You're given Q queries of the form (L, R).
For each query you have to find the number of such x that L ≤ x ≤ R and there exist integer numbers a > 0, p > 1 such that x = ap.
Input
The first line contains the number of queries Q (1 ≤ Q ≤ 105).
The next Q lines contains two integers L, R each (1 ≤ L ≤ R ≤ 1018).
Output
Output Q lines — the answers to the queries.
Example
input
Copy
6
1 4
9 9
5 7
12 29
137 591
1 1000000
output
2
1
0
3
17
1111
Note
In query one the suitable numbers are 1 and 4.
提供一种容斥原理的思想。
我们要求不大于n的所有幂数的个数。
把注意力先放在幂这个东西上
ci=pow(n,(1/i))可以得到所有以i为幂,小于等于n的底数的个数
那么最终答案是否是c1+c2+c3+...+ck呢
不是,因为有重复(例如:c2,c3间2^6这个数是被重复计算过的,但我们发现c2,c3的重复的这些数正好是c6)
进一步分析来看,
两个幂数:
ci,cj(i,j均可分解为奇数个不同质数的乘积)间重复的数为ck(k=lcm(i,j),且k一定可以分解为偶数个不同质数的乘积)
ans=ci+cj-ck
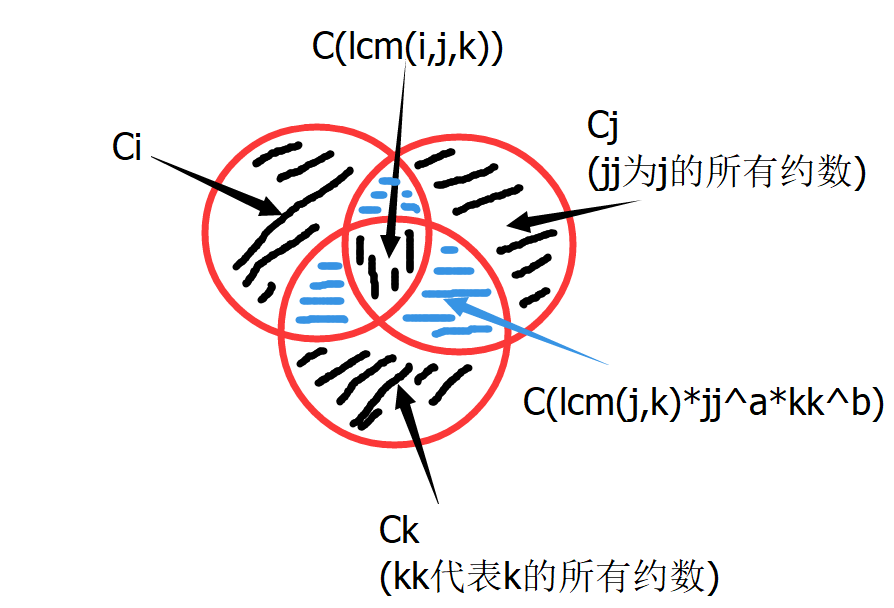
三个幂数:(看图)
ans=ci+cj+ck-c(ij)-c(jk)-c(ik)+c(ijk)
这不就是容斥原理么!!!
所以具体操作上,先打个容斥表
对象是幂

#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef long double lb; #define inf 2147483647 const ll INF = 0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3fll; #define ri register int template <class T> inline T min(T a, T b, T c) { return min(min(a, b), c); } template <class T> inline T max(T a, T b, T c) { return max(max(a, b), c); } template <class T> inline T min(T a, T b, T c, T d) { return min(min(a, b), min(c, d)); } template <class T> inline T max(T a, T b, T c, T d) { return max(max(a, b), max(c, d)); } #define scanf1(x) scanf("%d", &x) #define scanf2(x, y) scanf("%d%d", &x, &y) #define scanf3(x, y, z) scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z) #define scanf4(x, y, z, X) scanf("%d%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z, &X) #define pi acos(-1) #define me(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x)); #define For(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i <= b; i++) #define FFor(i, a, b) for (int i = a; i >= b; i--) #define bug printf("*********** "); #define mp make_pair #define pb push_back const int maxn = 10005; // name******************************* int a[100]; ll l,r,q; // function****************************** ll sol(ll x) { ll s=x?1:0;//大于1就先加上1 for(ll i=2; (1ll<<i)<=x; i++) s-=a[i]*((int)pow((lb)x+0.5,(lb)1/i)-1);//记得减一,1不能参与计数了 return s; } //*************************************** int main() { // ios::sync_with_stdio(0); // cin.tie(0); // freopen("test.txt", "r", stdin); // freopen("outout.txt","w",stdout); a[1]=1; for(int i=1; i<=50; i++) for(int j=i*2; j<=100; j+=i) a[j]-=a[i]; cin>>q; while(q--) { cin>>l>>r; cout<<sol(r)-sol(l-1)<<endl; } return 0; }