Properties类
特点:
1、Hashtable的子类,map集合中的方法都可以用;
2、该集合没有泛型,键值都是字符串;
3、是一个可以持久化的属性集,键值可以存到集合中,也可存到持久化的设备上,键值的来源也可是持久化的设备;
4、有和流技术相结合的方法:

代码演示:
public static void main(String[] args) { Properties pro=new Properties(); //存数据 pro.setProperty("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.driver"); pro.setProperty("username", "root"); pro.setProperty("password", "123456"); //取数据 //获取键集 Set<String> set= pro.stringPropertyNames(); for(String s:set){ System.out.println(s+"..."+pro.getProperty(s)); } } public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //从properties文件中读取键值对 Properties pro=new Properties(); FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\demo1.properties"); pro.load(fis); fis.close(); Set<String> set=pro.stringPropertyNames(); //遍历 for(String s:set){ System.out.println(s+"..."+pro.getProperty(s)); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //通过properties向文件中写键值对 //明确目的地 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\demo2.properties"); Properties pro=new Properties(); pro.setProperty("name", "xuezhiqian"); pro.setProperty("age", "34"); pro.store(fos, ""); }
序列化流与反序列化流:
读取对象的操作流ObjectInputStream:反序列化流
写入对象的操作流ObjectOutputStream:序列化流
特点:用于操作对象,可将对象写入到文件中,也可从文件中读取对象
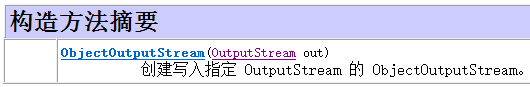
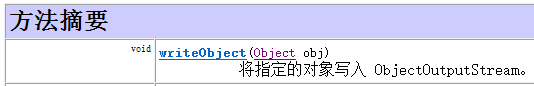
代码演示:
//序列化 public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { Person p=new Person("张三",18); //明确目的地 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\person.txt"); //创建序列化流 ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(fos); //写入对象 oos.writeObject(p); //释放资源 oos.close(); } 瞬态关键字 transient public class Person implements Serializable{ private String name; private transient int age;//瞬态关键字 private static final long serialVersionUID=123456789L; public Person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; }
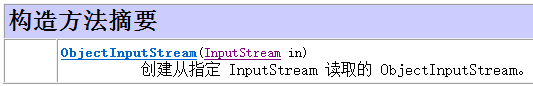
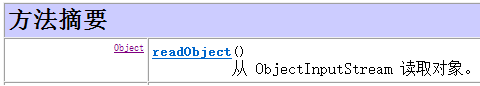
//反序列化 public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { //明确数据源 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\person.txt"); //创建反序列化对象 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(fis); //反序列化 Object obj=ois.readObject(); Person p=(Person)obj; System.out.println(p); }
打印流:(怎么写的怎么打印;不会有IOExecption异常)
字节打印流:PrintStream;
字符打印流:PrintWriter;
方法:void print(String str):输出任意类型的数据
void println(String str):输出任意类型的数据,自动写入换行操作
代码演示:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //打印流复制 //明确数据源 FileReader fr=new FileReader("x:\test\test.txt"); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr); //明确数据目的 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("x:\test\d\pig.txt"); PrintWriter pw=new PrintWriter(fw,true); //复制 String line=null; while((line=br.readLine())!=null){ pw.println(line); } //释放资源 br.close(); pw.close(); }
commons-IO:
导入jar包
FilenameUtils:用来处理文件
常用方法:
getExtension(String path):获取文件的扩展名
getName():获取文件名
isExtension(String filename,String ext):判断filename是否是ext后缀名
FileUtils:
常用方法:
readFileToString(File file):读取文件内容,返回一个String
writeString(File file,String content):将内容写到field中
copyDirectoryToDirectory(File srcDir,File destDir);文件夹复制
copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile);文件复制
代码演示:
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { //method1(); method2(); } public static void method1(){ //获取某文件扩展名 String name=FilenameUtils.getExtension("x:\test"); System.out.println(name); //获取某文件名 String filename=FilenameUtils.getName("x:\test\test.txt"); System.out.println(filename); //判断某文件是否以什么为结尾 boolean flag=FilenameUtils.isExtension("aaa.java", "java"); System.out.println(flag); } public static void method2() throws IOException{ FileUtils.copyDirectoryToDirectory(new File("x:\test"), new File("c:\")); } }