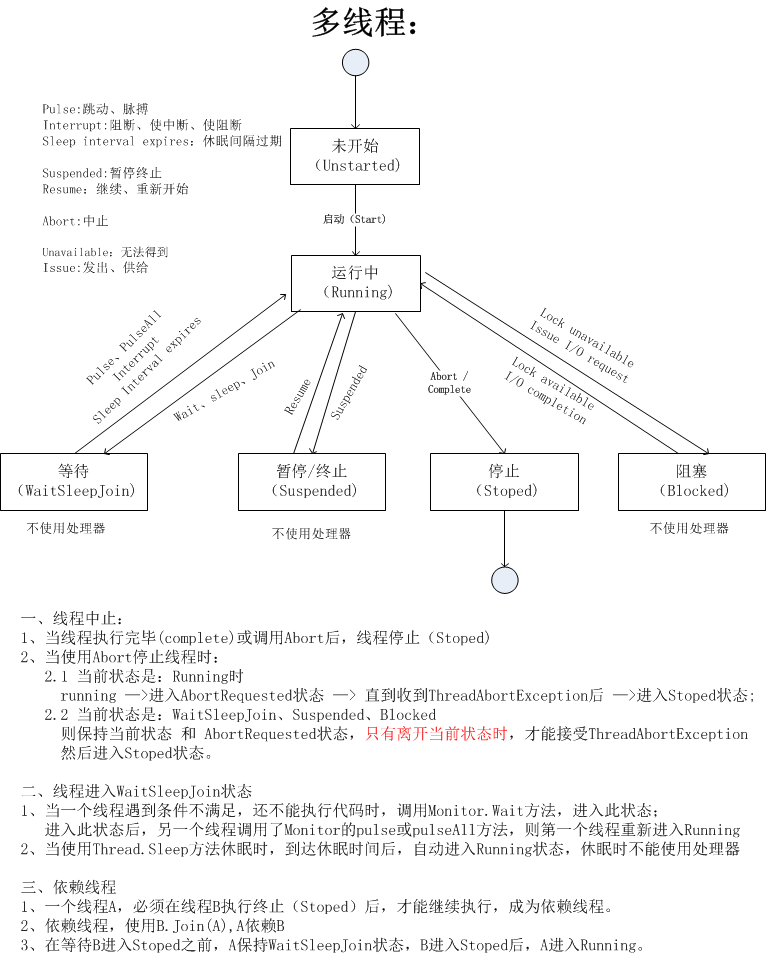
一、线程状态
二、线程优先级

三、初步尝试多线程

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { while (true) { MessagePrinter p1=new MessagePrinter(); Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p1.Print)); t1.Name = "t1"; t1.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest; MessagePrinter p2 = new MessagePrinter(); Thread t2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p2.Print)); t2.Name = "t2"; t2.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest; MessagePrinter p3 = new MessagePrinter(); Thread t3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p3.Print)); t3.Name = "t3"; t2.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest; Console.WriteLine("线程启动: "); t1.Start(); t2.Start(); t3.Start(); Console.WriteLine("线程结束: "); string r= Console.ReadLine(); if (r == "1") break; } } } class MessagePrinter { private int _sleepTime; private static Random _random=new Random(); public MessagePrinter() { _sleepTime = _random.Next(5001); } public void Print() { Thread current = Thread.CurrentThread; Console.WriteLine(string.Format("线程:{0},即将进入休眠状态:{1}毫秒", current.Name, _sleepTime)); Thread.Sleep(_sleepTime); Console.WriteLine(string.Format("线程:{0},结束休眠", current.Name)); } }
四、线程同步 与Monitor类

using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; /* * * 线程同步: * 1、作用:是保证多个线程之间同步处理【共享数据】的 * 2、使用Monitor: * > Enter:占用当前对象锁 * > Wait:等待 * > Pulse:让下一个其它线程开始运行 * > Exit:解除占用对象锁 * 3、一定要将Exit放到TryCatch块的finialy中,防止在占用锁后,出现异常,然后没有释放锁,导致死锁 * 4、使用Lock加锁,替代Enter和Exit; * * 死锁的几种情况: * 1、互等死:线程之间互相引用,导致都不能释放 * 2、等到死:线程使用Wait后,再没有其它线程使用Pulse或PulseAll进行唤醒 * 3、异常死:在某个线程占用锁后,发生了异常,没有执行Exit释放锁操作,导致死锁 * * */ namespace 线程同步与Monitor类 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { #region 非线程同步 // IBuffer buffer = new UnSynchronuzedBuffer();//非线程同步 //IBuffer buffer = new SynchronizedBuffer();//线程同步 IBuffer buffer = new CircularBuffer();//增加缓冲区空间,从而增加效率 Random r = new Random(); Producer p = new Producer(buffer, r); Consumer c = new Consumer(buffer, r); Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(p.Produce)); t1.Name = "Producer"; Thread t2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(c.Consume)); t2.Name = "Consumer"; t1.Start(); t2.Start(); #endregion #region 线程同步 #endregion Console.ReadLine(); } } #region 共享区 public interface IBuffer { int Buffer { get; set; } } /// <summary> /// 非线程同步缓冲区 /// </summary> public class UnSynchronuzedBuffer : IBuffer { private int _Buffer=-1; public int Buffer { get { Console.WriteLine(string.Format(" 线程:{0},读取 {1} ",Thread.CurrentThread.Name,_Buffer)); return _Buffer; } set { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("线程:{0},写入 {1} ", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, value)); _Buffer=value; } } } /// <summary> /// 线程同步,使用Monitor /// </summary> public class SynchronizedBuffer : IBuffer { private int _Buffer = -1; private int occupiedBufferCount = 0; public int Buffer { get { //锁定当前对象 Monitor.Enter(this); try { //如果没有Buffer中没有更新数据,则进入线程等待 if (occupiedBufferCount == 0) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format(" 线程:{0},试图读取缓冲区数据", Thread.CurrentThread.Name)); DisplayState(string.Format(" Buffer是空的,线程:{0}进行等待", Thread.CurrentThread.Name)); Console.WriteLine(" ===读取等待.........."); //释放 对象锁,并进入 WaitSleepJoin状态,等待再次获取锁 //本线程再次进入Running状态时,继续向下执行。 Monitor.Wait(this); Console.WriteLine(" ===读取结束-1.........."); } --occupiedBufferCount; Console.WriteLine(string.Format(" 线程:{0},开始读取:{1}",Thread.CurrentThread.Name,_Buffer)); //如果有其它线程,进行唤醒 Monitor.Pulse(this); //复制buffer的目的,是防止刚解锁,生成者就立马改变了数据 int bufferCopy=_Buffer; //返回副本 return bufferCopy; } catch (Exception ex) { throw; } finally { //释放对象上的锁 Monitor.Exit(this); } } set { if (!Monitor.TryEnter(this, 2)) { Console.WriteLine("【set时,TryEnter失败,将使用Enter进入。】"); Monitor.Enter(this); } if (occupiedBufferCount == 1) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("线程:{0},试图写入", Thread.CurrentThread.Name)); DisplayState(string.Format("Buffer 已满,线程:{0}等待", Thread.CurrentThread.Name)); Console.WriteLine("===写入等待.........."); //等待缓冲区数据被读取后,再写入 Monitor.Wait(this); Console.WriteLine("===写入等待结束-1.........."); } _Buffer = value; ++occupiedBufferCount; Console.WriteLine(string.Format("线程:{0},写入{1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, value)); Monitor.Pulse(this); Monitor.Exit(this); } } /// <summary> /// 展示当前的操作和Buffer的状态 /// </summary> /// <param name="operation"></param> public void DisplayState(string operation) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0,-35}{1,-9}{2} ", operation, _Buffer, occupiedBufferCount)); } } /// <summary> /// 当生产者与消费者速度基本同步时,适当增加缓冲区空间,从而减少互等时间。 /// 使用Lock代替Monitor.Enter和Exit方法 /// </summary> public class CircularBuffer : IBuffer { private int[] _Buffer = {-1,-1,-1}; private int occupiedBufferCount = 0; private int readLocation = 0;//当前读取位置 private int writeLocation = 0;//当前写入位置 public int Buffer { get { Monitor.Enter(this); try { if (occupiedBufferCount == 0) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format(" 【Read】缓冲区为空,进入等待状态")); Monitor.Wait(this); Console.WriteLine(string.Format(" 【Read】等待结束")); } int readValueCopy = _Buffer[readLocation]; Console.Write(string.Format(" 【Read】线程:{0},读取:{1}", Thread.CurrentThread.Name, readValueCopy)); --occupiedBufferCount; readLocation = (readLocation + 1) % _Buffer.Length; Console.WriteLine(CreateStateOutput()); Monitor.Pulse(this); return readValueCopy; } catch (Exception ex) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("异常:{0}",ex.Message.ToString())); return -1; } finally { Monitor.Exit(this); } } set { //使用lock 代替 Monitor.Enter 和 Monitor.Exit() lock (this) { if (occupiedBufferCount == _Buffer.Length) { Console.WriteLine(string.Format("缓冲区【已满】,进入等待状态")); Monitor.Wait(this); } _Buffer[writeLocation] = value; Console.Write(string.Format("已在位置{0},写入:{1}", writeLocation, value)); occupiedBufferCount++; writeLocation = (writeLocation + 1) % _Buffer.Length; Console.WriteLine(CreateStateOutput()); Monitor.Pulse(this); } } } private String CreateStateOutput() { string output = "(buffer occupied:" + occupiedBufferCount + ") buffers:"; for (int i = 0; i < _Buffer.Length; i++) output += " " + string.Format("{0,2}", _Buffer[i]) + " "; output += " "; output += " "; for (int i = 0; i < _Buffer.Length; i++) output += "-----"; output += " "; output += " "; for (int i = 0; i < _Buffer.Length; i++) { if (i == writeLocation && i == readLocation) output += " WR "; else if (i == writeLocation) output += " W "; else if (i == readLocation) output += " R "; else output += " "; } output += " "; return output; } } #endregion #region 生产者/消费者 public class Producer { private IBuffer sharedLocation; private Random random; public Producer(IBuffer buffer, Random random) { this.sharedLocation = buffer; this.random = random; } public void Produce() { for (int count = 1; count <= 10; count++) { Thread.Sleep(random.Next(1, 1001)); sharedLocation.Buffer = count; } Console.WriteLine(string.Format("=====生产者线程:{0},已执行完毕!", Thread.CurrentThread.Name)); } } public class Consumer { private IBuffer sharedLocation; private Random random; public Consumer(IBuffer buffer, Random random) { this.sharedLocation = buffer; this.random = random; } public void Consume() { int sum = 0; for (int count = 1; count <= 10; count++) { Thread.Sleep(random.Next(1, 1001)); sum+= sharedLocation.Buffer; } Console.WriteLine(string.Format("=======消费者线程:{0},已执行完毕,SUM={1}!", Thread.CurrentThread.Name,sum)); } } #endregion }
五、GUI与线程同步
* Window窗体控件不是线程安全的
* Control类的Invoke方法,就是将子线程中需要对 控件进行操作时,返回主线程中进行控件操作。

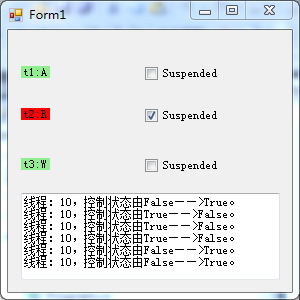
namespace GUI与多线程 { public partial class Form1 : Form { public Form1() { InitializeComponent(); } RandomLetters l1 = null; RandomLetters l2 = null; RandomLetters l3 = null; private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.FormClosing += new FormClosingEventHandler(Form1_FormClosing); l1 = new RandomLetters(label1,textBox1); l2 = new RandomLetters(label2, textBox1); l3 = new RandomLetters(label3, textBox1); Thread t1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(l1.GenerateRandomCharacters)); t1.Name = "t1"; t1.Start(); Thread t2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(l2.GenerateRandomCharacters)); t2.Name = "t2"; t2.Start(); Thread t3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(l3.GenerateRandomCharacters)); t3.Name = "t3"; t3.Start(); } void Form1_FormClosing(object sender, FormClosingEventArgs e) { System.Environment.Exit(System.Environment.ExitCode); } private void checkBox_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e) { if (sender == checkBox1) l1.Toggle(); else if (sender == checkBox2) l2.Toggle(); else if (sender == checkBox3) l3.Toggle(); } } #region GUI线程处理 public class RandomLetters { private static Random random = new Random(); private Label output = null;//需要输出到的Label private bool suspended = false;//是否暂停线程 private string threadName; public RandomLetters(Label lbl) { this.output = lbl; } /// <summary> /// 定义界面需要展示的字符 /// </summary> /// <param name="displayChar"></param> private delegate void DisplayDelegate(char displayChar); private void DisplayChar(char displayChar) { output.Text = threadName + ":" + displayChar; } public void GenerateRandomCharacters() { threadName = Thread.CurrentThread.Name; while (true) { Thread.Sleep(random.Next(1001)); lock (this) { while (suspended) { Monitor.Wait(this); } } //获取随机的26个大写字母中的一个 char displayChar = (Char)(random.Next(26) + 65); //Invoke 回到能够控制 GUI控件的线程中,执行委托的方法,并将相应的参数传递过去 output.Invoke(new DisplayDelegate(DisplayChar),displayChar); } } public void Toggle() { suspended = !suspended; output.BackColor = suspended ? Color.Red : Color.LightGreen; lock (this) { if (!suspended) Monitor.PulseAll(this); if (txtBoxShow != null) txtBoxShow.Text = string.Format("线程:{0},控制状态由{1}——>{2}。", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId, !suspended, suspended) + " " + txtBoxShow.Text; } } private TextBox txtBoxShow; public RandomLetters(Label lbl,TextBox txtBox) { this.output = lbl; this.txtBoxShow = txtBox; } } #endregion
实现效果如下:
六、死锁
* 死锁的几种情况:
* 1、互等死:线程之间互相引用,导致都不能释放
* 2、等到死:线程使用Wait后,再没有其它线程使用Pulse或PulseAll进行唤醒
* 3、异常死:在某个线程占用锁后,发生了异常,没有执行Exit释放锁操作,导致死锁
* 4、饿 死:一直有优先级高的线程加入,优先级低的线程始终没分配到处理器进行处理,这种无限延期称为饿死
