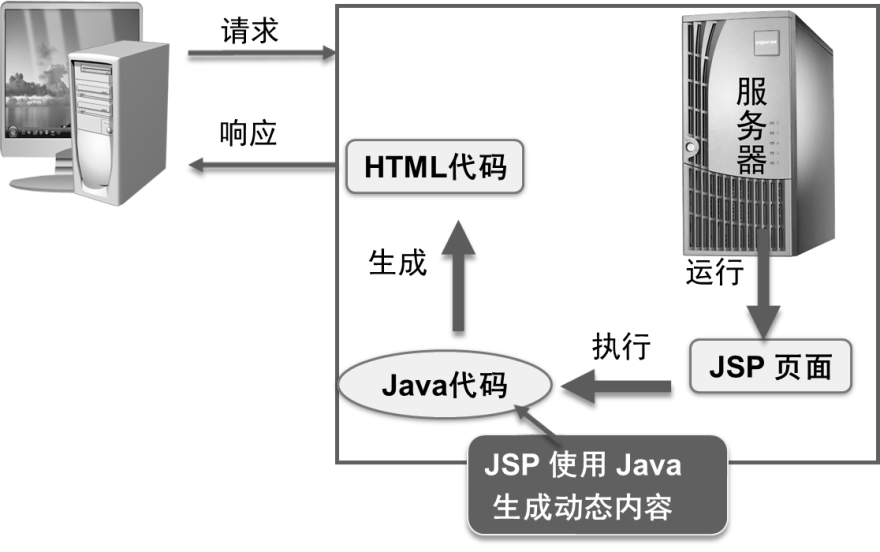
JSP中写入java代码,服务器运行JSP文件时,执行Java代码,动态获取数据,并生成HTML代码,响应到客户端,最终在客户端浏览器上显示。
在JSP技术出现之前,如果要生成动态HTML页面,只能在服务器上运行Java程序,并生成HTML格式内容。Servlet就是运行在服务器端的Java程序。如下图所示:
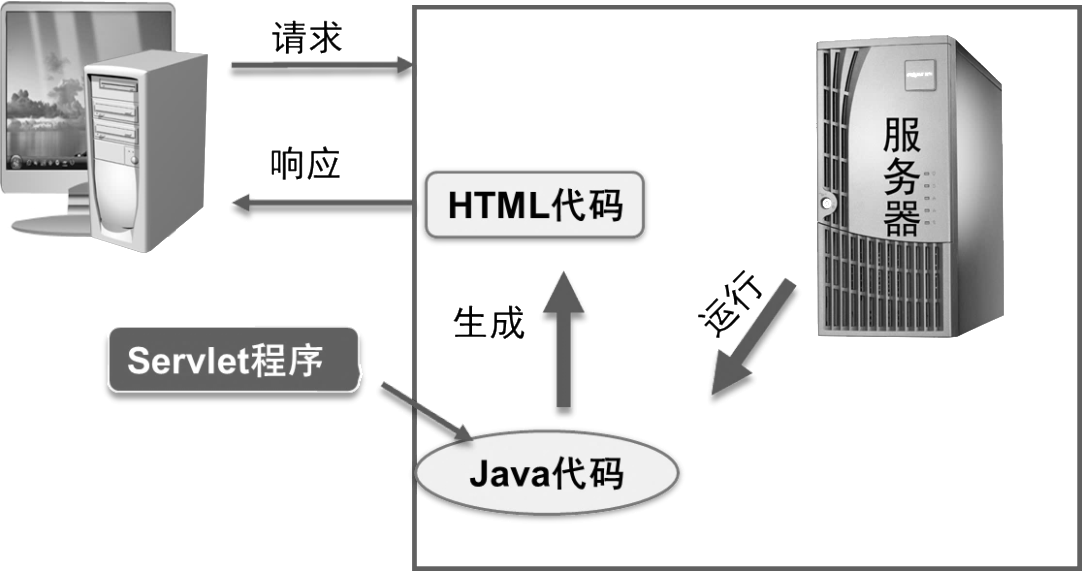
什么是Servlet
Servlet是符合特定规范的Java程序,是一个基于Java技术的组件,运行在服务器端,由Servlet容器管理,用户动态生成内容;Servlet是平台独立的Java类,编写一个Servlet,实际上就是按照Servlet规范写一个Java类,主要用于处理客户端请求并做出响应:
Servlet可以响应任何类型的请求,单是网络上绝大部分用户都是通过HTTP协议请求服务器资源,因此我们主要学习HttpServlet类。
Servlet容器、JSP容器、Web容器是同一个概念,他们是Web服务器或者应用程序服务器的一部分。
第一个Servlet程序
HelloServlet类
package action;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -905409470053831320L;
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");//乱码处理
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">");
out.println("<HTML>");
out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
out.println(" <BODY>");
out.print("你好,Servlet ");
out.println(" </BODY>");
out.println("</HTML>");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
Web.xml中添加Servlet映射(具体配置和部署后面详解)
<servlet> <servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>action.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/HelloServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
Servlet和JSP的关系
- JSP文件执行过程
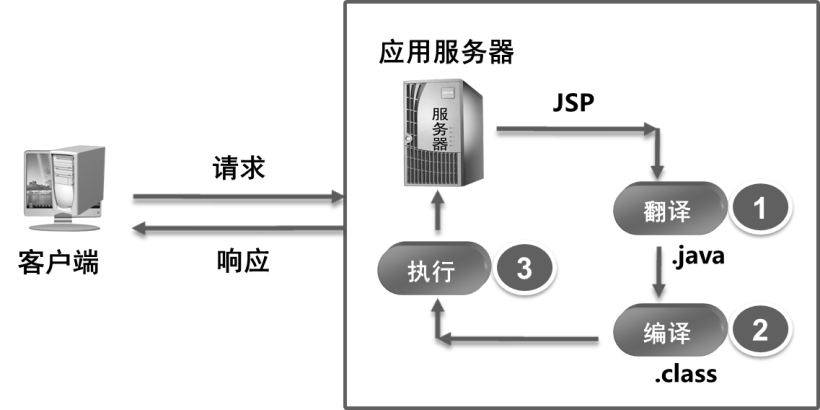
- MyJSP.jsp文件在部署运行后,会在服务器工作目录下生成MyJsp_jsp.java文件:
public final class MyJsp_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent,
org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceImports{
//……
}
HttpJspBase继承于HttpServlet类。因此,JSP文件运行时会被web容器翻译为一个Servlet。
不同开发环境的工作目录位置不同:
- MyEclipse10.6:服务器workcatalinalocalhost项目名..
- 高版本myeclipse和eclipse:工作空间服务器简写workCatalinalocalhost项目名...
- eclipse neno 3位置:E:MyJavaEE.metadata.pluginsorg.eclipse.wst.server.core mpXworkCatalinalocalhost项目名称...
ServletAPI
Servlet体系结构
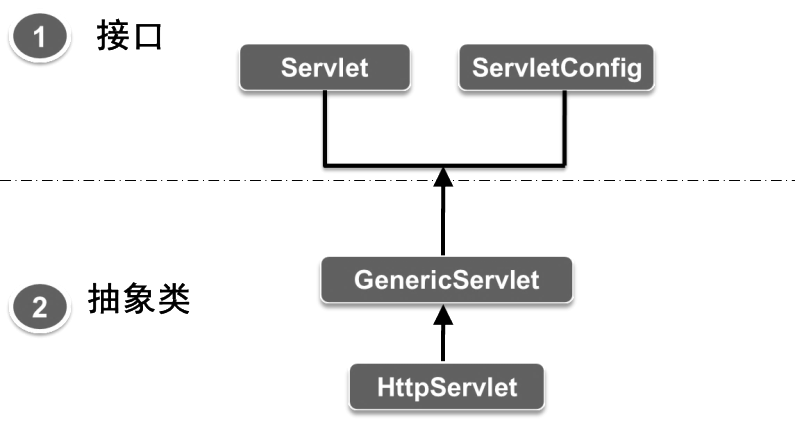
javax.servlet:该包中的类和接口支持通用的不依赖协议的Servlet,包括Servlet、ServletRequesst、ServletResponse、ServletConfig、ServletContext接口和抽象类GenericServlet。
javax.servlet.http:该包中的类和接口用于支持HTTP协议的Servlet API。
Servlet接口
定义了所有Servlet需要实现的方法。
Servlet接口的常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
void init(ServletConfig config) |
由 servlet 容器调用,用于完成Servlet对象在处理客户请求前的初始化工作 |
|
void service (ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) |
由 servlet 容器调用,用来处理客户端的请求 |
|
void destroy() |
由 servlet 容器调用,释放Servlet对象所使用的资源 |
|
ServletConfig getServletConfig() |
返回ServletConfig 对象,该对象包含此 servlet 的初始化和启动参数。返回的 ServletConfig 对象是传递给 init() 方法的对象 |
|
String getServletInfo() |
返回有关 servlet 的信息,比如作者、版本和版权。返回的字符串是纯文本,而不是任何种类的标记(比如 HTML、XML,等等) |
Servlet接口源代码:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Defines methods that all servlets must implement.
*
* <p>
* A servlet is a small Java program that runs within a Web server. Servlets
* receive and respond to requests from Web clients, usually across HTTP, the
* HyperText Transfer Protocol.
*
* <p>
* To implement this interface, you can write a generic servlet that extends
* <code>javax.servlet.GenericServlet</code> or an HTTP servlet that extends
* <code>javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet</code>.
*
* <p>
* This interface defines methods to initialize a servlet, to service requests,
* and to remove a servlet from the server. These are known as life-cycle
* methods and are called in the following sequence:
* <ol>
* <li>The servlet is constructed, then initialized with the <code>init</code>
* method.
* <li>Any calls from clients to the <code>service</code> method are handled.
* <li>The servlet is taken out of service, then destroyed with the
* <code>destroy</code> method, then garbage collected and finalized.
* </ol>
*
* <p>
* In addition to the life-cycle methods, this interface provides the
* <code>getServletConfig</code> method, which the servlet can use to get any
* startup information, and the <code>getServletInfo</code> method, which allows
* the servlet to return basic information about itself, such as author,
* version, and copyright.
*
* @see GenericServlet
* @see javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet
*/
public interface Servlet {
/**
* Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet
* is being placed into service.
*
* <p>
* The servlet container calls the <code>init</code> method exactly once
* after instantiating the servlet. The <code>init</code> method must
* complete successfully before the servlet can receive any requests.
*
* <p>
* The servlet container cannot place the servlet into service if the
* <code>init</code> method
* <ol>
* <li>Throws a <code>ServletException</code>
* <li>Does not return within a time period defined by the Web server
* </ol>
*
*
* @param config
* a <code>ServletConfig</code> object containing the servlet's
* configuration and initialization parameters
*
* @exception ServletException
* if an exception has occurred that interferes with the
* servlet's normal operation
*
* @see UnavailableException
* @see #getServletConfig
*/
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
/**
*
* Returns a {@link ServletConfig} object, which contains initialization and
* startup parameters for this servlet. The <code>ServletConfig</code>
* object returned is the one passed to the <code>init</code> method.
*
* <p>
* Implementations of this interface are responsible for storing the
* <code>ServletConfig</code> object so that this method can return it. The
* {@link GenericServlet} class, which implements this interface, already
* does this.
*
* @return the <code>ServletConfig</code> object that initializes this
* servlet
*
* @see #init
*/
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
/**
* Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to a
* request.
*
* <p>
* This method is only called after the servlet's <code>init()</code> method
* has completed successfully.
*
* <p>
* The status code of the response always should be set for a servlet that
* throws or sends an error.
*
*
* <p>
* Servlets typically run inside multithreaded servlet containers that can
* handle multiple requests concurrently. Developers must be aware to
* synchronize access to any shared resources such as files, network
* connections, and as well as the servlet's class and instance variables.
* More information on multithreaded programming in Java is available in <a
* href
* ="http://java.sun.com/Series/Tutorial/java/threads/multithreaded.html">
* the Java tutorial on multi-threaded programming</a>.
*
*
* @param req
* the <code>ServletRequest</code> object that contains the
* client's request
*
* @param res
* the <code>ServletResponse</code> object that contains the
* servlet's response
*
* @exception ServletException
* if an exception occurs that interferes with the servlet's
* normal operation
*
* @exception IOException
* if an input or output exception occurs
*/
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
/**
* Returns information about the servlet, such as author, version, and
* copyright.
*
* <p>
* The string that this method returns should be plain text and not markup
* of any kind (such as HTML, XML, etc.).
*
* @return a <code>String</code> containing servlet information
*/
public String getServletInfo();
/**
* Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet
* is being taken out of service. This method is only called once all
* threads within the servlet's <code>service</code> method have exited or
* after a timeout period has passed. After the servlet container calls this
* method, it will not call the <code>service</code> method again on this
* servlet.
*
* <p>
* This method gives the servlet an opportunity to clean up any resources
* that are being held (for example, memory, file handles, threads) and make
* sure that any persistent state is synchronized with the servlet's current
* state in memory.
*/
public void destroy();
}
ServeltConfig接口
- 在Servlet初始化过程中获取配置信息
- 一个Servlet只有一个ServletConfig对象
ServletConfig的常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
String getInitParameter(String name) |
获取web.xml中设置的以name命名的初始化参数值 |
|
ServletContext getServletContext( ) |
返回Servlet的上下文对象引用 |
GenericServlet抽象类
提供了Servlet与ServletConfig接口的默认实现方法
GenericServlet的常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
void init(ServletConfig config) |
调用Servlet接口中的init()方法。此方法还有一无参的重载方法,其功能与此方法相同 |
|
String getInitParameter(Stringname) |
返回名称为name的初始化参数的值 |
|
ServletContext getServletContext() |
返回ServletContext对象的引用 |
GenericServlet类源代码:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package javax.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
/**
* Defines a generic, protocol-independent servlet. To write an HTTP servlet for
* use on the Web, extend {@link javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet} instead.
* <p>
* <code>GenericServlet</code> implements the <code>Servlet</code> and
* <code>ServletConfig</code> interfaces. <code>GenericServlet</code> may be
* directly extended by a servlet, although it's more common to extend a
* protocol-specific subclass such as <code>HttpServlet</code>.
* <p>
* <code>GenericServlet</code> makes writing servlets easier. It provides simple
* versions of the lifecycle methods <code>init</code> and <code>destroy</code>
* and of the methods in the <code>ServletConfig</code> interface.
* <code>GenericServlet</code> also implements the <code>log</code> method,
* declared in the <code>ServletContext</code> interface.
* <p>
* To write a generic servlet, you need only override the abstract
* <code>service</code> method.
*/
public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig,
java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private transient ServletConfig config;
/**
* Does nothing. All of the servlet initialization is done by one of the
* <code>init</code> methods.
*/
public GenericServlet() {
// NOOP
}
/**
* Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet
* is being taken out of service. See {@link Servlet#destroy}.
*/
@Override
public void destroy() {
// NOOP by default
}
/**
* Returns a <code>String</code> containing the value of the named
* initialization parameter, or <code>null</code> if the parameter does not
* exist. See {@link ServletConfig#getInitParameter}.
* <p>
* This method is supplied for convenience. It gets the value of the named
* parameter from the servlet's <code>ServletConfig</code> object.
*
* @param name
* a <code>String</code> specifying the name of the
* initialization parameter
* @return String a <code>String</code> containing the value of the
* initialization parameter
*/
@Override
public String getInitParameter(String name) {
return getServletConfig().getInitParameter(name);
}
/**
* Returns the names of the servlet's initialization parameters as an
* <code>Enumeration</code> of <code>String</code> objects, or an empty
* <code>Enumeration</code> if the servlet has no initialization parameters.
* See {@link ServletConfig#getInitParameterNames}.
* <p>
* This method is supplied for convenience. It gets the parameter names from
* the servlet's <code>ServletConfig</code> object.
*
* @return Enumeration an enumeration of <code>String</code> objects
* containing the names of the servlet's initialization parameters
*/
@Override
public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() {
return getServletConfig().getInitParameterNames();
}
/**
* Returns this servlet's {@link ServletConfig} object.
*
* @return ServletConfig the <code>ServletConfig</code> object that
* initialized this servlet
*/
@Override
public ServletConfig getServletConfig() {
return config;
}
/**
* Returns a reference to the {@link ServletContext} in which this servlet
* is running. See {@link ServletConfig#getServletContext}.
* <p>
* This method is supplied for convenience. It gets the context from the
* servlet's <code>ServletConfig</code> object.
*
* @return ServletContext the <code>ServletContext</code> object passed to
* this servlet by the <code>init</code> method
*/
@Override
public ServletContext getServletContext() {
return getServletConfig().getServletContext();
}
/**
* Returns information about the servlet, such as author, version, and
* copyright. By default, this method returns an empty string. Override this
* method to have it return a meaningful value. See
* {@link Servlet#getServletInfo}.
*
* @return String information about this servlet, by default an empty string
*/
@Override
public String getServletInfo() {
return "";
}
/**
* Called by the servlet container to indicate to a servlet that the servlet
* is being placed into service. See {@link Servlet#init}.
* <p>
* This implementation stores the {@link ServletConfig} object it receives
* from the servlet container for later use. When overriding this form of
* the method, call <code>super.init(config)</code>.
*
* @param config
* the <code>ServletConfig</code> object that contains
* configuration information for this servlet
* @exception ServletException
* if an exception occurs that interrupts the servlet's
* normal operation
* @see UnavailableException
*/
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
this.config = config;
this.init();
}
/**
* A convenience method which can be overridden so that there's no need to
* call <code>super.init(config)</code>.
* <p>
* Instead of overriding {@link #init(ServletConfig)}, simply override this
* method and it will be called by
* <code>GenericServlet.init(ServletConfig config)</code>. The
* <code>ServletConfig</code> object can still be retrieved via
* {@link #getServletConfig}.
*
* @exception ServletException
* if an exception occurs that interrupts the servlet's
* normal operation
*/
public void init() throws ServletException {
// NOOP by default
}
/**
* Writes the specified message to a servlet log file, prepended by the
* servlet's name. See {@link ServletContext#log(String)}.
*
* @param msg
* a <code>String</code> specifying the message to be written to
* the log file
*/
public void log(String msg) {
getServletContext().log(getServletName() + ": " + msg);
}
/**
* Writes an explanatory message and a stack trace for a given
* <code>Throwable</code> exception to the servlet log file, prepended by
* the servlet's name. See {@link ServletContext#log(String, Throwable)}.
*
* @param message
* a <code>String</code> that describes the error or exception
* @param t
* the <code>java.lang.Throwable</code> error or exception
*/
public void log(String message, Throwable t) {
getServletContext().log(getServletName() + ": " + message, t);
}
/**
* Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to a
* request. See {@link Servlet#service}.
* <p>
* This method is declared abstract so subclasses, such as
* <code>HttpServlet</code>, must override it.
*
* @param req
* the <code>ServletRequest</code> object that contains the
* client's request
* @param res
* the <code>ServletResponse</code> object that will contain the
* servlet's response
* @exception ServletException
* if an exception occurs that interferes with the servlet's
* normal operation occurred
* @exception IOException
* if an input or output exception occurs
*/
@Override
public abstract void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException;
/**
* Returns the name of this servlet instance. See
* {@link ServletConfig#getServletName}.
*
* @return the name of this servlet instance
*/
@Override
public String getServletName() {
return config.getServletName();
}
}
HttpServlet抽象类
- 继承于GenericServlet
- 处理HTTP协议的请求和响应
HttpServlet的常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) |
调用GenericServlet类中service()方法的实现 |
|
void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse res) |
接收HTTP 请求,并将它们分发给此类中定义的 doXXX 方法 |
|
void doXXX(HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse res) |
根据请求方式的不同,分别调用相应的处理方法,例如doGet()、doPost()等 |
HttpServlet源代码:
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import javax.servlet.DispatcherType;
import javax.servlet.GenericServlet;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
/**
* Provides an abstract class to be subclassed to create
* an HTTP servlet suitable for a Web site. A subclass of
* <code>HttpServlet</code> must override at least
* one method, usually one of these:
*
* <ul>
* <li> <code>doGet</code>, if the servlet supports HTTP GET requests
* <li> <code>doPost</code>, for HTTP POST requests
* <li> <code>doPut</code>, for HTTP PUT requests
* <li> <code>doDelete</code>, for HTTP DELETE requests
* <li> <code>init</code> and <code>destroy</code>,
* to manage resources that are held for the life of the servlet
* <li> <code>getServletInfo</code>, which the servlet uses to
* provide information about itself
* </ul>
*
* <p>There's almost no reason to override the <code>service</code>
* method. <code>service</code> handles standard HTTP
* requests by dispatching them to the handler methods
* for each HTTP request type (the <code>do</code><i>Method</i>
* methods listed above).
*
* <p>Likewise, there's almost no reason to override the
* <code>doOptions</code> and <code>doTrace</code> methods.
*
* <p>Servlets typically run on multithreaded servers,
* so be aware that a servlet must handle concurrent
* requests and be careful to synchronize access to shared resources.
* Shared resources include in-memory data such as
* instance or class variables and external objects
* such as files, database connections, and network
* connections.
* See the
* <a href="http://java.sun.com/Series/Tutorial/java/threads/multithreaded.html">
* Java Tutorial on Multithreaded Programming</a> for more
* information on handling multiple threads in a Java program.
*/
public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final String METHOD_DELETE = "DELETE";
private static final String METHOD_HEAD = "HEAD";
private static final String METHOD_GET = "GET";
private static final String METHOD_OPTIONS = "OPTIONS";
private static final String METHOD_POST = "POST";
private static final String METHOD_PUT = "PUT";
private static final String METHOD_TRACE = "TRACE";
private static final String HEADER_IFMODSINCE = "If-Modified-Since";
private static final String HEADER_LASTMOD = "Last-Modified";
private static final String LSTRING_FILE =
"javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings";
private static final ResourceBundle lStrings =
ResourceBundle.getBundle(LSTRING_FILE);
/**
* Does nothing, because this is an abstract class.
*/
public HttpServlet() {
// NOOP
}
/**
* Called by the server (via the <code>service</code> method) to
* allow a servlet to handle a GET request.
*
* <p>Overriding this method to support a GET request also
* automatically supports an HTTP HEAD request. A HEAD
* request is a GET request that returns no body in the
* response, only the request header fields.
*
* <p>When overriding this method, read the request data,
* write the response headers, get the response's writer or
* output stream object, and finally, write the response data.
* It's best to include content type and encoding. When using
* a <code>PrintWriter</code> object to return the response,
* set the content type before accessing the
* <code>PrintWriter</code> object.
*
* <p>The servlet container must write the headers before
* committing the response, because in HTTP the headers must be sent
* before the response body.
*
* <p>Where possible, set the Content-Length header (with the
* {@link javax.servlet.ServletResponse#setContentLength} method),
* to allow the servlet container to use a persistent connection
* to return its response to the client, improving performance.
* The content length is automatically set if the entire response fits
* inside the response buffer.
*
* <p>When using HTTP 1.1 chunked encoding (which means that the response
* has a Transfer-Encoding header), do not set the Content-Length header.
*
* <p>The GET method should be safe, that is, without
* any side effects for which users are held responsible.
* For example, most form queries have no side effects.
* If a client request is intended to change stored data,
* the request should use some other HTTP method.
*
* <p>The GET method should also be idempotent, meaning
* that it can be safely repeated. Sometimes making a
* method safe also makes it idempotent. For example,
* repeating queries is both safe and idempotent, but
* buying a product online or modifying data is neither
* safe nor idempotent.
*
* <p>If the request is incorrectly formatted, <code>doGet</code>
* returns an HTTP "Bad Request" message.
*
* @param req an {@link HttpServletRequest} object that
* contains the request the client has made
* of the servlet
*
* @param resp an {@link HttpServletResponse} object that
* contains the response the servlet sends
* to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error is
* detected when the servlet handles
* the GET request
*
* @exception ServletException if the request for the GET
* could not be handled
*
* @see javax.servlet.ServletResponse#setContentType
*/
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, msg);
}
}
/**
* Returns the time the <code>HttpServletRequest</code>
* object was last modified,
* in milliseconds since midnight January 1, 1970 GMT.
* If the time is unknown, this method returns a negative
* number (the default).
*
* <p>Servlets that support HTTP GET requests and can quickly determine
* their last modification time should override this method.
* This makes browser and proxy caches work more effectively,
* reducing the load on server and network resources.
*
* @param req the <code>HttpServletRequest</code>
* object that is sent to the servlet
*
* @return a <code>long</code> integer specifying
* the time the <code>HttpServletRequest</code>
* object was last modified, in milliseconds
* since midnight, January 1, 1970 GMT, or
* -1 if the time is not known
*/
protected long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest req) {
return -1;
}
/**
* <p>Receives an HTTP HEAD request from the protected
* <code>service</code> method and handles the
* request.
* The client sends a HEAD request when it wants
* to see only the headers of a response, such as
* Content-Type or Content-Length. The HTTP HEAD
* method counts the output bytes in the response
* to set the Content-Length header accurately.
*
* <p>If you override this method, you can avoid computing
* the response body and just set the response headers
* directly to improve performance. Make sure that the
* <code>doHead</code> method you write is both safe
* and idempotent (that is, protects itself from being
* called multiple times for one HTTP HEAD request).
*
* <p>If the HTTP HEAD request is incorrectly formatted,
* <code>doHead</code> returns an HTTP "Bad Request"
* message.
*
* @param req the request object that is passed to the servlet
*
* @param resp the response object that the servlet
* uses to return the headers to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error occurs
*
* @exception ServletException if the request for the HEAD
* could not be handled
*/
protected void doHead(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
if (DispatcherType.INCLUDE.equals(req.getDispatcherType())) {
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
NoBodyResponse response = new NoBodyResponse(resp);
doGet(req, response);
response.setContentLength();
}
}
/**
* Called by the server (via the <code>service</code> method)
* to allow a servlet to handle a POST request.
*
* The HTTP POST method allows the client to send
* data of unlimited length to the Web server a single time
* and is useful when posting information such as
* credit card numbers.
*
* <p>When overriding this method, read the request data,
* write the response headers, get the response's writer or output
* stream object, and finally, write the response data. It's best
* to include content type and encoding. When using a
* <code>PrintWriter</code> object to return the response, set the
* content type before accessing the <code>PrintWriter</code> object.
*
* <p>The servlet container must write the headers before committing the
* response, because in HTTP the headers must be sent before the
* response body.
*
* <p>Where possible, set the Content-Length header (with the
* {@link javax.servlet.ServletResponse#setContentLength} method),
* to allow the servlet container to use a persistent connection
* to return its response to the client, improving performance.
* The content length is automatically set if the entire response fits
* inside the response buffer.
*
* <p>When using HTTP 1.1 chunked encoding (which means that the response
* has a Transfer-Encoding header), do not set the Content-Length header.
*
* <p>This method does not need to be either safe or idempotent.
* Operations requested through POST can have side effects for
* which the user can be held accountable, for example,
* updating stored data or buying items online.
*
* <p>If the HTTP POST request is incorrectly formatted,
* <code>doPost</code> returns an HTTP "Bad Request" message.
*
*
* @param req an {@link HttpServletRequest} object that
* contains the request the client has made
* of the servlet
*
* @param resp an {@link HttpServletResponse} object that
* contains the response the servlet sends
* to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error is
* detected when the servlet handles
* the request
*
* @exception ServletException if the request for the POST
* could not be handled
*
* @see javax.servlet.ServletOutputStream
* @see javax.servlet.ServletResponse#setContentType
*/
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, msg);
}
}
/**
* Called by the server (via the <code>service</code> method)
* to allow a servlet to handle a PUT request.
*
* The PUT operation allows a client to
* place a file on the server and is similar to
* sending a file by FTP.
*
* <p>When overriding this method, leave intact
* any content headers sent with the request (including
* Content-Length, Content-Type, Content-Transfer-Encoding,
* Content-Encoding, Content-Base, Content-Language, Content-Location,
* Content-MD5, and Content-Range). If your method cannot
* handle a content header, it must issue an error message
* (HTTP 501 - Not Implemented) and discard the request.
* For more information on HTTP 1.1, see RFC 2616
* <a href="http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2616.txt"></a>.
*
* <p>This method does not need to be either safe or idempotent.
* Operations that <code>doPut</code> performs can have side
* effects for which the user can be held accountable. When using
* this method, it may be useful to save a copy of the
* affected URL in temporary storage.
*
* <p>If the HTTP PUT request is incorrectly formatted,
* <code>doPut</code> returns an HTTP "Bad Request" message.
*
* @param req the {@link HttpServletRequest} object that
* contains the request the client made of
* the servlet
*
* @param resp the {@link HttpServletResponse} object that
* contains the response the servlet returns
* to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error occurs
* while the servlet is handling the
* PUT request
*
* @exception ServletException if the request for the PUT
* cannot be handled
*/
protected void doPut(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_put_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, msg);
}
}
/**
* Called by the server (via the <code>service</code> method)
* to allow a servlet to handle a DELETE request.
*
* The DELETE operation allows a client to remove a document
* or Web page from the server.
*
* <p>This method does not need to be either safe
* or idempotent. Operations requested through
* DELETE can have side effects for which users
* can be held accountable. When using
* this method, it may be useful to save a copy of the
* affected URL in temporary storage.
*
* <p>If the HTTP DELETE request is incorrectly formatted,
* <code>doDelete</code> returns an HTTP "Bad Request"
* message.
*
* @param req the {@link HttpServletRequest} object that
* contains the request the client made of
* the servlet
*
*
* @param resp the {@link HttpServletResponse} object that
* contains the response the servlet returns
* to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error occurs
* while the servlet is handling the
* DELETE request
*
* @exception ServletException if the request for the
* DELETE cannot be handled
*/
protected void doDelete(HttpServletRequest req,
HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String protocol = req.getProtocol();
String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_delete_not_supported");
if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, msg);
} else {
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST, msg);
}
}
private static Method[] getAllDeclaredMethods(Class<?> c) {
if (c.equals(javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.class)) {
return null;
}
Method[] parentMethods = getAllDeclaredMethods(c.getSuperclass());
Method[] thisMethods = c.getDeclaredMethods();
if ((parentMethods != null) && (parentMethods.length > 0)) {
Method[] allMethods =
new Method[parentMethods.length + thisMethods.length];
System.arraycopy(parentMethods, 0, allMethods, 0,
parentMethods.length);
System.arraycopy(thisMethods, 0, allMethods, parentMethods.length,
thisMethods.length);
thisMethods = allMethods;
}
return thisMethods;
}
/**
* Called by the server (via the <code>service</code> method)
* to allow a servlet to handle a OPTIONS request.
*
* The OPTIONS request determines which HTTP methods
* the server supports and
* returns an appropriate header. For example, if a servlet
* overrides <code>doGet</code>, this method returns the
* following header:
*
* <p><code>Allow: GET, HEAD, TRACE, OPTIONS</code>
*
* <p>There's no need to override this method unless the
* servlet implements new HTTP methods, beyond those
* implemented by HTTP 1.1.
*
* @param req the {@link HttpServletRequest} object that
* contains the request the client made of
* the servlet
*
* @param resp the {@link HttpServletResponse} object that
* contains the response the servlet returns
* to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error occurs
* while the servlet is handling the
* OPTIONS request
*
* @exception ServletException if the request for the
* OPTIONS cannot be handled
*/
protected void doOptions(HttpServletRequest req,
HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
Method[] methods = getAllDeclaredMethods(this.getClass());
boolean ALLOW_GET = false;
boolean ALLOW_HEAD = false;
boolean ALLOW_POST = false;
boolean ALLOW_PUT = false;
boolean ALLOW_DELETE = false;
boolean ALLOW_TRACE = true;
boolean ALLOW_OPTIONS = true;
for (int i=0; i<methods.length; i++) {
Method m = methods[i];
if (m.getName().equals("doGet")) {
ALLOW_GET = true;
ALLOW_HEAD = true;
}
if (m.getName().equals("doPost"))
ALLOW_POST = true;
if (m.getName().equals("doPut"))
ALLOW_PUT = true;
if (m.getName().equals("doDelete"))
ALLOW_DELETE = true;
}
String allow = null;
if (ALLOW_GET)
allow=METHOD_GET;
if (ALLOW_HEAD)
if (allow==null) allow=METHOD_HEAD;
else allow += ", " + METHOD_HEAD;
if (ALLOW_POST)
if (allow==null) allow=METHOD_POST;
else allow += ", " + METHOD_POST;
if (ALLOW_PUT)
if (allow==null) allow=METHOD_PUT;
else allow += ", " + METHOD_PUT;
if (ALLOW_DELETE)
if (allow==null) allow=METHOD_DELETE;
else allow += ", " + METHOD_DELETE;
if (ALLOW_TRACE)
if (allow==null) allow=METHOD_TRACE;
else allow += ", " + METHOD_TRACE;
if (ALLOW_OPTIONS)
if (allow==null) allow=METHOD_OPTIONS;
else allow += ", " + METHOD_OPTIONS;
resp.setHeader("Allow", allow);
}
/**
* Called by the server (via the <code>service</code> method)
* to allow a servlet to handle a TRACE request.
*
* A TRACE returns the headers sent with the TRACE
* request to the client, so that they can be used in
* debugging. There's no need to override this method.
*
* @param req the {@link HttpServletRequest} object that
* contains the request the client made of
* the servlet
*
* @param resp the {@link HttpServletResponse} object that
* contains the response the servlet returns
* to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error occurs
* while the servlet is handling the
* TRACE request
*
* @exception ServletException if the request for the
* TRACE cannot be handled
*/
protected void doTrace(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException
{
int responseLength;
String CRLF = "
";
StringBuilder buffer = new StringBuilder("TRACE ").append(req.getRequestURI())
.append(" ").append(req.getProtocol());
Enumeration<String> reqHeaderEnum = req.getHeaderNames();
while( reqHeaderEnum.hasMoreElements() ) {
String headerName = reqHeaderEnum.nextElement();
buffer.append(CRLF).append(headerName).append(": ")
.append(req.getHeader(headerName));
}
buffer.append(CRLF);
responseLength = buffer.length();
resp.setContentType("message/http");
resp.setContentLength(responseLength);
ServletOutputStream out = resp.getOutputStream();
out.print(buffer.toString());
out.close();
return;
}
/**
* Receives standard HTTP requests from the public
* <code>service</code> method and dispatches
* them to the <code>do</code><i>Method</i> methods defined in
* this class. This method is an HTTP-specific version of the
* {@link javax.servlet.Servlet#service} method. There's no
* need to override this method.
*
* @param req the {@link HttpServletRequest} object that
* contains the request the client made of
* the servlet
*
* @param resp the {@link HttpServletResponse} object that
* contains the response the servlet returns
* to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error occurs
* while the servlet is handling the
* HTTP request
*
* @exception ServletException if the HTTP request
* cannot be handled
*
* @see javax.servlet.Servlet#service
*/
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
if (lastModified == -1) {
// servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason
// to go through further expensive logic
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
long ifModifiedSince;
try {
ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException iae) {
// Invalid date header - proceed as if none was set
ifModifiedSince = -1;
}
if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) {
// If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet()
// Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare
// A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doGet(req, resp);
} else {
resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED);
}
}
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) {
long lastModified = getLastModified(req);
maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified);
doHead(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) {
doDelete(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) {
doOptions(req,resp);
} else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) {
doTrace(req,resp);
} else {
//
// Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever
// method was requested, anywhere on this server.
//
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = method;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg);
}
}
/*
* Sets the Last-Modified entity header field, if it has not
* already been set and if the value is meaningful. Called before
* doGet, to ensure that headers are set before response data is
* written. A subclass might have set this header already, so we
* check.
*/
private void maybeSetLastModified(HttpServletResponse resp,
long lastModified) {
if (resp.containsHeader(HEADER_LASTMOD))
return;
if (lastModified >= 0)
resp.setDateHeader(HEADER_LASTMOD, lastModified);
}
/**
* Dispatches client requests to the protected
* <code>service</code> method. There's no need to
* override this method.
*
* @param req the {@link HttpServletRequest} object that
* contains the request the client made of
* the servlet
*
* @param res the {@link HttpServletResponse} object that
* contains the response the servlet returns
* to the client
*
* @exception IOException if an input or output error occurs
* while the servlet is handling the
* HTTP request
*
* @exception ServletException if the HTTP request cannot
* be handled
*
* @see javax.servlet.Servlet#service
*/
@Override
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request;
HttpServletResponse response;
try {
request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response");
}
service(request, response);
}
}
/*
* A response wrapper for use in (dumb) "HEAD" support.
* This just swallows that body, counting the bytes in order to set
* the content length appropriately. All other methods delegate to the
* wrapped HTTP Servlet Response object.
*/
// file private
class NoBodyResponse extends HttpServletResponseWrapper {
private final NoBodyOutputStream noBody;
private PrintWriter writer;
private boolean didSetContentLength;
// file private
NoBodyResponse(HttpServletResponse r) {
super(r);
noBody = new NoBodyOutputStream();
}
// file private
void setContentLength() {
if (!didSetContentLength) {
if (writer != null) {
writer.flush();
}
super.setContentLength(noBody.getContentLength());
}
}
// SERVLET RESPONSE interface methods
@Override
public void setContentLength(int len) {
super.setContentLength(len);
didSetContentLength = true;
}
@Override
public void setContentLengthLong(long len) {
super.setContentLengthLong(len);
didSetContentLength = true;
}
@Override
public void setHeader(String name, String value) {
super.setHeader(name, value);
checkHeader(name);
}
@Override
public void addHeader(String name, String value) {
super.addHeader(name, value);
checkHeader(name);
}
@Override
public void setIntHeader(String name, int value) {
super.setIntHeader(name, value);
checkHeader(name);
}
@Override
public void addIntHeader(String name, int value) {
super.addIntHeader(name, value);
checkHeader(name);
}
private void checkHeader(String name) {
if ("content-length".equalsIgnoreCase(name)) {
didSetContentLength = true;
}
}
@Override
public ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException {
return noBody;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getWriter() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
if (writer == null) {
OutputStreamWriter w;
w = new OutputStreamWriter(noBody, getCharacterEncoding());
writer = new PrintWriter(w);
}
return writer;
}
}
/*
* Servlet output stream that gobbles up all its data.
*/
// file private
class NoBodyOutputStream extends ServletOutputStream {
private static final String LSTRING_FILE =
"javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings";
private static final ResourceBundle lStrings =
ResourceBundle.getBundle(LSTRING_FILE);
private int contentLength = 0;
// file private
NoBodyOutputStream() {
// NOOP
}
// file private
int getContentLength() {
return contentLength;
}
@Override
public void write(int b) {
contentLength++;
}
@Override
public void write(byte buf[], int offset, int len) throws IOException {
if (buf == null) {
throw new NullPointerException(
lStrings.getString("err.io.nullArray"));
}
if (offset < 0 || len < 0 || offset+len > buf.length) {
String msg = lStrings.getString("err.io.indexOutOfBounds");
Object[] msgArgs = new Object[3];
msgArgs[0] = Integer.valueOf(offset);
msgArgs[1] = Integer.valueOf(len);
msgArgs[2] = Integer.valueOf(buf.length);
msg = MessageFormat.format(msg, msgArgs);
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(msg);
}
contentLength += len;
}
@Override
public boolean isReady() {
// TODO SERVLET 3.1
return false;
}
@Override
public void setWriteListener(javax.servlet.WriteListener listener) {
// TODO SERVLET 3.1
}
}
ServeltContext对象
- 一个ServeltContext对象表示一个web应用的上下文,Servlet使用ServletContext接口定义的方法与Servlet容器进行通信。
- Servlet容器厂商负责提供ServeltContext接口实现,容器在加载应用程序的时候创建ServeltContext对象,ServeltContext对象被Servlet容器中的所有Servlet共享,例如application对象就是ServletContext的实例。
ServeltContext对象常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
String getInitParameter(String name) |
获取名称为name的系统范围内的初始化参数值,系统范围内的初始化参数可以在部署描述符中使用<context-param>元素定义 |
|
void setAttribute(String name,Ojbect object) |
设置名称为name的属性 |
|
Object getAttribute(String name) |
获取名称为name的属性 |
|
String getRealPath(String path) |
返回参数所代表目录的真实路径 |
|
void log(String message) |
记录一般日志信息 |
请求、响应相关接口

- ServletRequest接口:获取客户端的请求数据
常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
Object getAttribute(String name) |
获取名称为name的属性值 |
|
void setAttribute(String name, Object object) |
在请求中保存名称为name的属性 |
|
void removeAttribute(String name) |
清除请求中名字为name的属性 |
- HttpServletRequest接口:除了继承ServletRequest接口中的方法,还增加了一些用于读取请求信息的方法。
HttpServletRequest的常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
public String getContextPath() |
返回请求URI中表示请求上下文的路径,上下文路径是请求URI的开始部分 |
|
public Cookie[ ] getCookies() |
返回客户端在此次请求中发送的所有cookie对象 |
|
public HttpSession getSession() |
返回和此次请求相关联的session,如果没有给客户端分配session,则创建一个新的session |
|
public String getMethod() |
返回此次请求所使用的HTTP方法的名字,如GET、POST |
- ServletResponse接口:向客户端发送响应数据。
ServletResponse接口的常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
PrintWriter getWriter() |
返回PrintWrite对象,用于向客户端发送文本 |
|
String getCharacterEncoding() |
返回在响应中发送的正文所使用的字符编码 |
|
void setCharacterEncoding() |
设置发送到客户端的响应的字符编码 |
|
void setContentType(String type) |
设置发送到客户端的响应的内容类型,此时响应的状态属于尚未提交 |
- HttpServletResponse接口:除了继承ServletResponse接口中的方法,还增加了新的方法
HttpServletResponse的常用方法:
|
方法名称 |
功能描述 |
|
void addCookie(Cookie cookie) |
增加一个cookie到响应中,这个方法可多次调用,设置多个cookie |
|
void addHeader(String name,String value) |
将一个名称为name,值为value的响应报头添加到响应中 |
|
void sendRedirect(String location) |
发送一个临时的重定向响应到客户端,以便客户端访问新的URL |
|
void encodeURL(String url) |
使用session ID对用于重定向的URL进行编码 |
Servlet生命周期
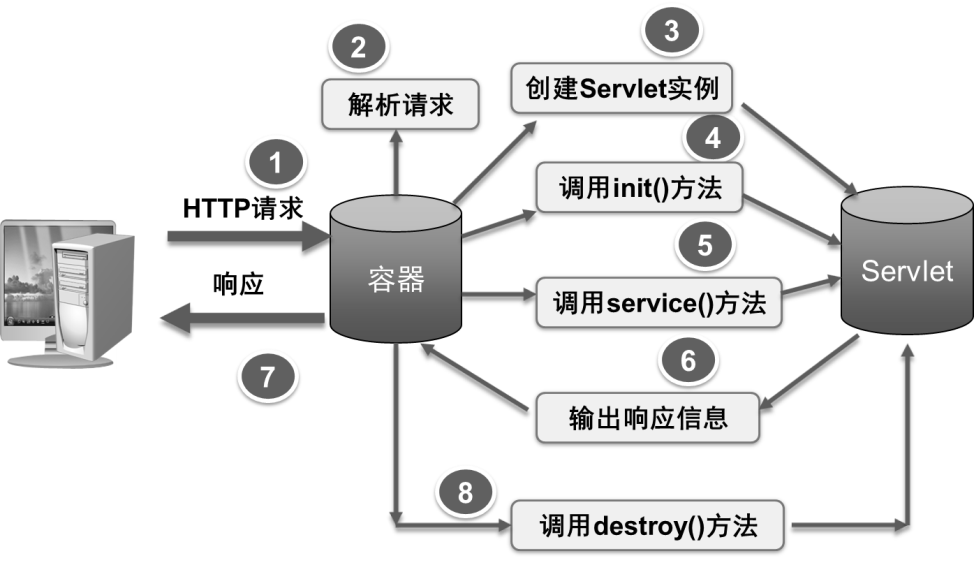
加载和实例化
- 当Servlet容器启动或者当客户端发送一个请求时,Servlet容器会查找内存中是否存在该Servlet的实例,如果不存在,就创建一个Servlet实例;如果存在,就直接从内存中取出该实例响应请求。
- Servlet容器根据Servlet类的位置加载Servlet类,成功加载后,由容器创建Servlet的实例。
初始化
- Servlet容器完成Servlet实例化后,Servlet容器将调用Servlet的init()方法进行初始化。
- 对于每一个Servlet实例,init()方法只被调用一次。
服务
- Servlet被实例化后,就处于能够响应请求的就绪状态。
- 当Servlet容器接收客户端请求时,调用Servlet的service()方法处理客户端请求。
- Servlet实例通过ServletRequest对象获得客户端请求,通过调用ServletResponse对象的方法设置响应信息。
销毁
- Servlet实例的创建和销毁都是由Servlet容器负责处理。
- Servlet容器判断Servlet对象是否应当被释放时(容器关闭或者资源回收),容器就会调用Servlet的destroy()方法。
- destroy()方法指明哪些系统资源可以被系统回收,而不是由destroy()方法直接回收。
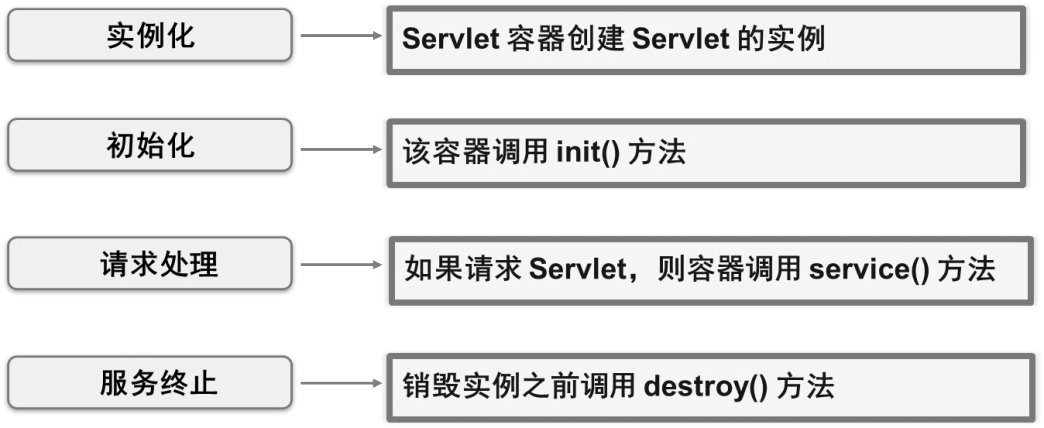
Servlet生命周期过程和相应的方法
Servlet生命周期实例代码
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
/**构造函数*/
public HelloServlet() {
System.out.println("构造方法被调用!");
}
/**初始化方法*/
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
System.out.println("初始化时,init()方法被调用");
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("处理请求时,doGet()方法被调用!");
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("处理请求时,doPost()方法被调用!");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
super.destroy();
System.out.println("释放系统资源时,destroy()方法被调用!");
}
}
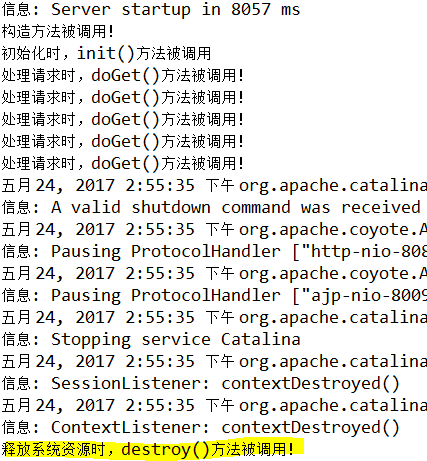
HelloServlet第一次被调用时,一次执行荧光笔标识部分:

在ie地址栏中,HelloServlet被请求一次,就调用doGet()方法一次。
destroy()方法什么时候被执行?服务器停止的时候,或者系统回收资源时。
Servlet应用
Servlet的编译和部署
- 创建Servlet
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");//输出文本编码设置,避免乱码
String name=request.getParameter("name").trim();
if(name.length()!=0){
name=new String(name.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"),"UTF-8");
}else{
name="游客";
}
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">");
out.println("<HTML>");
out.println(" <HEAD><TITLE>A Servlet</TITLE></HEAD>");
out.println(" <BODY>");
out.print("欢迎"+name+"来到Servlet世界");
out.println(" </BODY>");
out.println("</HTML>");
out.flush();
out.close();
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
}
}
2.部署Servlet
在web.xml中,添加对Servlet的配置。
<servlet>元素:把Servlet内部名映射到一个Servlet类全限定名。
<servlet-mapping>元素:把用户访问的URL映射到Servlet。
实例代码:
<web-app> <servlet> <servlet-name>TestServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>action.TestServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>TestServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/login.action</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
注意点:
-
- servlet-name元素中的名字在同一个web项目中必须唯一
- servlet-class元素中的类名是类的全限定名
- url-patter元素中的URL参数是相对与web程序的路径,例如该例中web项目名为news,则该路径为:http://localhost:8080/news/login.action
url-pattern设置方法:
-
- 精确匹配:<url-pattern>/xxx</url-pattern>
- 路径匹配:<url-pattern>/xxx/*</url-pattern>
- 扩展名匹配:<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
3.编写JSP访问Servlet
<form action="login.action" method="post"> 姓名:<input type="text" name="name"> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form>
4.启动Tomcat访问Servlet
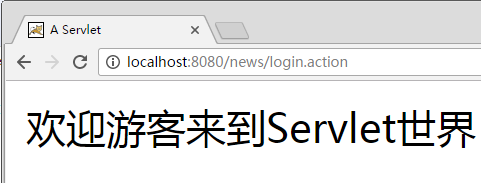

上机练习:使用Servlet实现用户登录
需求描述
- 编写Servlet,验证用户登录,如果用户名与密码都为“admin”则验证通过,跳转欢迎页面,否则弹出提示信息“用户名或密码错误,请重新输入!”,点击“确定”后跳转至登录页面。
实现思路
- 建立Web应用配置web.xml
- 编写Servlet继承自HttpServlet
- 配置web.xml
- 启动Tomcat,访问Servlet
关键代码参考
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
String uName=request.getParameter("userName");
String pwd=request.getParameter("pwd");
if("admin".equals(uName)&&"admin".equals(pwd)){
HttpSession session=request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("login", uName);
response.sendRedirect("welcome.jsp");
}else{
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("<script type='text/javascript'>alert('用户名或密码错误,请重新输入!');location.href='index.jsp';</script>");
out.close();
}
获得Servlet初始化参数
Servlet初始化参数配置
<servlet>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.jbit.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>initParam</param-name>
<param-value>Hello Servlet</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>HelloServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/HelloServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
获取初始化参数
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doGet(request, response);
System.out.println("处理请求时,doGet()方法被调用。");
//根据参数名获取初始化参数
String initParam = getInitParameter("initParam");
System.out.println(initParam);
}
上机练习:编写Servlet类获取初始化参数
需求说明
- 编写Servlet,并设置Servlet初始化参数,然后调用Servlet,在控制台输出显示“欢迎XXX”。
实现思路
- 修改web.xml配置的初始化参数,添加<init-param>元素,并设定参数名称及参数值。
- 编写Servlet继承自HttpServlet,在doGet()方法中获取初始化参数,输出到控制台显示。
获取Web程序上下文参数
配置初始化上下文
<web-app>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextParam</param-name>
<param-value>Hello Servlet</param-value>
</context-param>
<!--省略其他配置-->
</web-app>
注意事项:<context-param>元素必须出现在所有Servlet配置元素之前。
获取Servlet上下文参数
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
System.out.println("处理请求时,doGet()方法被调用。");
String initParam = getInitParameter("initParam");
String contextParam =
this.getServletContext().getInitParameter("contextParam");
System.out.println("Servlet初始化参数" + initParam);
System.out.println("系统初始化参数" + contextParam);
}
上机练习:编写Servlet类获取系统上下文参数
需求描述
编写Servlet,并设置系统初始化参数,部署运行输出显示“系统的初始化参数是:This is System’s parameter”
使用Servlet作为Web项目的控制器
Servlet和JSP的区别
JSP在用户请求完后后被编译成Servlet,所有JSP可以看作是运行时的Servlet,他们之间的主要区别:
- Servlet是在服务器上执行和解释浏览器的请求,承担客户端和其他应用程序之间的中间层的角色,Servlet主要是把动态的内容混合到静态内容中以产生HTML。
- JSP页面在HTML元素中嵌入Java脚本代码和JSP标记,使文件格式更清晰。
- 使用JSP不需要在web.xml中配置每一个文件,只需要扩展名是.jsp,JSP容器便会自动识别,将其转换为Servlet为客户端服务。
使用Servlet实现控制器
在实际应用中,我们根据Servlet和JSP各种的擅长来决定如何使用它们:
- Servlet:流程控制和事务处理
- JSP:展示数据
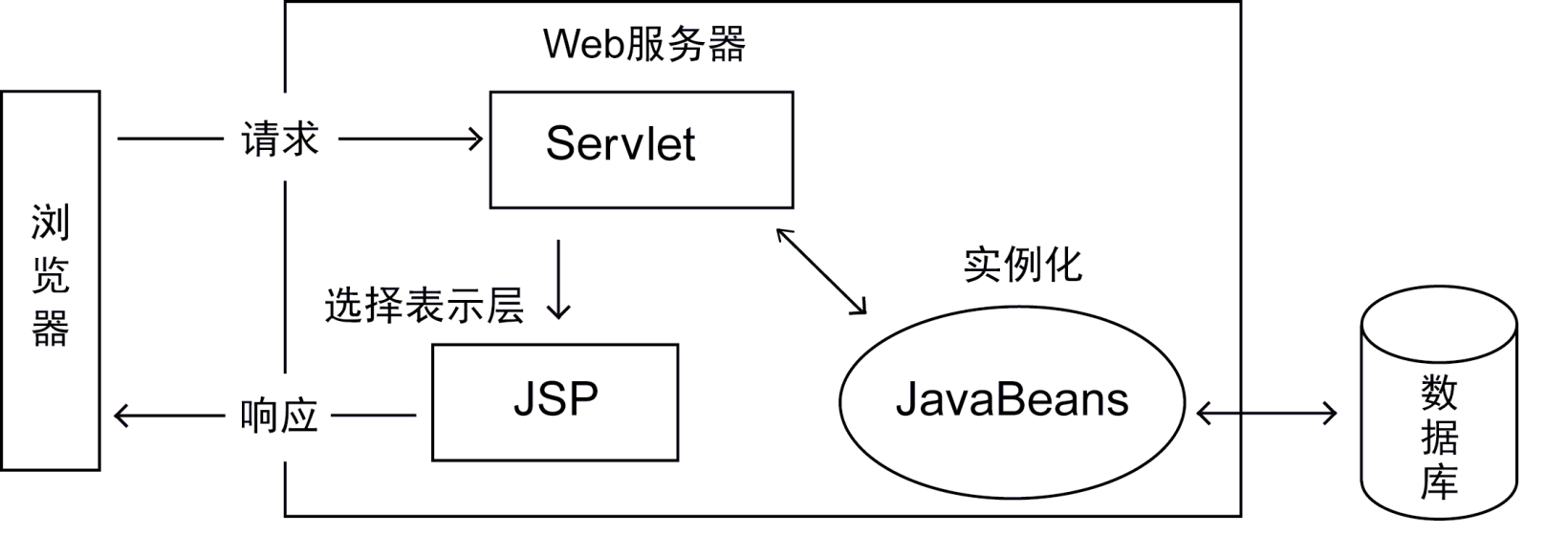
之前新闻发布系统中使用JSP作为控制页,在学习完Servlet后,可以把这一部分功能交给Servlet处理。Servlet作为web系统的控制器角色,负责接受请求,实例化JavaBean对象,对业务逻辑进行处理,为JSP页面准备封装数据的JavaBean对象,并将请求分发给适当的JSP页面来产生相应。这也是Web项目采用的逻辑设计模式:MVC(Model-View-Control)。
上机练习:使用Servlet修改新闻发布系统
需求说明
- 修改登陆管理控制器为Servlet
- 修改主题管理控制器为Servlet
- 修改新闻管理控制器为Servlet
- 修改评论管理控制器为Servlet
实现思路
- 创建相应Servlet
- 配置web.xml
- 修改页面链接
主题管理Servlet参考代码
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.jms.Topic;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class TopicServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
doPost(request, response);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
request.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
response.setContentType("text/html;charset=UTF-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
String opr = request.getParameter("opr");
TopicsBiz topicsBiz = new TopicsBizImpl();
// 获取应用上下文路径(当前web应用路径)
String contextPath = request.getContextPath();
if (opr.equals("update")) { // 更新主题
String tid = request.getParameter("tid");
String tname = request.getParameter("tname");
Map<String, String> topic = new HashMap<String, String>();
topic.put("tid", tid);
topic.put("tname", tname);
if (topicsBiz.updateTopic(topic) > 0) {
out.print("<script type='text/javascript'>"
+ "alert('已经成功更新主题,点击确认返回主题列表');" + "location.href='"
+ contextPath + "/TopicServlet?opr=list';</script>");
} else {
out.print("<script type='text/javascript'>"
+ "alert('更新主题失败,点击确认返回主题列表');" + "location.href='"
+ contextPath + "/newspages/topic_list.jsp'; </script>");
}
} else if (opr.equals("list")) {//查找所有主题
List<Topic> list = topicsBiz.getAllTopics();
request.getSession().setAttribute("list", list);
response.sendRedirect(contextPath + "/newspages/topic_list.jsp");
} else if (opr.equals("add")) {// 添加主题
String tname = request.getParameter("tname");
Topic topic = topicsBiz.findTopicByName(tname);
if (topic == null) {
topicsBiz.addTopic(tname);
List<Topic> list4 = topicsBiz.getAllTopics();
request.getSession().setAttribute("list4", list4);
out.print("<script type='text/javascript'>"
+ "alert('当前主题创建成功,点击确认返回主题列表!');"
+ "location.href='topic_ control.jsp?opr=list'; "
+ "</script>");
}else{
out.print("<script type='text/javascript'>"
+ "alert('当前主题已存在,请输入不同的主题!');"
+ "location.href='../newspages/topic_add.jsp'; "
+ "</script>");
}
}else if(opr.equals("del")){//删除主题
String tid = request.getParameter("tid");
int result=topicsBiz.deleteTopic(tid);
if(result==1){
List<Topic> list4 = topicsBiz.getAllTopics();
request.getSession().setAttribute("list4",list4);//所有的主题
out.print("<script type='text/javascript'>"
+ "alert('已经成功删除主题,点击确认返回原来页面!');"
+ "location.href='topic_ control.jsp?opr=list'; "
+ "</script>");
}else if(result==-1){
out.print("<script type='text/javascript'>"
+ "alert('删除主题失败!请联系管理员查找原因!点击确认返回原来页面!');"
+ "location.href='topic_ control.jsp?opr=list'; "
+ "</script>");
}else{
out.print("<script type='text/javascript'>"
+ "alert('该主题下还有文章,不能删除!');"
+ "location.href='topic_ control.jsp?opr=list'; "
+ "</script>");
}
}
out.flush();
out.close();
}
}