断言 assert()
#include <assert.h>
void assert(scalar expression);
无返回值
相当于一个条件判断函数
看一个例子
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <assert.h> int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { int i = 0; printf("zhixing 1 "); assert(i<5); //此时满足条件 printf("zhixing 2 "); return 0; }
运行结果:
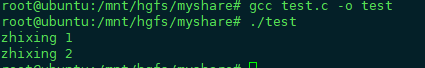
把断言中的符号改变一下
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <assert.h> int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { int i = 0; printf("zhixing 1 "); assert(i>5); //此时不满足条件 printf("zhixing 2 "); return 0; }
执行结果如下:

assert() 内 判断为真,则继续执行后续语句。若为假,打印错误信息然后终止程序运行
需要注意每个assert只能检验一个条件
不能使用改变环境的语句 比如 assert( i ++ < 5 ) 这种用法错误
刷新缓冲区 fflush()
#include <stdio.h>
int fflush(FILE *stream);
返回值:
Upon successful completion 0 is returned. Otherwise, EOF is returned and errno is set to indicate the error.
成功返回0 错误返回EOF
函数可以清除一个流
fflush(stdin); //清除输入流缓冲区
fflush(stdout); //清除输出流缓冲区
举个真实的例子:
int fdserver = open(SERVER_FIFO_NAME, O_WRONLY); if(-1 == fdserver) { printf("%s, %d, Client: Can't open fifo. ", __FILE__, __LINE__); fflush(stdout); assert(false); exit(1); } int fdclient = open(CLIENT_FIFO_NAME, O_RDWR); if(-1 == fdclient) { close(fdserver); printf("%s, %d, Cann't open client fifo. ", __FILE__, __LINE__); assert(false); exit(1); }