cp命令
cp source_file target_file
能够复制文件,如果target_file所指定的文件不存在,cp就创建这个文件,如果已经存在,就把文件内容清空并把source_file的内容添加到target_file中。
cp命令的工作流程
open sourcefile for reading
open targetfile for writing
+--> read from source to buffer ---- eof ? --- +
| |
----- write from buffer to copy <------------- +
close sourcefile
close targetfile
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <fcntl.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 6 #define BUFFERSIZE 4096 7 #define COPYMODE 0644 8 9 void oops(char *s1, char *s2); 10 int main(int ac,char *av[]) 11 { 12 int in_fd,out_fd,n_chars; 13 char buf[BUFFERSIZE]; 14 15 if(ac != 3) 16 { 17 fprintf(stderr,"usage:%s source destination ",*av); 18 exit(1); 19 } 20 21 if( (in_fd = open(av[1],O_RDONLY)) == -1) 22 { 23 oops("Cannot open" , av[1]); 24 } 25 26 if( (out_fd = creat(av[2],COPYMODE)) == -1 ) 27 { 28 oops("Cannot open" , av[2]); 29 } 30 31 while( ( n_chars = read(in_fd,buf,BUFFERSIZE)) > 0 ) 32 if( (write(out_fd,buf,n_chars)) != n_chars) 33 oops("Write error to ", av[2]); 34 35 if(n_chars == -1) 36 oops("Read error from ",av[1]); 37 38 if(close(in_fd) == -1 || close(out_fd) == -1) 39 oops("Error closing files",""); 40 41 } 42 43 void oops(char *s1, char *s2) 44 { 45 fprintf(stderr,"Error:%s",s1); 46 perror(s2); 47 exit(1); 48 49 }
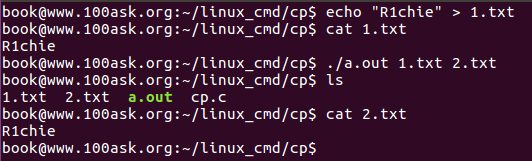
效果如下
使用到的函数:
1.int fd = creat(char * filename, mode_t mode)
creat告诉内核创建一个filename的文件,如果不存在,则直接创建,如果存在,则先把文件的内容清空,把文件长度设置为0。并且把文件的权限设置为mode
2.ssize_t result = write(int fd,void * buf,size_t amt)
write这个系统调用告诉内核把数据写入文件中,如果写入失败返回 -1 ,成功返回写入的字节数。
cp命令的分析
1. 缓冲区的影响
缓冲区的大小对我们这个程序的运行速度是有影响的,举一个例子:用小勺子把汤从一个碗里盛到另一个碗里,可能要盛十几次,当换成一个大一点的勺子,可能只需要几次。
2. 系统调用的开销
使用系统调用会消耗很多时间,用户进程位于用户空间,内核进程位于内核空间,磁盘只能被内核直接访问。当我们要读取文件时,需要使用系统调用read,而read在内核空间中,因此,执行的时候是从用户空间切换到内核空间,这是需要时间的。为什么需要时间?当CPU从用户模式切换到管理员模式时,需要进行一些环境的配置,如一些特殊的堆栈和内存环境。当使用完系统调用时,CPU就又要从管理员模式切换到用户模式,也需要花费一些时间,因此,在一些程序中应该节约类似于模式切换的开销。
本篇笔记自拜读《 Unix/Linux编程实践教程》
我也推荐和我一样的初学者去拜读这本书,让你对linux有可下手的地方。