本文内容:
- 异常的介绍
- 处理异常
- 断言
首发日期:2018-03-26
异常:
- 异常是程序运行中发生的错误,比较常见的比如“除零异常”,如果一个除数为零,那么会发生这个异常
- 异常会影响程序的正常运行,所以我们需要处理异常。

- 所有的异常类是从 java.lang.Exception 类继承的子类。 异常类有两个主要的子类:IOException 类和 RuntimeException 类。
常见异常:
算术异常类:ArithmeticExecption
空指针异常类:NullPointerException
类型强制转换异常:ClassCastException
数组下标越界异常:ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
输入输出异常:IOException
处理异常:
-
异常的捕获:try…catch…finally
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { // int a=10/0; try{ int a=10/0; }catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println("run in ArithmeticException "+e); //run in ArithmeticException java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e); }finally { System.out.println("最终执行的");//最终执行的 } } }
-
异常的声明:
throws用于声明异常,声明函数可能发生的异常。【当函数中有throw来抛出异常时,函数头必须使用throws声明异常】
-
抛出异常:
throw用于手动抛出异常,可以抛出自定义异常信息:throw 异常类型(异常信息)
public class Demo2 { static int div(int a,int b) throws ArithmeticException{ if (b==0){ throw new ArithmeticException("发生除零异常了!"); } return a/b; } public static void main(String args[]) { try { System.out.println(div(2,0)); }catch(ArithmeticException e) { System.out.println(e.getMessage());//发生除零异常了! }finally { System.out.println("in finally");//in finally } System.out.println("after finally");//after finally } }
一般对于不想在函数中处理异常时,一般采用异常抛出处理(throw throws);否则使用try…catch…finally捕获异常。
自定义异常:
有时候没有定义我们想要的异常(比如我们MYSQL连接异常),那么我们可以自定义异常。
- 所有异常都必须是 Throwable 的子类。
- 如果希望写一个检查性异常类(是一些编译器会帮忙检查的异常),则需要继承 Exception 类。
- 如果你想写一个运行时异常类(异常比如说,数组下标越界和访问空指针异常),那么需要继承 RuntimeException 类【这种异常类不需要throws】。
class MyException extends Exception{ public MyException() {} public MyException(String msg) { super(msg); } } public class Demo3 { static int div(int a,int b) throws MyException { if (b==0){ throw new MyException("发生异常了!"); } return a/b; } public static void main(String args[]) { try { System.out.println(div(2,0)); }catch(Exception e) { System.out.println(e);//异常.MyException: 发生除零异常了! } } }
断言:
- assertion(断言)在软件开发中是一种常用的调试方式
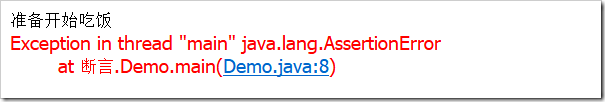
- 断言一般是判断条件是否符合来决定程序是否继续执行的。【比如,你要吃饭,那么assert一下饭到手了没有,不然你可能会吃空气】
- 断言的开启:eclipse、myeclipse的assert默认是关闭,想开启assert需要在设置perferences-》Java-》installed jres中配置一下虚拟机参数,配置成-ea或者-enableassertions

- Java中使用assert来定义断言:格式:assert [boolean 表达式]
public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { Boolean food=false; System.out.println("准备开始吃饭"); assert food; System.out.println("饭来了"); } }