835D - Palindromic characteristics
Observation I.
If the string is k-palindrome, then it is (k - 1)-palindrome.
Observation II.
The string is k-palindrome if and only if the both following conditions are true:
- It is a palindrome.
- It's left half is non-empty (k - 1)-palindrome.
Solution.
Let's calculate the following dp.
- dp[l][r] is the maximum k such that the substring built from characters from l to r is k-palindrome.
- The dynamics is calculated in the order of non-decreasing of substring lengths.
- The values for l = r and l = r - 1 are computed trivially.
- Let r - l > 1. Then, if s[l] ≠ s[r] or dp[l + 1][r - 1] = 0, dp[l][r] = 0. Otherwise dp[l][r] = dp[l][m] + 1, where
 .
.
When we have dp values, we can calculate cnt[k] — the number of substrings, which dp value is k. Then the number of substrings that are k-palindromes is 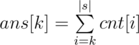 .
.
The solution works in O(|s|2) time and uses O(|s|2) memory.
Also, you could notice that the string can be no more than 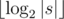 -palindrome, and solve the problem in
-palindrome, and solve the problem in  time, reducing the memory usage to O(|s|).
time, reducing the memory usage to O(|s|).
C++ code: 29077222
Java code: 29077251
Python code: 29077276
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 using namespace std; 4 const int N = 5005; 5 string s; 6 int n; 7 short dp[N][N];//dp[l][r] is the maximum k 8 int ans[N]; 9 int main() 10 { 11 ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 12 cin >> s; 13 int n = (int)s.size(); 14 for (int len = 1; len <= n; ++len) { 15 int l_r = n - len + 1; 16 for (int l = 0; l < l_r; ++l) { 17 int r = l + len;//dp[l][r], s[l,r) 18 if (len == 1) { dp[l][r] = 1; continue; } 19 if (len == 2) { dp[l][r] = (s[l] == s[r - 1] ? 2 : 0); continue; } 20 if (s[l] != s[r - 1] || dp[l + 1][r - 1] == 0) continue; 21 dp[l][r] = 1; 22 int m = l + r >> 1; 23 if (dp[l][m] && dp[m + (len&1)][r]) dp[l][r] = dp[l][m] + 1; 24 } 25 } 26 for (int len = 1; len <= n; ++len) { 27 int l_r = n - len + 1; 28 for (int l = 0; l < l_r; ++l) { 29 int r = l + len; 30 ans[dp[l][r]]++; 31 } 32 } 33 for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; --i) 34 ans[i] += ans[i + 1]; 35 cout << ans[1]; 36 for (int i = 2; i <= n; ++i) 37 cout << " " << ans[i]; 38 cout << endl; 39 40 return 0; 41 }
by wjsay 2017/8/1