简介
本文介绍下golang的基本数据结构切片的代码实现。源码基于go1.14.2
给个不严谨的定义,go的切片是一种"动态数组的引用",与C++的vector类型类似,都是线性结构,都有内存分配,都有扩容操作。
TODO文末会附上一个C实现的Slice,供C背景的读者参考
slice定义
代码位于runtime包下
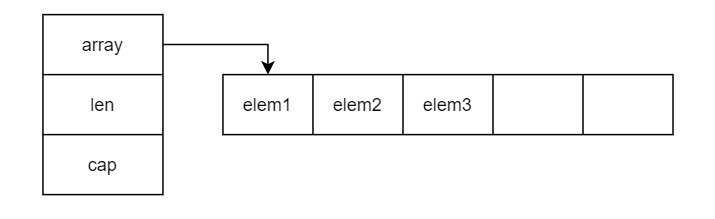
type slice struct {
array unsafe.Pointer
len int
cap int
}
unsafe.Pointer类似于C的void*,指向存储数据的内存
len是存储数据的个数
cap是array最多能存储的数据个数。自然,cap>=len.当cap==len时,再想append数据会进行内存扩容。这部分之后会说
比如我们定义一个切片sliceA := make([]int, 3, 5),如图
创建切片
func makeslice(et *_type, len, cap int) unsafe.Pointer {
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(cap))
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc || len < 0 || len > cap {
mem, overflow := math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(len))
if overflow || mem > maxAlloc || len < 0 {
panicmakeslicelen()
}
panicmakeslicecap()
}
return mallocgc(mem, et, true)
}
math.MulUintptr文档
func MulUintptr(a, b uintptr) (uintptr, bool)
MulUintptr returns a * b and whether the multiplication overflowed. On supported platforms this is an intrinsic lowered by the compiler.
64位的版本只是转换下,看看数据是否支持64位
func makeslice64(et *_type, len64, cap64 int64) unsafe.Pointer {
len := int(len64)
if int64(len) != len64 {
panicmakeslicelen()
}
cap := int(cap64)
if int64(cap) != cap64 {
panicmakeslicecap()
}
return makeslice(et, len, cap)
}
扩容
扩容这部分代码很清晰,传入old切片,分配一个cap更大的new切片,new切片拷贝old的数据后,返回new切片
cap扩容策略:当len<1024时,新切片的cap是老切片的2倍;否则增加25%
// growslice handles slice growth during append.
// It is passed the slice element type, the old slice, and the desired new minimum capacity,
// and it returns a new slice with at least that capacity, with the old data
// copied into it.
// The new slice's length is set to the old slice's length,
// NOT to the new requested capacity.
// This is for codegen convenience. The old slice's length is used immediately
// to calculate where to write new values during an append.
// TODO: When the old backend is gone, reconsider this decision.
// The SSA backend might prefer the new length or to return only ptr/cap and save stack space.
func growslice(et *_type, old slice, cap int) slice {
if raceenabled {
callerpc := getcallerpc()
racereadrangepc(old.array, uintptr(old.len*int(et.size)), callerpc, funcPC(growslice))
}
if msanenabled {
msanread(old.array, uintptr(old.len*int(et.size)))
}
if cap < old.cap {
panic(errorString("growslice: cap out of range"))
}
if et.size == 0 {
// append should not create a slice with nil pointer but non-zero len.
// We assume that append doesn't need to preserve old.array in this case.
return slice{unsafe.Pointer(&zerobase), old.len, cap}
}
newcap := old.cap
doublecap := newcap + newcap
if cap > doublecap {
newcap = cap
} else {
if old.len < 1024 {
newcap = doublecap
} else {
// Check 0 < newcap to detect overflow
// and prevent an infinite loop.
for 0 < newcap && newcap < cap {
newcap += newcap / 4
}
// Set newcap to the requested cap when
// the newcap calculation overflowed.
if newcap <= 0 {
newcap = cap
}
}
}
var overflow bool
var lenmem, newlenmem, capmem uintptr
// Specialize for common values of et.size.
// For 1 we don't need any division/multiplication.
// For sys.PtrSize, compiler will optimize division/multiplication into a shift by a constant.
// For powers of 2, use a variable shift.
switch {
case et.size == 1:
lenmem = uintptr(old.len)
newlenmem = uintptr(cap)
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap))
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > maxAlloc
newcap = int(capmem)
case et.size == sys.PtrSize:
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) * sys.PtrSize
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) * sys.PtrSize
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) * sys.PtrSize)
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > maxAlloc/sys.PtrSize
newcap = int(capmem / sys.PtrSize)
case isPowerOfTwo(et.size):
var shift uintptr
if sys.PtrSize == 8 {
// Mask shift for better code generation.
shift = uintptr(sys.Ctz64(uint64(et.size))) & 63
} else {
shift = uintptr(sys.Ctz32(uint32(et.size))) & 31
}
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) << shift
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) << shift
capmem = roundupsize(uintptr(newcap) << shift)
overflow = uintptr(newcap) > (maxAlloc >> shift)
newcap = int(capmem >> shift)
default:
lenmem = uintptr(old.len) * et.size
newlenmem = uintptr(cap) * et.size
capmem, overflow = math.MulUintptr(et.size, uintptr(newcap))
capmem = roundupsize(capmem)
newcap = int(capmem / et.size)
}
// The check of overflow in addition to capmem > maxAlloc is needed
// to prevent an overflow which can be used to trigger a segfault
// on 32bit architectures with this example program:
//
// type T [1<<27 + 1]int64
//
// var d T
// var s []T
//
// func main() {
// s = append(s, d, d, d, d)
// print(len(s), "
")
// }
if overflow || capmem > maxAlloc {
panic(errorString("growslice: cap out of range"))
}
var p unsafe.Pointer
if et.ptrdata == 0 {
p = mallocgc(capmem, nil, false)
// The append() that calls growslice is going to overwrite from old.len to cap (which will be the new length).
// Only clear the part that will not be overwritten.
memclrNoHeapPointers(add(p, newlenmem), capmem-newlenmem)
} else {
// Note: can't use rawmem (which avoids zeroing of memory), because then GC can scan uninitialized memory.
p = mallocgc(capmem, et, true)
if lenmem > 0 && writeBarrier.enabled {
// Only shade the pointers in old.array since we know the destination slice p
// only contains nil pointers because it has been cleared during alloc.
bulkBarrierPreWriteSrcOnly(uintptr(p), uintptr(old.array), lenmem)
}
}
memmove(p, old.array, lenmem)
return slice{p, old.len, newcap}
}