adb做为android的调试桥,在做app自动化中有着巨大的用处,可以帮助我们解决问题,今天主要认识adb shell input
adb shell input
我们首先通过cmd输入adb shell input有哪些内容
$ adb shell input Usage: input [<source>] <command> [<arg>...] The sources are: mouse keyboard joystick touchnavigation touchpad trackball stylus dpad touchscreen gamepad The commands and default sources are: text <string> (Default: touchscreen) keyevent [--longpress] <key code number or name> ... (Default: keyboard) tap <x> <y> (Default: touchscreen) swipe <x1> <y1> <x2> <y2> [duration(ms)] (Default: touchscreen) press (Default: trackball) roll <dx> <dy> (Default: trackball)
上面这么多到底讲的啥?
其实说白了就是支持一下内容
1、text:支持输入文本内容(暂不支持中文)
2、keyevent:模拟按键
3、tap:点击
4、swipe:滑动
5、press:轨迹球按下
6、roll:轨迹球滚动
text
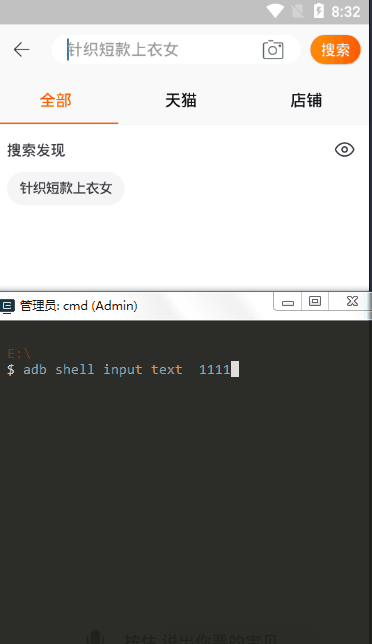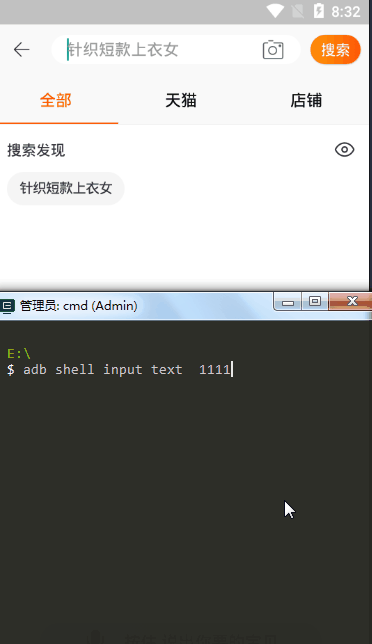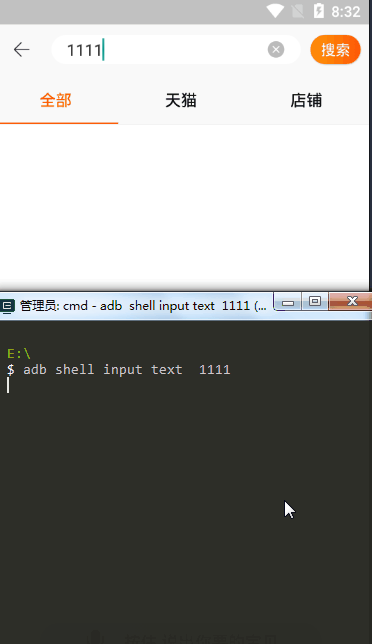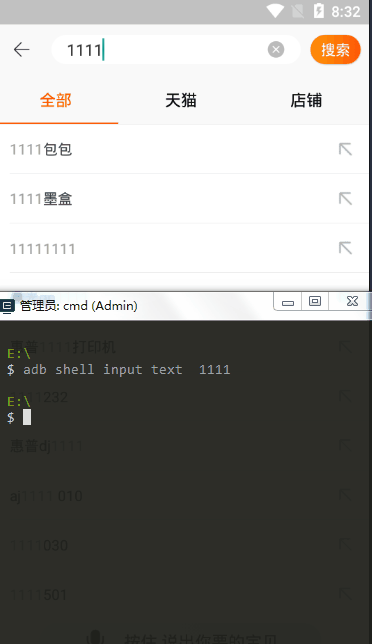
直接打开终端输入
# 输入内容(暂不支持中文) adb shell input text 1111
keyevent
直接打开输入对应的值
# 模拟手机按键home adb shell input keyevent 3
tap
选取手机上的坐标,然后直接输入
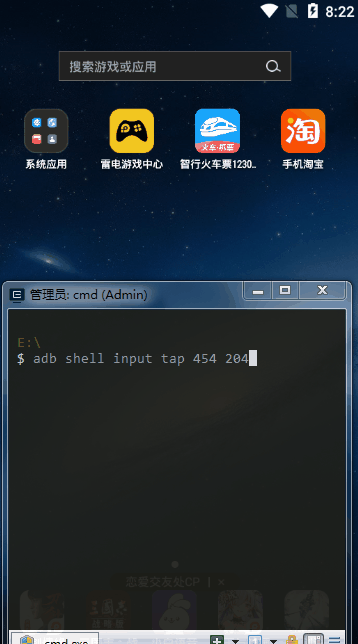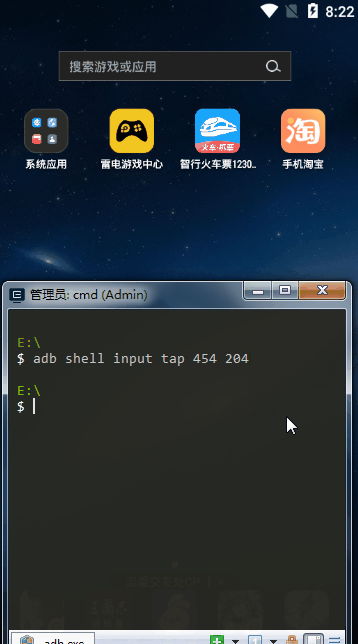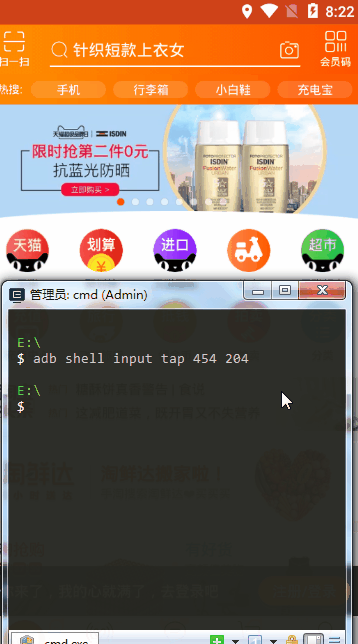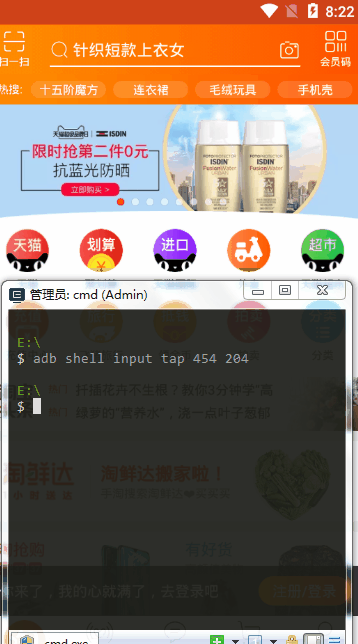
# tap点击 adb shell input tap 454 204
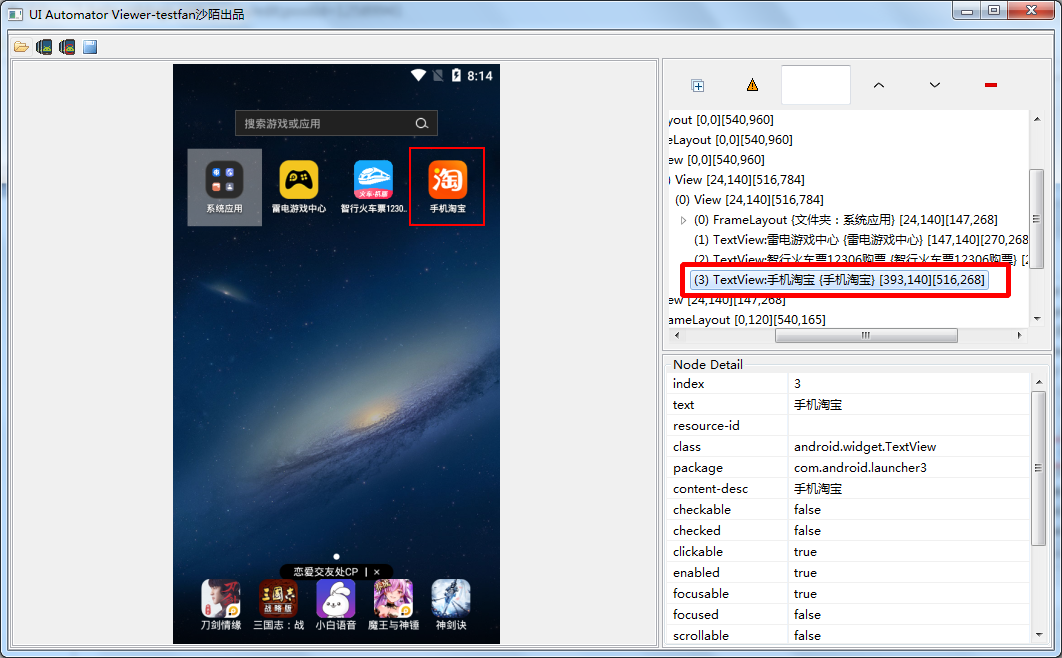
坐标怎么来的:通过uiautomatorviewer.bat定位工具查看坐标[393,140] [516,268],然后求出中间值[454 204]
swipe
和tap一样,选取两个坐标进行滑动,坐标安静这边选取的是(x*1/2 Y*3/4 x*1/2 Y*1/4)
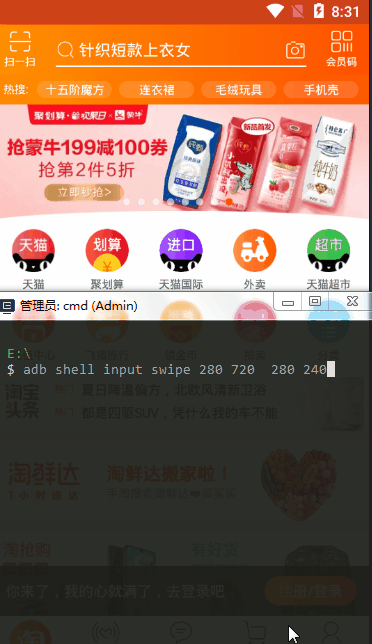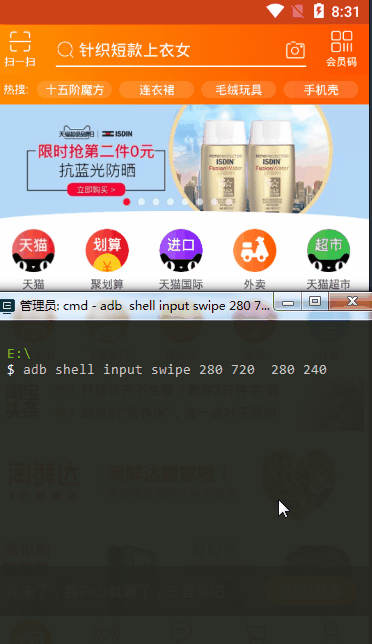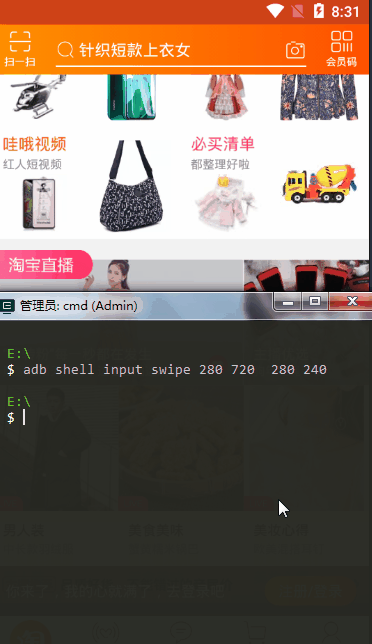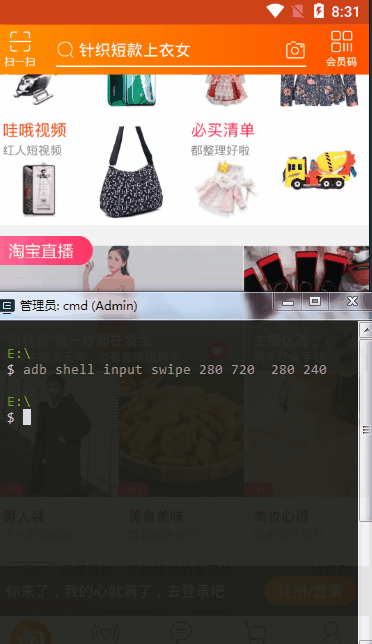
代码中的input
上面这么多都是在cmd中敲出来的,真正的自动化确实要在代码中,我们可以进行对这些常用的adb命令进行封装起来
import os class input(object): # 输入文字 def text(self,text): adb = 'adb shell input text %s'%text os.popen(adb) # 滑动 def swipe(self,x,y,x1,y1): adb = 'adb shell input swipe %s %s %s %s '%(x,y,x1,y1) os.popen(adb) # 模拟按键 def keyevent(self,k): adb = 'adb shell input keyevent %s'%k os.popen(adb) if __name__ == '__main__': adb = input() adb.text(1111) adb.swipe(280,720,280,240) adb.keyevent(3)
PS:其实写了这么多会发现方法有很多种,具体用那种,就要看大家用哪种比较方便就用哪种。