1.创建项目
scrapy startproject weather # weather是项目名称
scrapy crawl spidername开始运行,程序自动使用start_urls构造Request并发送请求,然后调用parse函数对其进行解析,
在这个解析过程中使用rules中的规则从html(或xml)文本中提取匹配的链接,通过这个链接再次生成Request,如此不断循环,直到返回的文本中再也没有匹配的链接,或调度器中的Request对象用尽,程序才停止。
2.确定爬取目标:
scrapy构建的爬虫的爬取过程:
scrapy crawl spidername开始运行,程序自动使用start_urls构造Request并发送请求,然后调用parse函数对其进行解析,在这个解析过程中使用rules中的规则从html(或xml)文本中提取匹配的链接,
通过这个链接再次生成Request,如此不断循环,直到返回的文本中再也没有匹配的链接,或调度器中的Request对象用尽,程序才停止。
allowed_domains:顾名思义,允许的域名,爬虫只会爬取该域名下的url
rule:定义爬取规则,爬虫只会爬取符合规则的url
rule有allow属性,使用正则表达式书写匹配规则.正则表达式不熟悉的话可以写好后在网上在线校验,尝试几次后,简单的正则还是比较容易的,我们要用的也不复杂.
rule有callback属性可以指定回调函数,爬虫在发现符合规则的url后就会调用该函数,注意要和默认的回调函数parse作区分.(爬取的数据在命令行里都可以看到)
rule有follow属性.为True时会爬取网页里所有符合规则的url,反之不会. 我这里设置为了False,因为True的话要爬很久.大约两千多条天气信息
import scrapy from weather.items import WeatherItem from scrapy.spiders import Rule, CrawlSpider from scrapy.linkextractors import LinkExtractor class Spider(CrawlSpider): name = 'weatherSpider' #allowed_domains = "www.weather.com.cn" start_urls = [ #"http://www.weather.com.cn/weather1d/101020100.shtml#search" "http://www.weather.com.cn/forecast/" ] rules = ( #Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=('http://www.weather.com.cn/weather1d/101d{6}.shtml#around2')), follow=False, callback='parse_item'), Rule(LinkExtractor(allow=('http://www.weather.com.cn/weather1d/101d{6}.shtml$')), follow=True,callback='parse_item'), ) #多页面爬取时需要自定义方法名称,不能用parse def parse_item(self, response): item = WeatherItem() #city = response.xpath("//div[@class='crumbs fl']/a[2]/text()").extract_first() item['city'] = response.xpath("//div[@class='crumbs fl']/a[2]/text()").extract_first() # 获取省或者直辖市名称 #if city == '>': #item['city'] = response.xpath("//div[@class='crumbs fl']/a[last()-1]/text()").extract_first()#获取非直辖省 #item['city'] = response.xpath("//div[@class ='crumbs fl']/a[2]/text()").extract_first()#获取直辖市 #item['city_addition'] = response.xpath("//div[@class ='crumbs fl']/a[last()]/text()").extract_first()#获取直辖市 #city_addition = response.xpath("//div[@class ='crumbs fl']/a[last()]/text()").extract_first() #获取>字符 #print("aaaaa"+city) #print("nnnnn"+city_addition) #if city_addition != city: #item['city_addition'] = response.xpath("//div[@class='crumbs fl']/a[2]/text()").extract_first() item['city_addition'] = response.xpath("//div[@class ='crumbs fl']/a[last()]/text()").extract_first() # 获取城市名或者直辖市名称 #else: #item['city_addition'] = '' #item['city_addition2'] = response.xpath("//div[@class='crumbs fl']/span[3]/text()").extract_first() weatherData = response.xpath("//div[@class='today clearfix']/input[1]/@value").extract_first() #获取当前的气温 item['data'] = weatherData[0:6] #获取日期 print("data:"+item['data']) item['weather'] = response.xpath("//p[@class='wea']/text()").extract_first() #获取天气 item['temperatureMax'] = response.xpath("//ul[@class='clearfix']/li[1]/p[@class='tem']/span[1]/text()").extract_first() #最高温度 item['temperatureMin'] = response.xpath("//ul[@class='clearfix']/li[2]/p[@class='tem']/span[1]/text()").extract_first() #最低温度 yield item
spider.py顾名思义就是爬虫文件
在填写spider.py之前,我们先看看如何获取需要的信息
刚才的命令行应该没有关吧,关了也没关系
win+R在打开cmd,键入:scrapy shell http://www.weather.com.cn/weather1d/101020100.shtml#search #网址是你要爬取的url
这是scrapy的shell命令,可以在不启动爬虫的情况下,对网站的响应response进行处理调试等,主要是调试xpath获取元素的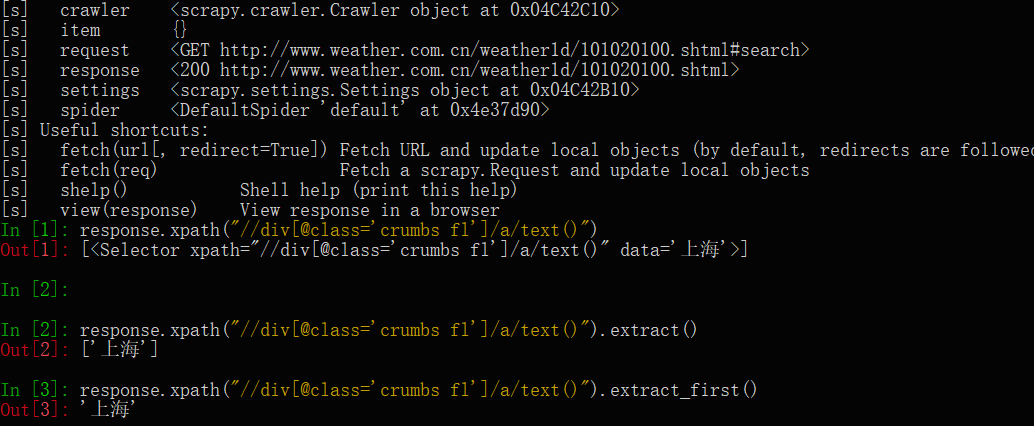
3.填写Items.py
Items.py只用于存放你要获取的字段:
给自己要获取的信息取个名字:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define here the models for your scraped items # # See documentation in: # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/items.html import scrapy class WeatherItem(scrapy.Item): # define the fields for your item here like: # name = scrapy.Field() city = scrapy.Field() city_addition = scrapy.Field() city_addition2 = scrapy.Field() weather = scrapy.Field() data = scrapy.Field() temperatureMax = scrapy.Field() temperatureMin = scrapy.Field() pass
这里写了管道文件,还要在settings.py设置文件里启用这个pipeline:
6.填写settings.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Scrapy settings for weather project # # For simplicity, this file contains only settings considered important or # commonly used. You can find more settings consulting the documentation: # # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html # https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html BOT_NAME = 'weather' SPIDER_MODULES = ['weather.spiders'] NEWSPIDER_MODULE = 'weather.spiders' # Crawl responsibly by identifying yourself (and your website) on the user-agent #USER_AGENT = 'weather (+http://www.yourdomain.com)' # Obey robots.txt rules ROBOTSTXT_OBEY = False # Configure maximum concurrent requests performed by Scrapy (default: 16) #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS = 32 # Configure a delay for requests for the same website (default: 0) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/settings.html#download-delay # See also autothrottle settings and docs DOWNLOAD_DELAY = 1 # The download delay setting will honor only one of: #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_DOMAIN = 16 #CONCURRENT_REQUESTS_PER_IP = 16 # Disable cookies (enabled by default) #COOKIES_ENABLED = False # Disable Telnet Console (enabled by default) #TELNETCONSOLE_ENABLED = False # Override the default request headers: #DEFAULT_REQUEST_HEADERS = { # 'Accept': 'text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8', # 'Accept-Language': 'en', #} # Enable or disable spider middlewares # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/spider-middleware.html #SPIDER_MIDDLEWARES = { # 'weather.middlewares.WeatherSpiderMiddleware': 543, #} # Enable or disable downloader middlewares # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html #DOWNLOADER_MIDDLEWARES = { # 'weather.middlewares.WeatherDownloaderMiddleware': 543, #} # Enable or disable extensions # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/extensions.html #EXTENSIONS = { # 'scrapy.extensions.telnet.TelnetConsole': None, #} # Configure item pipelines # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html ITEM_PIPELINES = { 'weather.pipelines.TxtPipeline': 600, #'weather.pipelines.JsonPipeline': 6, #'weather.pipelines.ExcelPipeline': 300, } # Enable and configure the AutoThrottle extension (disabled by default) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/autothrottle.html #AUTOTHROTTLE_ENABLED = True # The initial download delay #AUTOTHROTTLE_START_DELAY = 5 # The maximum download delay to be set in case of high latencies #AUTOTHROTTLE_MAX_DELAY = 60 # The average number of requests Scrapy should be sending in parallel to # each remote server #AUTOTHROTTLE_TARGET_CONCURRENCY = 1.0 # Enable showing throttling stats for every response received: #AUTOTHROTTLE_DEBUG = False # Enable and configure HTTP caching (disabled by default) # See https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/downloader-middleware.html#httpcache-middleware-settings #HTTPCACHE_ENABLED = True #HTTPCACHE_EXPIRATION_SECS = 0 #HTTPCACHE_DIR = 'httpcache' #HTTPCACHE_IGNORE_HTTP_CODES = [] #HTTPCACHE_STORAGE = 'scrapy.extensions.httpcache.FilesystemCacheStorage'
5.填写pipeline.py
但要保存爬取的数据的话,还需写下pipeline.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Define your item pipelines here # # Don't forget to add your pipeline to the ITEM_PIPELINES setting # See: https://doc.scrapy.org/en/latest/topics/item-pipeline.html import os import codecs import json import csv from scrapy.exporters import JsonItemExporter from openpyxl import Workbook base_dir = os.getcwd() filename = base_dir + '\' + 'weather.txt' with open(filename,'w+') as f:#打开文件 f.truncate()#清空文件内容 class JsonPipeline(object): # 使用FeedJsonItenExporter保存数据 def __init__(self): self.file = open('weather1.json','wb') self.exporter = JsonItemExporter(self.file,ensure_ascii =False) self.exporter.start_exporting() def process_item(self,item,spider): print('Write') self.exporter.export_item(item) return item def close_spider(self,spider): print('Close') self.exporter.finish_exporting() self.file.close() class TxtPipeline(object): def process_item(self, item, spider): #获取当前工作目录 #base_dir = os.getcwd() #filename = base_dir + 'weather.txt' #print('创建Txt') print("city:"+item['city']) print("city_addition:"+item['city_addition']) #从内存以追加方式打开文件,并写入对应的数据 with open(filename, 'a') as f: #追加 if item['city'] != item['city_addition']: f.write('城市:' + item['city'] + '>') f.write(item['city_addition'] + ' ') else: f.write('城市:' + item['city'] + ' ') #f.write(item['city_addition'] + ' ') f.write('日期:' + item['data'] + ' ') f.write('天气:' + item['weather'] + ' ') f.write('温度:' + item['temperatureMin'] + '~' + item['temperatureMax'] + '℃ ') class ExcelPipeline(object): #创建EXCEL,填写表头 def __init__(self): self.wb = Workbook() self.ws = self.wb.active #设置表头 self.ws.append(['省', '市', '县(乡)', '日期', '天气', '最高温', '最低温']) def process_item(self, item, spider): line = [item['city'], item['city_addition'], item['city_addition2'], item['data'], item['weather'], item['temperatureMax'], item['temperatureMin']] self.ws.append(line) #将数据以行的形式添加仅xlsx中 self.wb.save('weather.xlsx') return item '''def process_item(self, item, spider): base_dir = os.getcwd() filename = base_dir + 'weather.csv' print('创建EXCEL') with open(filename,'w') as f: fieldnames = ['省','市', '县(乡)', '天气', '日期', '最高温','最低温'] # 定义字段的名称 writer = csv.DictWriter(f,fieldnames=fieldnames) # 初始化一个字典对象 write.writeheader() # 调用writeheader()方法写入头信息 # 传入相应的字典数据 write.writerow(dict(item)) '''
爬虫效果:

确定爬取目标:
这里选择中国天气网做爬取素材,爬取网页之前一定要先分析网页,要获取那些信息,怎么获取更加方便,网页源代码这里只展示部分:
<div class="ctop clearfix"> <div class="crumbs fl"> <a href="http://js.weather.com.cn" target="_blank">江苏</a> <span>></span> <a href="http://www.weather.com.cn/weather/101190801.shtml" target="_blank">徐州</a><span>></span> <span>鼓楼</span> </div> <div class="time fr"></div> </div>
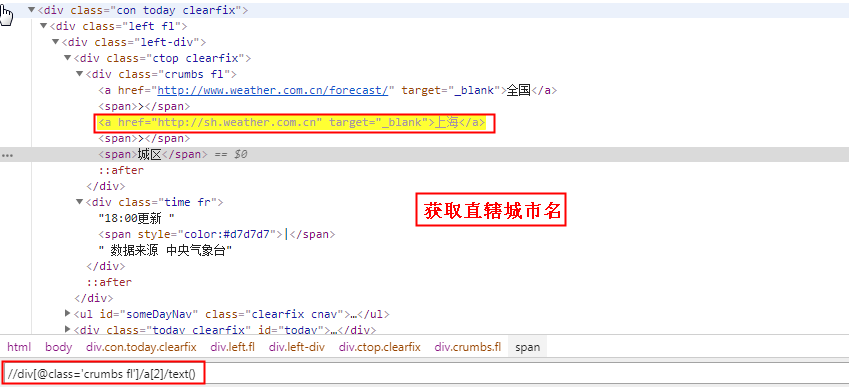
如果是非直辖市:获取省名称
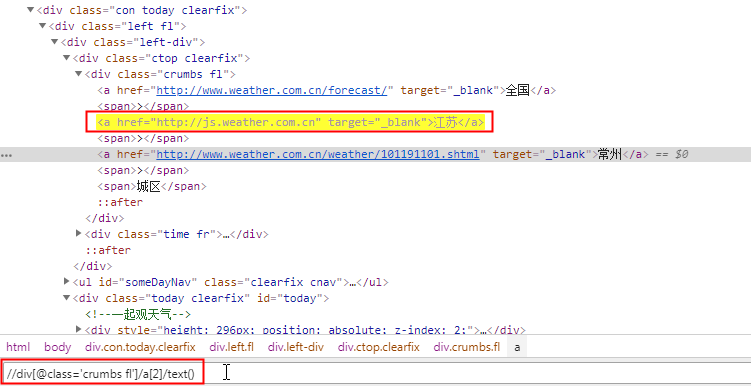
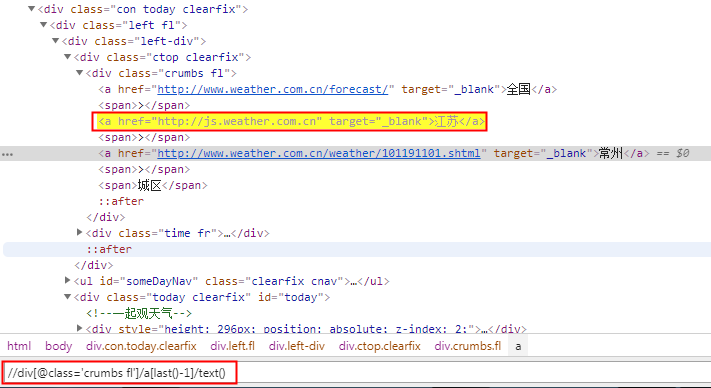
//div[@class='crumbs fl']/a[last()-1]/text()
取xpath最后一个book元素
book[last()]
取xpath最后第二个book元素
book[last()-1]