问题描述:
有六个原子, 其中原子随意编号, 给定五条原子之间相连的边, 判断输入结构是下图的哪一种
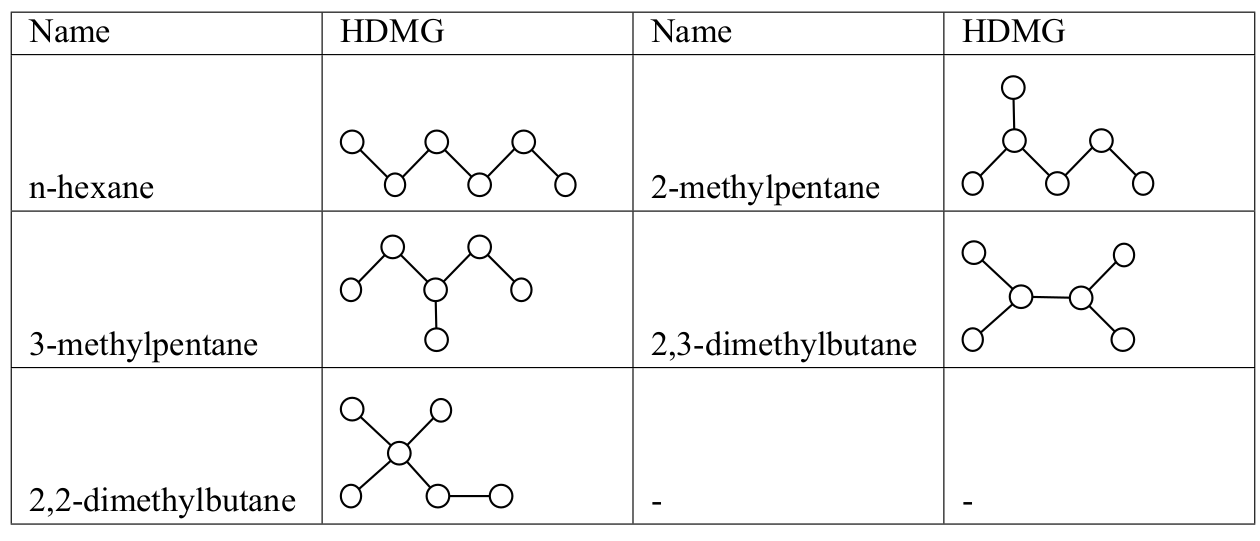
思路:
很显然可以用每个原子的度来判断,但是有两个结构的最大度数都是3,"3-methy"和"2-methy", 进一步判断发现3-methy连接了两个度为2的原子, 根据此就能区分这两个。最初的代码比较繁琐,后来经过Code Review借鉴学习了一下,发现可以使用一个二维数组degree,其中degree[i][j]==k表示度为i的点连接了度为j的点,整个结构中有k个这样的边(但是如果i==j,整个结构中只有k/2个这样的边,因为被算了两次,见程序)。用degree数组能直接区分五种情况。
普通的抽象是考虑点的度,更高的抽象是考虑各个点的度之间的关系
两点总结:
1.问题抽象层次越高越好,问题的低层抽象大部分人都能想到,应该在已经抽象的基础上进一步探索,这样处理问题就会更简洁。
2.开始学习使用vector,我发现vector提供的接口很方便编程
代码:
最初版本:

1 /* a数组存储边,count存储点的度*/ 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 int a[6][3]; 6 int count[10]; 7 int func(int max) 8 { 9 int num=0; 10 for(int i=1;i<=6;i++) 11 if(count[i]==max) num=i; 12 13 //有三个度为1的点,先找出来 14 int b[10]={0}; 15 int tot=0; 16 for(int i=1;i<=6;i++) 17 if(count[i]==1) b[++tot]=i; 18 //统计与3相连的有几个度为1的点 19 tot=0; 20 for(int j=1;j<=3;j++) 21 { 22 for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) 23 { 24 if(a[i][1]==b[j]&&a[i][2]==num) tot++; 25 else if(a[i][2]==b[j] &&a[i][1]==num) tot++; 26 } 27 } 28 if(tot==2) cout<<"2-methylpentane"<<endl; 29 else cout<<"3-methylpentane"<<endl; 30 } 31 int main() 32 { 33 //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); 34 int t; 35 cin>>t; 36 while(t--) 37 { 38 //每组数据都要重置cout数组 39 for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) count[i]=0; 40 41 for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) 42 for(int j=1;j<=2;j++) 43 { 44 scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); 45 count[ a[i][j] ]++; 46 } 47 //统计count中的最大值 48 int max_=-1; 49 for(int i=1;i<=6;i++) 50 if(count[i]>max_) max_=count[i]; 51 //对最大值讨论,特殊情况是最大值3 52 if(max_==2) cout<<"n-hexane"<<endl; 53 else if(max_==4) cout<<"2,2-dimethylbutane"<<endl; 54 else if(max_==3) 55 { 56 //确定是否有两个3 57 int tot=0; 58 for(int i=1;i<=6;i++) 59 if(count[i]==max_) tot++; 60 if(tot==2) cout<<"2,3-dimethylbutane"<<endl; 61 else 62 { 63 func(max_); 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 return 0; 68 }
总结修改后版本:

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <cstring> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 char s[][20]={"2-methylpentane","3-methylpentane","n-hexane","2,2-dimethylbutane","2,3-dimethylbutane"}; 8 vector<int> v[10]; 9 int deg[10][10]; 10 int main() 11 { 12 //freopen("a.in","r",stdin); 13 int t; 14 cin>>t; 15 while(t--) 16 { 17 memset( deg,0,sizeof(deg) ); 18 for(int i=1;i<=6;i++) v[i].clear(); 19 20 for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) 21 { //存边 22 int a,b; 23 scanf("%d %d",&a,&b); 24 v[a].push_back(b); 25 v[b].push_back(a); 26 } 27 for(int i=1;i<=6;i++) 28 { 29 /*for(int j=0,n=v[i].size();j<n;j++) 30 { 31 int x=v[i][j]; //x是与i直接相连的点 32 deg[ v[i].size() ] [ v[x].size() ] ++; 33 }*/ 34 //用range-for简写 35 for(auto x:v[i]) deg[ v[i].size() ] [ v[x].size() ] ++; 36 } 37 if(deg[4][1]==3) cout<<s[3]<<endl; 38 else if(deg[3][1]==4) cout<<s[4]<<endl; 39 else if(deg[3][1]==2) cout<<s[0]<<endl; 40 else if(deg[3][1]==1) cout<<s[1]<<endl; 41 else cout<<s[2]<<endl; 42 } 43 return 0; 44 }
