1.算法
在高并发的应用中,限流是一个绕不开的话题。限流可以保障我们的 API 服务对所有用户的可用性,也可以防止网络攻击。
一般开发高并发系统常见的限流有:限制总并发数(比如数据库连接池、线程池)、限制瞬时并发数(如 nginx 的 limit_conn 模块,用来限制瞬时并发连接数)、限制时间窗口内的平均速率(如 Guava 的 RateLimiter、nginx 的 limit_req 模块,限制每秒的平均速率);其他还有如限制远程接口调用速率、限制 MQ 的消费速率。另外还可以根据网络连接数、网络流量、CPU 或内存负载等来限流。
限流算法
做限流 (Rate Limiting/Throttling) 的时候,除了简单的控制并发,如果要准确的控制 TPS,简单的做法是维护一个单位时间内的 Counter,如判断单位时间已经过去,则将 Counter 重置零。此做法被认为没有很好的处理单位时间的边界,比如在前一秒的最后一毫秒里和下一秒的第一毫秒都触发了最大的请求数,也就是在两毫秒内发生了两倍的 TPS。
常用的更平滑的限流算法有两种:漏桶算法和令牌桶算法。很多传统的服务提供商如华为中兴都有类似的专利,参考采用令牌漏桶进行报文限流的方法。
漏桶算法
漏桶(Leaky Bucket)算法思路很简单,水(请求)先进入到漏桶里,漏桶以一定的速度出水(接口有响应速率),当水流入速度过大会直接溢出(访问频率超过接口响应速率),然后就拒绝请求,可以看出漏桶算法能强行限制数据的传输速率。
可见这里有两个变量,一个是桶的大小,支持流量突发增多时可以存多少的水(burst),另一个是水桶漏洞的大小(rate)。因为漏桶的漏出速率是固定的参数,所以,即使网络中不存在资源冲突(没有发生拥塞),漏桶算法也不能使流突发(burst)到端口速率。因此,漏桶算法对于存在突发特性的流量来说缺乏效率。
令牌桶算法
令牌桶算法(Token Bucket)和 Leaky Bucket 效果一样但方向相反的算法,更加容易理解。随着时间流逝,系统会按恒定 1/QPS 时间间隔(如果 QPS=100,则间隔是 10ms)往桶里加入 Token(想象和漏洞漏水相反,有个水龙头在不断的加水),如果桶已经满了就不再加了。新请求来临时,会各自拿走一个 Token,如果没有 Token 可拿了就阻塞或者拒绝服务。
令牌桶的另外一个好处是可以方便的改变速度。一旦需要提高速率,则按需提高放入桶中的令牌的速率。一般会定时(比如 100 毫秒)往桶中增加一定数量的令牌,有些变种算法则实时的计算应该增加的令牌的数量。Guava 中的 RateLimiter 采用了令牌桶的算法,设计思路参见 How is the RateLimiter designed, and why?,详细的算法实现参见源码。

本文讨论在gateway集成的实现
2.创建gateway工程
详情见:spring cloud网关gateway
在此基础上pom中加入
<!--RequestRateLimiter限流--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive</artifactId> </dependency>
3.配置类
package com.common.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.ratelimit.KeyResolver; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; /** * @Title: * @Auther: * @Date: 2019/8/28 17:13 * @Version: 1.0 * @Description: */ @Configuration public class RequestRateLimiterConfig { @Bean @Primary KeyResolver apiKeyResolver() { //按URL限流,即以每秒内请求数按URL分组统计,超出限流的url请求都将返回429状态 return exchange -> Mono.just(exchange.getRequest().getPath().toString()); } @Bean KeyResolver userKeyResolver() { //按用户限流 return exchange -> Mono.just(exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("user")); } @Bean KeyResolver ipKeyResolver() { //按IP来限流 return exchange -> Mono.just(exchange.getRequest().getRemoteAddress().getHostName()); } }
4.yml配置
application.yml
spring: application: name: gateway8710 cloud: gateway: default-filter: routes: - id: user-server predicates: - Path=/java/** filters: - StripPrefix=1 # 限流过滤器,使用gateway内置令牌算法 - name: RequestRateLimiter args: # 令牌桶每秒填充平均速率,即行等价于允许用户每秒处理多少个请求平均数 redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 10 # 令牌桶的容量,允许在一秒钟内完成的最大请求数 redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 20 # 用于限流的键的解析器的 Bean 对象的名字。它使用 SpEL 表达式根据#{@beanName}从 Spring 容器中获取 Bean 对象。 key-resolver: "#{@apiKeyResolver}" uri: lb://service-helloword # uri: "http://192.168.111.133:8708/project/hello" redis: #Redis数据库索引(默认为0) database: 0 #连接超时时间(毫秒) springboot2.0 中该参数的类型为Duration,这里在配置的时候需要指明单位 timeout: 20s #密码 password: test cluster: # 获取失败 最大重定向次数 max-redirects: 3 #测试环境redis nodes: - 10.0.0.1:6380 - 10.0.0.2:6380 - 10.0.0.3:6380 - 10.0.0.1:6381 - 10.0.0.2:6381 - 10.0.0.3:6381 lettuce: pool: #连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制) max-active: 300 #连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制) max-wait: -1s #连接池中的最大空闲连接 max-idle: 100 #连接池中的最小空闲连接 min-idle: 20 server: port: 8710 eureka: client: serviceUrl: #指向注册中心 defaultZone: http://192.168.111.133:8888/eureka/ instance: # 每间隔1s,向服务端发送一次心跳,证明自己依然”存活“ lease-renewal-interval-in-seconds: 1 # 告诉服务端,如果我2s之内没有给你发心跳,就代表我“死”了,将我踢出掉。 lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds: 2
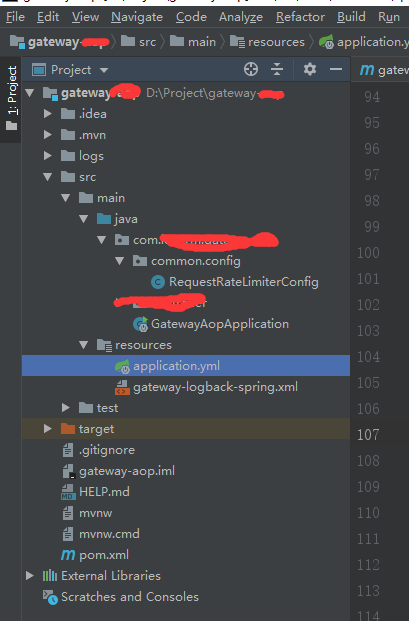
目录结构如下
5.启动测试
需要用jmeter来做并发测试,一秒内启30个进程,重复发请求10000次。详情见并发测试JMeter及发送Json请求
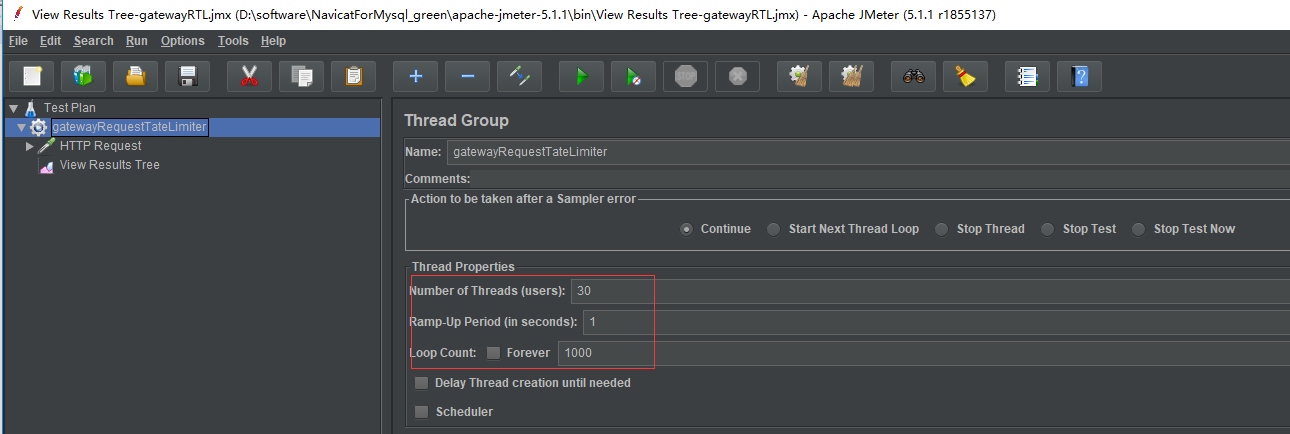
测试结果,没有抢到令牌的请求就返回429,这边的限流相当于平均request:10/s

redis中存储项
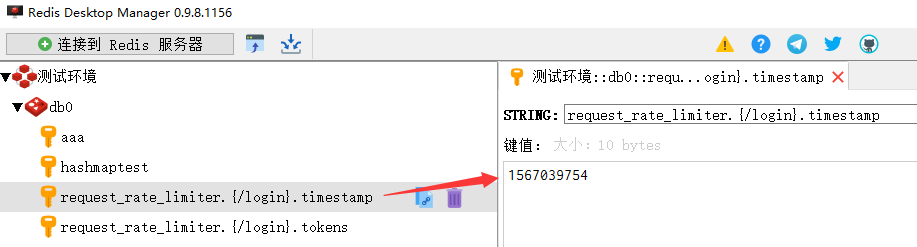
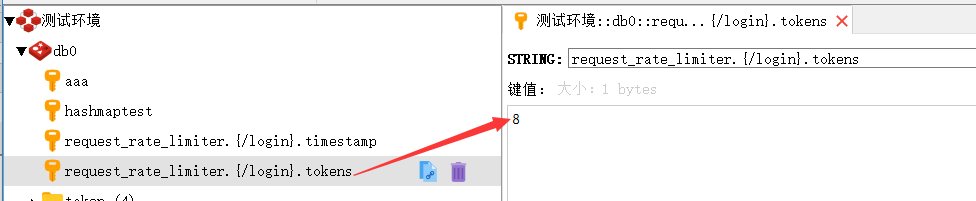
多个请求,如两个(url分别为/project/getToken,/project/login)不同的并发请求

6.原理
基于redis+lua
lua脚本路径
local tokens_key = KEYS[1] local timestamp_key = KEYS[2] local rate = tonumber(ARGV[1]) local capacity = tonumber(ARGV[2]) local now = tonumber(ARGV[3]) local requested = tonumber(ARGV[4]) local fill_time = capacity/rate local ttl = math.floor(fill_time*2) local last_tokens = tonumber(redis.call("get", tokens_key)) if last_tokens == nil then last_tokens = capacity end --redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "last_tokens " .. last_tokens) local last_refreshed = tonumber(redis.call("get", timestamp_key)) if last_refreshed == nil then last_refreshed = 0 end --redis.log(redis.LOG_WARNING, "last_refreshed " .. last_refreshed) local delta = math.max(0, now-last_refreshed) local filled_tokens = math.min(capacity, last_tokens+(delta*rate)) local allowed = filled_tokens >= requested local new_tokens = filled_tokens local allowed_num = 0 if allowed then new_tokens = filled_tokens - requested allowed_num = 1 end redis.call("setex", tokens_key, ttl, new_tokens) redis.call("setex", timestamp_key, ttl, now) return { allowed_num, new_tokens }
引入脚本的地方
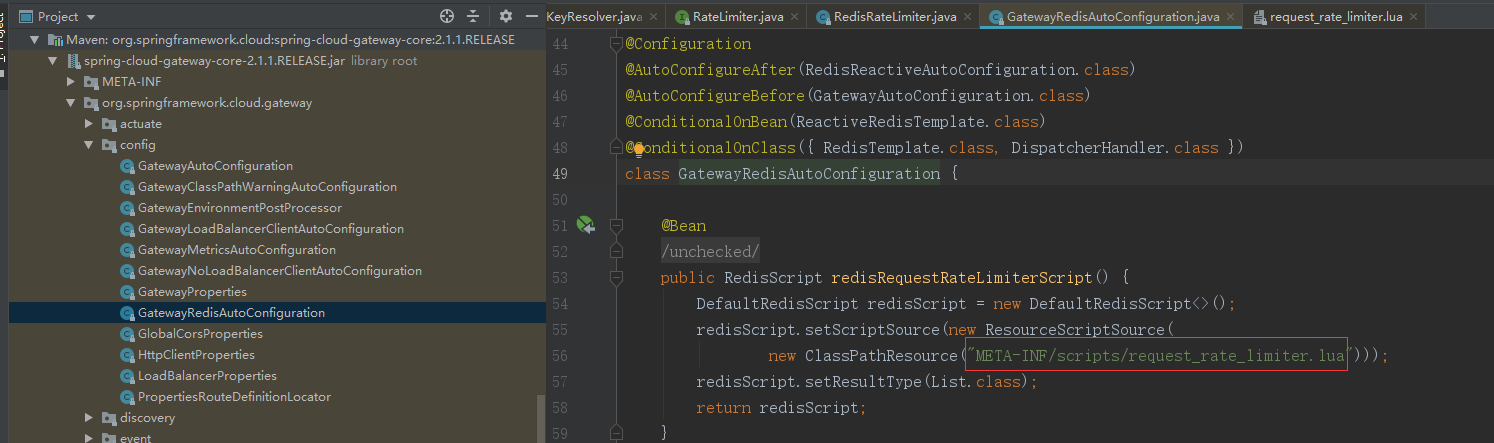
相关源码:
限流源码RedisRateLimiter
/* * Copyright 2017-2019 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.ratelimit; import java.time.Instant; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicBoolean; import javax.validation.constraints.Min; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.jetbrains.annotations.NotNull; import reactor.core.publisher.Flux; import reactor.core.publisher.Mono; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinitionRouteLocator; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ReactiveRedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript; import org.springframework.validation.Validator; import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated; /** * See https://stripe.com/blog/rate-limiters and * https://gist.github.com/ptarjan/e38f45f2dfe601419ca3af937fff574d#file-1-check_request_rate_limiter-rb-L11-L34. * * @author Spencer Gibb * @author Ronny Bräunlich */ @ConfigurationProperties("spring.cloud.gateway.redis-rate-limiter") public class RedisRateLimiter extends AbstractRateLimiter<RedisRateLimiter.Config> implements ApplicationContextAware { /** * @deprecated use {@link Config#replenishRate} */ @Deprecated public static final String REPLENISH_RATE_KEY = "replenishRate"; /** * @deprecated use {@link Config#burstCapacity} */ @Deprecated public static final String BURST_CAPACITY_KEY = "burstCapacity"; /** * Redis Rate Limiter property name. */ public static final String CONFIGURATION_PROPERTY_NAME = "redis-rate-limiter"; /** * Redis Script name. */ public static final String REDIS_SCRIPT_NAME = "redisRequestRateLimiterScript"; /** * Remaining Rate Limit header name. */ public static final String REMAINING_HEADER = "X-RateLimit-Remaining"; /** * Replenish Rate Limit header name. */ public static final String REPLENISH_RATE_HEADER = "X-RateLimit-Replenish-Rate"; /** * Burst Capacity Header name. */ public static final String BURST_CAPACITY_HEADER = "X-RateLimit-Burst-Capacity"; private Log log = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); private ReactiveRedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate; private RedisScript<List<Long>> script; private AtomicBoolean initialized = new AtomicBoolean(false); private Config defaultConfig; // configuration properties /** * Whether or not to include headers containing rate limiter information, defaults to * true. */ private boolean includeHeaders = true; /** * The name of the header that returns number of remaining requests during the current * second. */ private String remainingHeader = REMAINING_HEADER; /** The name of the header that returns the replenish rate configuration. */ private String replenishRateHeader = REPLENISH_RATE_HEADER; /** The name of the header that returns the burst capacity configuration. */ private String burstCapacityHeader = BURST_CAPACITY_HEADER; public RedisRateLimiter(ReactiveRedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate, RedisScript<List<Long>> script, Validator validator) { super(Config.class, CONFIGURATION_PROPERTY_NAME, validator); this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate; this.script = script; initialized.compareAndSet(false, true); } public RedisRateLimiter(int defaultReplenishRate, int defaultBurstCapacity) { super(Config.class, CONFIGURATION_PROPERTY_NAME, null); this.defaultConfig = new Config().setReplenishRate(defaultReplenishRate) .setBurstCapacity(defaultBurstCapacity); } static List<String> getKeys(String id) { // use `{}` around keys to use Redis Key hash tags // this allows for using redis cluster // Make a unique key per user. String prefix = "request_rate_limiter.{" + id; // You need two Redis keys for Token Bucket. String tokenKey = prefix + "}.tokens"; String timestampKey = prefix + "}.timestamp"; return Arrays.asList(tokenKey, timestampKey); } public boolean isIncludeHeaders() { return includeHeaders; } public void setIncludeHeaders(boolean includeHeaders) { this.includeHeaders = includeHeaders; } public String getRemainingHeader() { return remainingHeader; } public void setRemainingHeader(String remainingHeader) { this.remainingHeader = remainingHeader; } public String getReplenishRateHeader() { return replenishRateHeader; } public void setReplenishRateHeader(String replenishRateHeader) { this.replenishRateHeader = replenishRateHeader; } public String getBurstCapacityHeader() { return burstCapacityHeader; } public void setBurstCapacityHeader(String burstCapacityHeader) { this.burstCapacityHeader = burstCapacityHeader; } @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext context) throws BeansException { if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) { this.redisTemplate = context.getBean("stringReactiveRedisTemplate", ReactiveRedisTemplate.class); this.script = context.getBean(REDIS_SCRIPT_NAME, RedisScript.class); if (context.getBeanNamesForType(Validator.class).length > 0) { this.setValidator(context.getBean(Validator.class)); } } } /* for testing */ Config getDefaultConfig() { return defaultConfig; } /** * This uses a basic token bucket algorithm and relies on the fact that Redis scripts * execute atomically. No other operations can run between fetching the count and * writing the new count. */ @Override @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// routeId也就是我们的fsh-house,id就是限流的URL,也就是/project/hello。 public Mono<Response> isAllowed(String routeId, String id) {
// 会判断RedisRateLimiter是否初始化了 if (!this.initialized.get()) { throw new IllegalStateException("RedisRateLimiter is not initialized"); }
// 获取routeId对应的限流配置 Config routeConfig = loadConfiguration(routeId);
// 允许用户每秒做多少次请求 // How many requests per second do you want a user to be allowed to do? int replenishRate = routeConfig.getReplenishRate();
// 令牌桶的容量,允许在一秒钟内完成的最大请求数 // How much bursting do you want to allow? int burstCapacity = routeConfig.getBurstCapacity(); try { List<String> keys = getKeys(id);
// 限流key的名称(request_rate_limiter.{/login}.timestamp,request_rate_limiter.{/login}.tokens) // The arguments to the LUA script. time() returns unixtime in seconds. List<String> scriptArgs = Arrays.asList(replenishRate + "", burstCapacity + "", Instant.now().getEpochSecond() + "", "1");
// 执行LUA脚本 // allowed, tokens_left = redis.eval(SCRIPT, keys, args) Flux<List<Long>> flux = this.redisTemplate.execute(this.script, keys, scriptArgs); // .log("redisratelimiter", Level.FINER); return flux.onErrorResume(throwable -> Flux.just(Arrays.asList(1L, -1L))) .reduce(new ArrayList<Long>(), (longs, l) -> { longs.addAll(l); return longs; }).map(results -> { boolean allowed = results.get(0) == 1L; Long tokensLeft = results.get(1); Response response = new Response(allowed, getHeaders(routeConfig, tokensLeft)); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("response: " + response); } return response; }); } catch (Exception e) { /* * We don't want a hard dependency on Redis to allow traffic. Make sure to set * an alert so you know if this is happening too much. Stripe's observed * failure rate is 0.01%. */ log.error("Error determining if user allowed from redis", e); } return Mono.just(new Response(true, getHeaders(routeConfig, -1L))); } /* for testing */ Config loadConfiguration(String routeId) { Config routeConfig = getConfig().getOrDefault(routeId, defaultConfig); if (routeConfig == null) { routeConfig = getConfig().get(RouteDefinitionRouteLocator.DEFAULT_FILTERS); } if (routeConfig == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "No Configuration found for route " + routeId + " or defaultFilters"); } return routeConfig; } @NotNull public Map<String, String> getHeaders(Config config, Long tokensLeft) { Map<String, String> headers = new HashMap<>(); if (isIncludeHeaders()) { headers.put(this.remainingHeader, tokensLeft.toString()); headers.put(this.replenishRateHeader, String.valueOf(config.getReplenishRate())); headers.put(this.burstCapacityHeader, String.valueOf(config.getBurstCapacity())); } return headers; } @Validated public static class Config { @Min(1) private int replenishRate; @Min(1) private int burstCapacity = 1; public int getReplenishRate() { return replenishRate; } public Config setReplenishRate(int replenishRate) { this.replenishRate = replenishRate; return this; } public int getBurstCapacity() { return burstCapacity; } public Config setBurstCapacity(int burstCapacity) { this.burstCapacity = burstCapacity; return this; } @Override public String toString() { return "Config{" + "replenishRate=" + replenishRate + ", burstCapacity=" + burstCapacity + '}'; } } }