Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
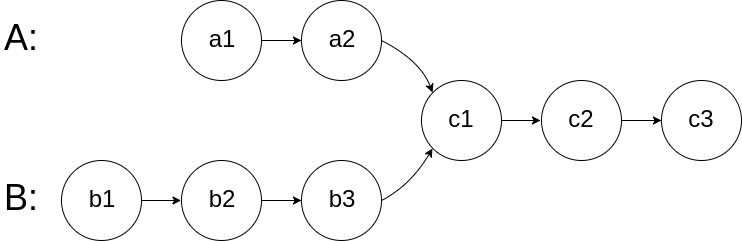
For example, the following two linked lists:
begin to intersect at node c1.
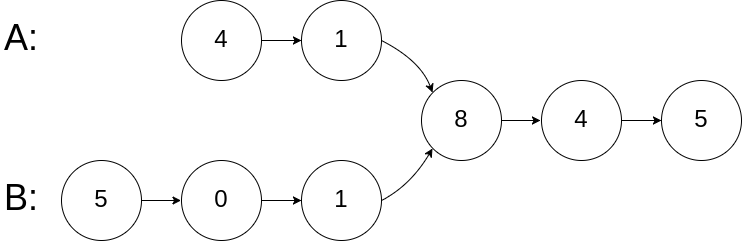
Example 1:
Input: intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 Output: Reference of the node with value = 8 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 8 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [4,1,8,4,5]. From the head of B, it reads as [5,0,1,8,4,5]. There are 2 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in B.
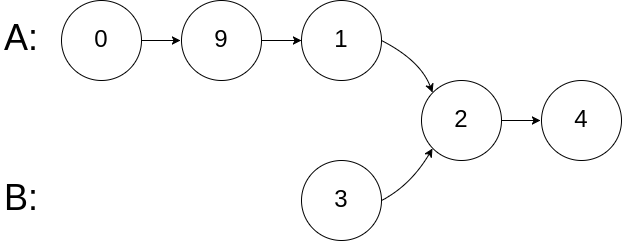
Example 2:
Input: intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 Output: Reference of the node with value = 2 Input Explanation: The intersected node's value is 2 (note that this must not be 0 if the two lists intersect). From the head of A, it reads as [0,9,1,2,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [3,2,4]. There are 3 nodes before the intersected node in A; There are 1 node before the intersected node in B.
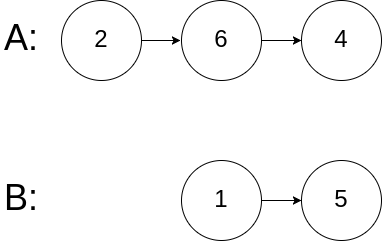
Example 3:
Input: intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 Output: null Input Explanation: From the head of A, it reads as [2,6,4]. From the head of B, it reads as [1,5]. Since the two lists do not intersect, intersectVal must be 0, while skipA and skipB can be arbitrary values. Explanation: The two lists do not intersect, so return null.
Notes:
- If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return
null. - The linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
- You may assume there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Your code should preferably run in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory.
1 /** 2 * Definition for singly-linked list. 3 * struct ListNode { 4 * int val; 5 * ListNode *next; 6 * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {} 7 * }; 8 */ 9 class Solution { 10 public: 11 // 时间复杂度O(n2), 空间复杂度O(1) 12 // ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { 13 // ListNode *pa = headA, *pb; 14 // while(pa != NULL) { 15 // for (pb = headB; pb != NULL; pb = pb->next) { 16 // if (pb == pa) 17 // return pa; 18 // } 19 // pa = pa->next; 20 // } 21 // return NULL; 22 // } 23 // 时间复杂度O(m + n), 空间复杂度O(m) 24 // 哈希表,保存A的节点地址,找到B中第一个和A中节点一样的节点 25 // ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { 26 // map<ListNode*, int> mp; 27 // if (headA == NULL || headB == NULL) 28 // return NULL; 29 // ListNode *pa = headA; 30 // while (pa != NULL) { 31 // mp[pa]++; 32 // pa = pa->next; 33 // } 34 // ListNode *pb = headB; 35 // while (pb != NULL) { 36 // if (mp.count(pb) != 0) 37 // return pb; 38 // pb = pb->next; 39 // } 40 // return NULL; 41 // } 42 // 时间复杂度O(k), 空间复杂度O(m + n) 43 // 双栈,只要栈顶节点一样,一直往外弹出,找到最后一个相同的节点。 44 // ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { 45 // stack<ListNode*> sa, sb; 46 // ListNode *pa = headA, *pb = headB; 47 // while (pa != NULL) { 48 // sa.push(pa); 49 // pa = pa->next; 50 // } 51 // while (pb != NULL) { 52 // sb.push(pb); 53 // pb = pb->next; 54 // } 55 // ListNode *res = NULL; 56 // while (!sa.empty() && !sb.empty() && sa.top() == sb.top()) { 57 // res = sa.top(); 58 // sa.pop(); 59 // sb.pop(); 60 // } 61 // return res; 62 // } 63 // 时间复杂度O(m + n), 空间复杂度O(1) 64 // ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { 65 // ListNode *pa = headA, *pb = headB; 66 // //把两个链表连接起来. pa: headA->headB, pb: headB->headA。通过这种方式会实现最后面公共节点的对齐, 67 // //有公共节点的时候,遇到就返回,无公共节点的时候,同时到达最后面的NULL,返回NULL 68 // while (pa != pb) { 69 // pa = pa != NULL ? pa->next : headB; 70 // pb = pb != NULL ? pb->next : headA; 71 // } 72 // return pa; 73 // } 74 // 时间复杂度:O(m + n), 空间复杂度O(1) 75 ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) { 76 ListNode *pa = headA, *pb = headB; 77 int lena = 0; 78 int lenb = 0; 79 while (pa != NULL) { 80 lena++; 81 pa = pa->next; 82 } 83 while (pb != NULL) { 84 lenb++; 85 pb = pb->next; 86 } 87 pa = headA; 88 pb = headB; 89 if (lena > lenb) { 90 int diff = lena - lenb; 91 for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) { 92 pa = pa->next; 93 } 94 } else { 95 int diff = lenb - lena; 96 for (int i = 0; i < diff; i++) { 97 pb = pb->next; 98 } 99 } 100 while (pa != pb) { 101 pa = pa->next; 102 pb = pb->next; 103 } 104 return pa; 105 } 106 };