Code-First from an Existing Database:
Here, you will learn how to generate code-first context and entity classes for an existing database.
Entity Framework provides an easy way to use code-first approach for an existing database. It will create entity classes for all the tables & views in your existing database and configure it with DataAnnotations attributes and Fluent API.
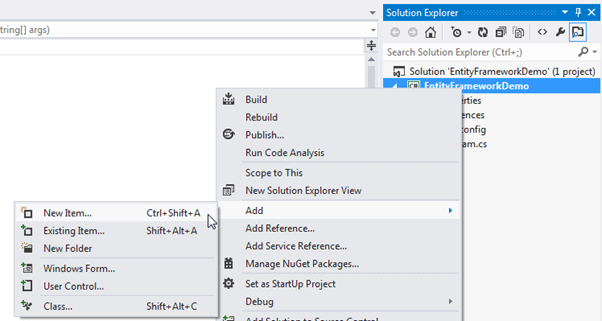
To use code-first for an existing database, right click on your project in Visual Studio -> Add -> New Item..
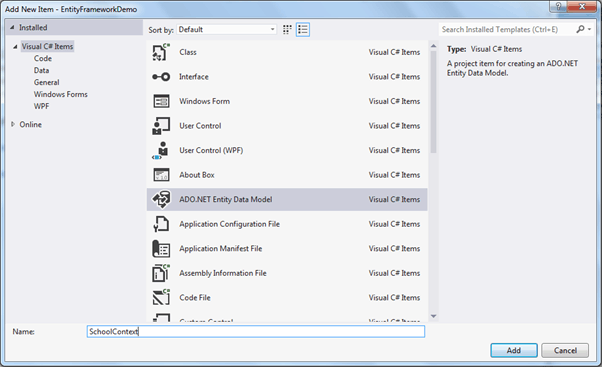
Select ADO.NET Entity Data Model in the Add new item dialog box and specify model name (This will be a context class name) and click on Add.
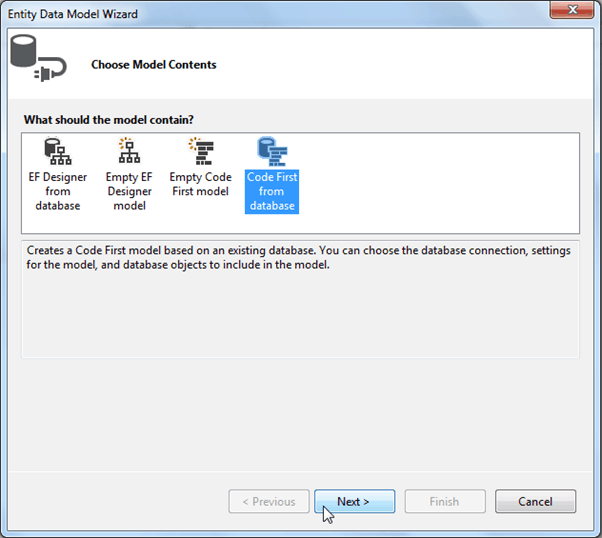
This will open Entity Data Model wizard as shown below. Select Code first from database option and click Next.
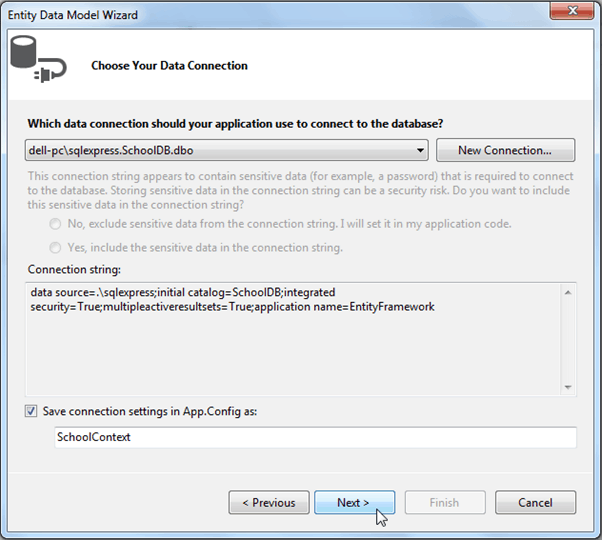
Now, select data connection for existing database. Create new connection for your database if dropdown does not include connection to your existing database. Click Next to continue.
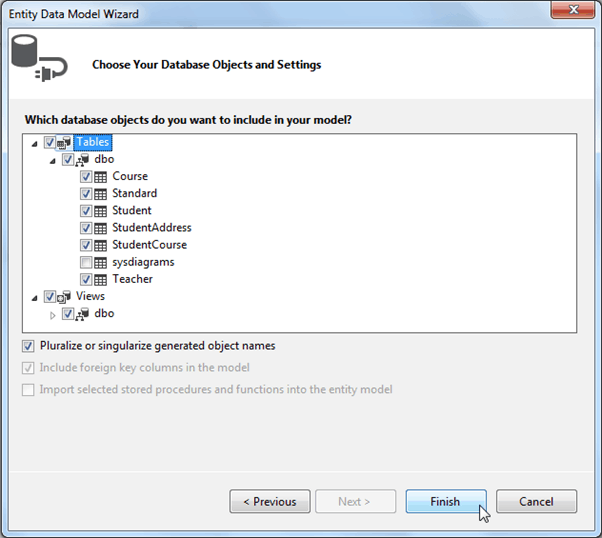
Now, choose tables and views for which you want to generate classes and click on Finish.
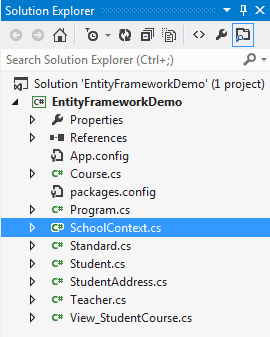
This will generate all the entity classes for your DB tables and views as shown below.
For example, it will create following context class which uses Fluent API to configure entity classes as per your database.
namespace EFDemo { using System; using System.Data.Entity; using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations.Schema; using System.Linq; public partial class SchoolContext : DbContext { public SchoolContext() : base("name=SchoolContext2") { } public virtual DbSet<Course> Courses { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<Standard> Standards { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<StudentAddress> StudentAddresses { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<Teacher> Teachers { get; set; } public virtual DbSet<View_StudentCourse> View_StudentCourse { get; set; } protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Course>() .Property(e => e.CourseName) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<Course>() .HasMany(e => e.Students) .WithMany(e => e.Courses) .Map(m => m.ToTable("StudentCourse").MapLeftKey("CourseId").MapRightKey("StudentId")); modelBuilder.Entity<Standard>() .Property(e => e.StandardName) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<Standard>() .Property(e => e.Description) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<Standard>() .HasMany(e => e.Students) .WithOptional(e => e.Standard) .WillCascadeOnDelete(); modelBuilder.Entity<Standard>() .HasMany(e => e.Teachers) .WithOptional(e => e.Standard) .WillCascadeOnDelete(); modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .Property(e => e.StudentName) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .Property(e => e.RowVersion) .IsFixedLength(); modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .HasOptional(e => e.StudentAddress) .WithRequired(e => e.Student) .WillCascadeOnDelete(); modelBuilder.Entity<StudentAddress>() .Property(e => e.Address1) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<StudentAddress>() .Property(e => e.Address2) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<StudentAddress>() .Property(e => e.City) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<StudentAddress>() .Property(e => e.State) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<Teacher>() .Property(e => e.TeacherName) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<Teacher>() .HasMany(e => e.Courses) .WithOptional(e => e.Teacher) .WillCascadeOnDelete(); modelBuilder.Entity<View_StudentCourse>() .Property(e => e.StudentName) .IsUnicode(false); modelBuilder.Entity<View_StudentCourse>() .Property(e => e.CourseName) .IsUnicode(false); } } }