browser objec tmodel浏览器对象模型
BOM里面的方法大多在window对象底下,window代表窗口,也就是说,在BOM里面大多调用window下面的东西。
1.open方法是window底下的一个方法
window.open(页面的地址URL,打开的方式)方法,打开一个新的界面
如果URL为空,则默认打开一个空白页面;如果打开方式为空,则默认新窗口方式打开
返回值:返回新打开的窗口的window对象
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="点击跳转" id="btn"> </body> <script> function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id) } $('btn').onclick=function(){ var newPage=window.open() alert(newPage) } </script> </html>
得到:

因此可以设置新界面
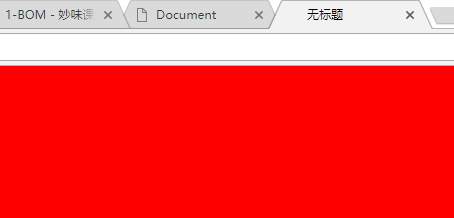
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="点击跳转" id="btn"> </body> <script> function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id) } $('btn').onclick=function(){ var newPage=window.open() newPage.document.body.style.background='red'//将新界面的背景色设置为红 } </script> </html>
运行为:
2.close()方法 关闭当前窗口
火狐:不关闭
谷歌:直接关闭
IE:先询问
注意:可以在本窗口关闭通过Js打开的新窗口
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <input type="button" value="点击跳转" id="btn1"> <input type="button" value="关闭窗口" id="btn2"> </body> <script> function $(id) { return document.getElementById(id) } $('btn1').onclick=function(){ newPage=window.open()//前期知识,不带var的变量为全局变量 } $('btn2').onclick=function(){ newPage.close() } </script> </html>
3.window.navigator.userAgent------获取浏览器信息
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> </body> <script> alert(window.navigator.userAgent); </script> </html>
不同的浏览器,信息不同
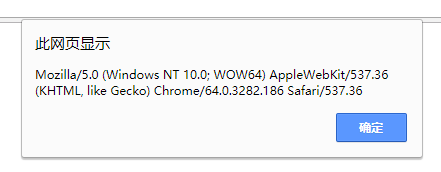
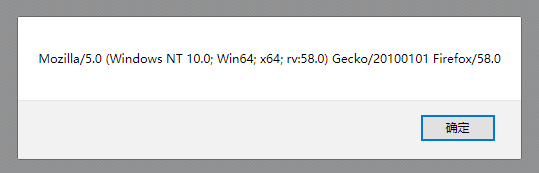
所以,根据这个属性,可以判断是否是某个浏览器。比如:如果是谷歌浏览器,则弹出我是谷歌,否则弹出我不是谷歌。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> </body> <script> if(window.navigator.userAgent.indexOf('Chrome')){ alert('我是谷歌'); }else{ alert('我不是谷歌') } </script> </html>
运行为:

4.window.location------地址栏上的信息
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> </body> <script> alert(window.location); </script> </html>

注意:其值为一个数组

其中window.location后面还有几个属性
1)window.location.href------同样获取地址栏的全部信息,即相当于url
2)window.location.search-------地址栏?后面的内容(包括问号)
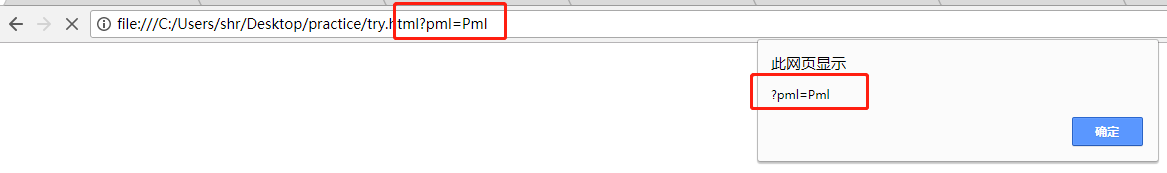
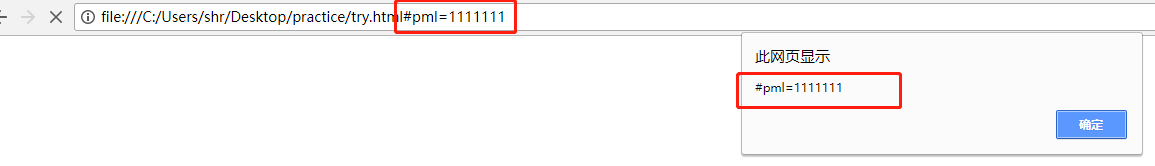
3)window.location.hash------地址栏#后面的值(包括#)