理解
1.Vuex 的状态存储是响应式的。当 Vue 组件从 store 中读取状态的时候,若 store 中的状态发生变化,那么相应的组件也会相应地得到高效更新。
2.不能直接改变 store 中的状态。改变 store 中的状态的唯一途径就是显式地提交 commit/mutation。
action通过commit调用mutation
vue通过commit调用mutation
vue通过dispatch调用action
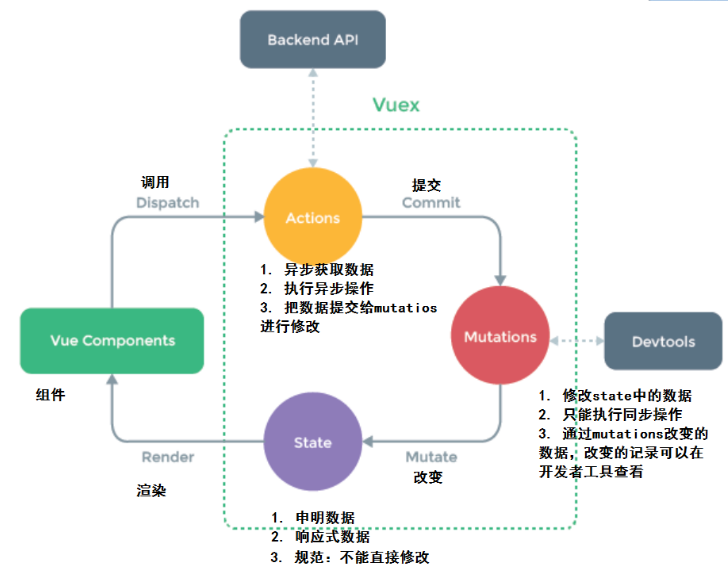
组成
state/getter/mutation/action/module
store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
state.count++
}
}
})
//可以通过store.state来获取状态对象 通过store.commit方法触发变更
store.commit('increment')
console.log(store.state.count) // -> 1
//注入到vue
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store: store,
})
在vue中可以通过 this.$store.commit("increment") [methods中]
getters
//getter=>computed
getters: {
doneTodos: state => {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
// return getters.doneTodos.length //就像是组件中的计算属性一样调用,而不是像函数调用一样
}
}
//getters中的访问器函数,默认会传递2个参数(state, getters),使用第一个参数state可以访问数据,使用getters参数可以访问访问器中的其它访问器函数。大部分情况下
//只需要使用第一个参数,定义访问器函数就只写第一个参数即可,就像上面的例子。访问这些访问器属性时,就像是组件中的计算属性一样调用,而不是像函数调用一样
mutation
mutations: {
// payload = {title,list} 约定数据格式
setListPageData (state, payload) {
state.title = payload.title
state.list = payload.list
}
},
//store.commit("setListPageData ",{})
action中
//context.commit("setListPageData ",{})
action
1. actions: {
increment (context) {
context.commit('increment')
}
2.actions: {
increment ({ commit }) {
commit('increment')
}
}
通过dispatch分发 store.dispatch("increment")
module
const moduleA = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: () => ({ ... }),
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
// 命名空间
namespaced:true
// 当模块被注册后 getter/action/mutation都会根据模块注册的路径调整命名
// 带命名空间的模块访问全局内容
// 如果希望使用全局 state或getter,rootState和rotterGetter会作为第三和第四个参数
//若需要在全局命名空间内分发 action 或提交 mutation,将 { root: true } 作为第三参数传给 dispatch 或 commit 即可
getters: {
// 在这个模块的 getter 中,`getters` 被局部化了
// 你可以使用 getter 的第四个参数来调用 `rootGetters`
someGetter (state, getters, rootState, rootGetters) {
getters.someOtherGetter // -> 'foo/someOtherGetter'
rootGetters.someOtherGetter // -> 'someOtherGetter'
},
someOtherGetter: state => { ... }
},
actions: {
// 在这个模块中, dispatch 和 commit 也被局部化了
// 他们可以接受 `root` 属性以访问根 dispatch 或 commit
someAction ({ dispatch, commit, getters, rootGetters }) {
getters.someGetter // -> 'foo/someGetter'
rootGetters.someGetter // -> 'someGetter'
dispatch('someOtherAction') // -> 'foo/someOtherAction'
dispatch('someOtherAction', null, { root: true }) // -> 'someOtherAction'
commit('someMutation') // -> 'foo/someMutation'
commit('someMutation', null, { root: true }) // -> 'someMutation'
}