数组定义:(3种)
数组存储的数据类型[] 数组名字 = new 数组存储的数据类型[长度];
int[] arr = new int[3];
数据类型[] 数组名 = new 数据类型[]{元素1,元素2,元素3...};
int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
数据类型[] 数组名 = {元素1,元素2,元素3...};
int[] arr = {1,2,3,4,5};
数组名[索引]=数值,为数组中的元素赋值
变量=数组名[索引],获取出数组中的元素
//为0索引元素赋值为6
arr[0] = 6;
//获取数组0索引上的元素
int i = arr[0];
System.out.println(i);
越界异常和空指针异常

数组遍历和反转
public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; for (int min = 0, max = arr.length ‐ 1; min <= max; min++, max‐‐) { int temp = arr[min]; arr[min] = arr[max]; arr[max] = temp; } for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.println(arr[i]); } }
----------------------------------------------------------------------
ArrayList(集合类) 需要类型
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();

遍历 list.size list.get list.add
list.add(r);


-----------------------------------------------------------------------
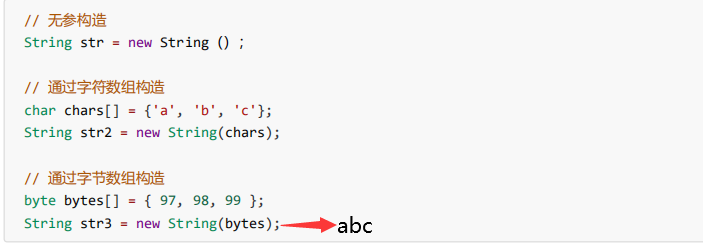
String类
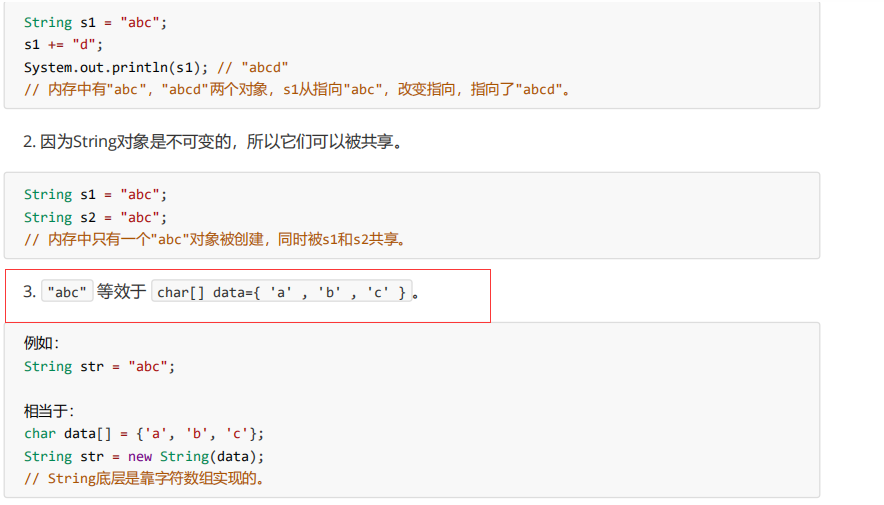
1. 字符串不变:字符串的值在创建后不能被更改。



IT 替换 it





-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Arrays
Arrays .tostring(arr)

排序:
Arrays.sort(arr);
