1、if语句
结构:
if condition:
do something
elif other_condition:
do something
number = 60 guess = int(input('Enter an integer : ')) if (guess == number): # New block starts here print('Bingo! you guessed it right.') # New block ends here elif (guess < number): # Another block print('No, the number is higher than that') # You can do whatever you want in a block ... else: print('No, the number is a lower than that') # you must have guessed > number to reach here print('Done')
2、循环语句允许我们执行一个语句或语句组多次,下面是在大多数编程语言中的循环语句的一般形式:
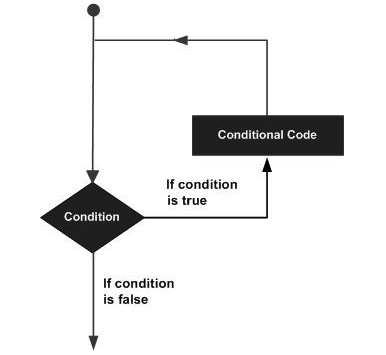
3、for语句
for i in range(1, 10): print(i) else: print('The for loop is over') #遍历List a_list = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] for i in a_list: print(i) #遍历Tuple a_tuple = (1, 3, 5, 7, 9) for i in a_tuple: print(i) #遍历Dict a_dict = {'Tom':'111', 'Jerry':'222', 'Cathy':'333'} for key in a_dict: print(key, a_dict[key]) for (key, elem) in a_dict.items(): print(key, elem)
运行结果:

4、while语句
number = 59 guess_flag = False while (guess_flag == False): guess = int(input('Enter an integer : ')) if guess == number: guess_flag = True elif guess < number: print('No, the number is higher than that, keep guessing') else: print('No, the number is a lower than that, keep guessing') print('Bingo! you guessed it right.')
5、break, continue, pass
(1) break 语句:跳出循环
(2) continue 语句:进行下一次循环
(3) pass 语句:什么都不做
number = 59 while True: guess = int(input('Enter an integer : ')) if guess == number: break if guess < number: print('No, the number is higher than that, keep guessing') continue else: print('No, the number is a lower than that, keep guessing') continue print('Bingo! you guessed it right.') print('Done')