4.0 C++语言引用
也就是变量的别名
基本数据类型的引用
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(void) { int a = 3; int &b = a; //引用必须初始化 b = 10; cout << a << endl; return 0; }
结构体类型的引用
#include <iostream> using namespace std; typedef struct { int x; int y; }Coor; int main(void) { Coor c1; Coor& c = c1; c.x = 10; c.y = 20; cout << c1.x << " " << c1.y << endl; return 0; }
指针类型的引用
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(void) { int a = 10; int *p = &a; int *&q = p; *q = 20; cout << a << endl; return 0; }
引用做函数参数
void fun(int &a, int &b) { int c = 0; c = a; a = b; b = c; } int x = 10, y = 20; fun(x, y); // 引用
#include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; void fun(int &a, int &b); void fun(int &a, int &b) { int c = 0; c = a; a = b; b = c; } int main(void) { int x = 10; int y = 20; cout << x << "," << y << endl; fun(x,y); cout << x << "," << y << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }

4.1 控制变化的 const
int x = 3; const int * p = &x; p = &y; // 正确 *p = 4; //错误
int x = 3; int* const p = &x; p = &y; // 错误的
const int x = 3; const int* const p = &x; p = &y;//错误 *p = 4;//错误
// const 与引用 int x = 3; const int& y = x; x = 10; // 正确 y = 20; // 错误
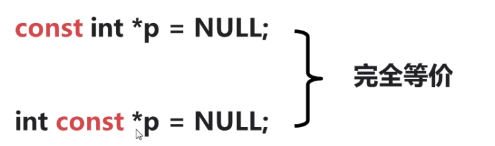
指针指向const修饰的变量时(int const a = 3;),应该是const int const *p = &a;


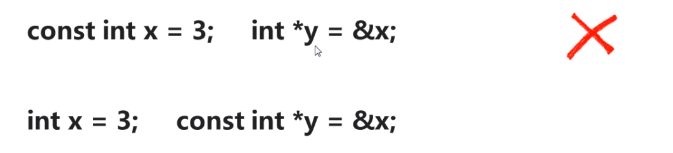

4.1 C++函数特性
void fun(int i, int j =5, int k =10); //(O) void fun(int i, int j = 5, int k);// (X)
有默认参数值的参数必须在参数表的最右端
//无实参则用默认值,否则实参覆盖默认值 void fun(int i, int j = 5, int k = 10); void fun(int i, int j, int k) { cout << i << j << k; } int main() { fun(20); fun(20, 30); fun(20, 30, 40); return 0; }
4.2 函数重载
在相同作用域内,用同一函数名定义的多个函数,参数多个和参数类型不同
getMax(int x, int y, int z) // getMax_int_int_int getMax(double x, double y) //getMax_double_double
内联函数
// 内联函数关键字 : inline inline int max(int a, int b, int c); int main() { int i = 10, j = 20, k = 30; m = max(i, j, k); cout << "max=" << m << endl; return 0; }
内联编译是建议性的,由编译器决定
逻辑简单,调用频繁的函数建议使用内联
递归函数无法使用内联方式

函数重载练习
/*****************************/ /*现有一个数组, 定义一个方法getMax(),利用函数的重载 *分别实现: * 1.随意取出数组中的两个元素,传到方法getMax()中, *可以返回较大的一个元素。 * * 2.将整个数组传到方法getMax()中,可以返回数组中最 *大的一个元素。 * */ /*****************************/ #include <iostream> #include <stdlib.h> using namespace std; // 函数功能:返回a和b的最大值 int getMax(int a, int b) { return a > b ? a : b; } // 函数功能:返回数组中的最大值 int getMax(int* arr, int count) { int maxNum = arr[0]; for (int i = 1;i < count;i++) { if (maxNum < arr[i]) { maxNum = arr[i]; } } return maxNum; } int main(void) { int numArr[3] = {9,8,6}; //自动调用返回数组中的最大值 cout << getMax(numArr, 3) << endl; //自动调用返回a和b最大值 cout << getMax(numArr[0], numArr[2]) << endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
4.3 内存管理
new 申请
delete 释放
示例代码:
#include<iostream> #include<stdlib.h> using namespace std; int main() { int* p = new int[100]; if (NULL == p) { system("pause"); return 0; } p[0] = 10; p[1] = 17; cout << p[0] << "," << p[1] << endl; delete[]p;//数组空间的删除 p = NULL; system("pause"); return 0;
代码示例:
/***************/ /*在堆中申请100个char类型的内存,拷贝Hello imooc字符串到 *分配的堆中内存中,打印字符串,最后释放内存 */ /***************/ #include <string.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(void) { //在堆中申请100个char类型的内存 char *str = new char[100]; //拷贝Hello imooc字符串到分配的堆中的内存中 strcpy(str, "Hello imooc"); //打印字符串 cout << str << endl; //释放字符串 delete []str; str = NULL; return 0; }