leetcode中的LRU Cache题
网址:http://oj.leetcode.com/problems/lru-cache/
要求实现LRU Cache,及在一个容量有限的存储空间中,存放最近实用过的n组数据。
我最开始的实现方法:
public class LRUCache { Stack<Integer> stk; Map<Integer, Integer> map; int capacity, number; public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; number = 0; stk = new Stack<Integer>(); map = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); } public int get(int key) { if(map.containsKey(key)) { stk.remove((Integer)key); stk.push(key); return map.get(key); } return -1; } public void set(int key, int value) { if(map.containsKey(key)) { //change value and change stack map.put(key, value); stk.remove((Integer)key); stk.push(key); }else { if(number < capacity) { //don't need replace stk.push(key); map.put(key, value); number ++; }else { //replace //remove int popKey = stk.remove(0); map.remove(popKey); //put stk.push(key); map.put(key, value); } } } }
提交结果显示 : Time Limit Exceeded
分析算法,capacity大小为n, 操作个数为m, get()函数的复杂度为 O(n),set()函数的复杂度为O(n)。
由于在这个程序中,一定需要记录2种数据 (1. key对应的value; 2. 哪些key是在最近使用的n个数中),记录<key, value>对用HashMap肯定比较好,操作复杂度为O(1),记录前n个key则用双向链表,这样插入和移动比较简单,双向链表最大的缺点也就是查找复杂度为O(n), 那么可以把前面的HashMap和链表结合起来,查找时用HashMap,这样所有的复杂度就都能降到O(1)了。
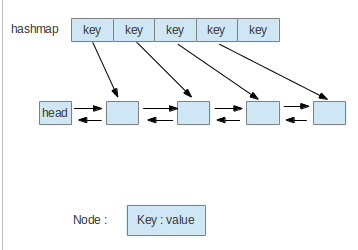
然后具体的实现代码为:
public class LRUCache { class Node { int key; int val; Node pre, next; public Node(int key, int val) { this.key = key; this.val = val; this.pre = null; this.next = null; } public Node() { this.pre = null; this.next = null; } } int capacity; int number; Map<Integer, Node> map; Node head, last; public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; number = 0; last = null; head = new Node(); map = new HashMap<Integer, Node>(); } public int get(int key) { if(map.containsKey(key)) { Node node = map.get(key); int value = node.val; if(node == last) { if(node.pre != head) { last = node.pre; }else { //no nothing } } node.pre.next = node.next; if(node.next != null) { node.next.pre = node.pre; } node.next = head.next; if(head.next != null) { head.next.pre = node; } head.next = node; node.pre = head; return value; } return -1; } public void set(int key, int value) { if(map.containsKey(key)) { Node node = map.get(key); node.val = value; //deal with order if(node == last) { if(node.pre != head) { last = node.pre; }else { //no nothing } } node.pre.next = node.next; if(node.next != null) { node.next.pre = node.pre; } node.next = head.next; if(head.next != null) { head.next.pre = node; } head.next = node; node.pre = head; }else { if(number < capacity) { Node node = new Node(key, value); map.put(key, node); if(last == null) { last = node; } node.next = head.next; node.pre = head; if(head.next != null) { head.next.pre = node; } head.next = node; number ++; }else { Node node = new Node(key, value); node.next = head.next; node.pre = head; if(head.next != null) { head.next.pre = node; } head.next = node; Node removeNode = last; last = last.pre; map.remove(removeNode.key); map.put(key, node); if(last == head) { last = null; } } } } }