SpringBoot整合jdbcTemplate
单数据源
jdbcTemplate是Spring core包的核心类,是对jdbc的简单封装,帮我们简化了对jdbc的使用。在SpringBoot中使用jdbcTemplate无需导入额外的包,只需要添加数据库驱动以及数据源的包就可以了。
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
配置数据源参数:
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=
使用方法:
@Service public class UserInfoService { @Autowired JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; /** * 添加数据 * @param userInfo */ public void insertUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo){ jdbcTemplate.update("insert into user_info(username,password) values(?,?)",userInfo.getUsername(),userInfo.getPassword()); } /** * 更新数据 */ public void updateUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo){ jdbcTemplate.update("update user_info set username=? , password=? where id = ?", userInfo.getUsername(), userInfo.getPassword(), userInfo.getId()); } /** * 删除数据 * @param userInfo */ public void deleteUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo){ jdbcTemplate.update("delete from user_info where id=?", userInfo.getId()); } /** * 查询数据 * @param userInfo * @return */ public List<UserInfo> selectUserInfo(UserInfo userInfo){ return jdbcTemplate.query("select * from user_info", new RowMapper<UserInfo>() { @Override public UserInfo mapRow(ResultSet resultSet, int i) throws SQLException { UserInfo userInfo1 = new UserInfo(); Integer id = resultSet.getInt("id"); String username = resultSet.getString("username"); String password = resultSet.getString("password"); userInfo1.setId(id); userInfo1.setUsername(username); userInfo1.setPassword(password); return userInfo1; } }); } }
多数据源
目前我使用的SpringBoot版本为:2.3.1.RELEASE,配置多数据源的时候,有几个坑,不同的数据源所需要的参数是不一样的。下面以druid为例
配置文件:
spring.datasource.druid.one.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.datasource.druid.one.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.druid.one.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false spring.datasource.druid.one.username=root spring.datasource.druid.one.password= spring.datasource.druid.two.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.datasource.druid.two.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.druid.two.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test2?useSSL=false spring.datasource.druid.two.username=root spring.datasource.druid.two.password=
配置类(可以分下来写):
@Configuration public class DataSoureConfig { @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.one.type}") private Class<? extends DataSource> dataSourceType; @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.one") DataSource dataSourceOne(){ return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); } @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.two") DataSource dataSourceTwo(){ return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); } @Bean JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateOne(@Qualifier("dataSourceOne") DataSource dataSourceOne){ return new JdbcTemplate(dataSourceOne); } @Bean JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateTwo(@Qualifier("dataSourceTwo") DataSource dataSourceTwo){ return new JdbcTemplate(dataSourceTwo); } }
可以看到,需要制定数据源的类型。如果不指定数据源类型:
@Configuration public class DataSoureConfig { // @Value("${spring.datasource.druid.one.type}") // private Class<? extends DataSource> dataSourceType; @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.one") DataSource dataSourceOne(){ // return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.two") DataSource dataSourceTwo(){ // return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); return DataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } @Bean JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateOne(@Qualifier("dataSourceOne") DataSource dataSourceOne){ return new JdbcTemplate(dataSourceOne); } @Bean JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplateTwo(@Qualifier("dataSourceTwo") DataSource dataSourceTwo){ return new JdbcTemplate(dataSourceTwo); } }
配置文件(注意url的写法,不这么写会报错):
spring.datasource.druid.one.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.datasource.druid.one.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.druid.one.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useSSL=false spring.datasource.druid.one.username=root spring.datasource.druid.one.password=Ph0716 spring.datasource.druid.two.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource spring.datasource.druid.two.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver spring.datasource.druid.two.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test2?useSSL=false spring.datasource.druid.two.username=root spring.datasource.druid.two.password=Ph0716
启动测试类,控制台打印信息:

可以发现,即使配置了type,也是不解析的,默认使用了hikari数据源。而且hikari要求的url写法为:”jdbc-url“,否则会报错。druid直接写url就可以了。所以说,如果使用其他第三方的数据源,需要考虑路径问题,以及类型注入。
更新一下————————————————————————————————————————————————
上面用的是DataSourceBuilder是SpringBoot自带的,所以除非指定第三方数据源的类型,否则都会用默认的数据源。如果想要使用Druid,可以用阿里提供的builder,就不用特地注入Type了
@Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.one") DataSource dataSourceOne(){ return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build(); }
SpringBoot整合Mybatis
单数据源
SpringBoot整合Mybatis还是比较方便的(除了xml文件的位置放法有点坑外)
引包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
目录结构:
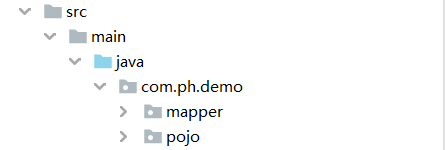
在mapper目录下创建映射接口:
@Mapper public interface UserInfoMapper { List<UserInfo>selectAllUser(); @Select("select * from user_info") List<UserInfo>selectAllUser2(); }
可以通过xml或者注解的方式来配置sql。
如果用xml的方式有以下几种方式:
1、xml文件放在接口所在的mapper文件夹内:

一群java类中冒出来一个xml文件是不和谐的,也不符合maven目录结构的规范,maven在打包的时候会自动忽略java文件夹下的xml文件。所以需要在pom文件的中(build节点内)添加额外的申明:
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
添加完之后就可以正常使用,不会报错了。
2、xml文件放在resources目录下
放在resources目录下,又有两种情况,一种放在与mapper接口所在包相同名称的文件夹里,是不是有点拗口,见图;
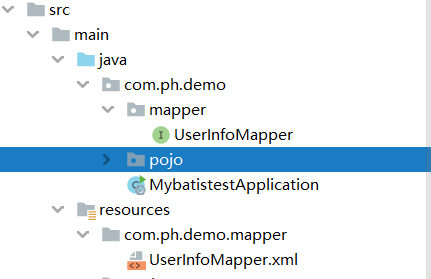
文件夹与java包是不一样的,如果创建的时候直接输入com.ph.demo.mapper,那么只会创建一个名为”com.ph.demo.mapper“的文件夹,而不是多个文件夹。所以多层文件夹应该一个一个创建。
我个人一般喜欢放在mapper文件夹下,如图:
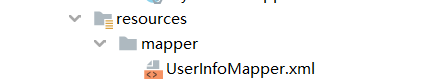
只是这么做的话,需要在配置文件中添加额外的配置:
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath*:mapper/*.xml
这样就大功告成了,个人推荐还是放在resource目录下,还是规范点比较好。
多数据源
目录结构:
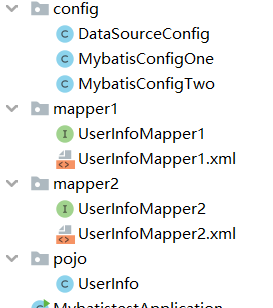
数据源配置类:
@Configuration public class DataSourceConfig { @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.one") DataSource dataSourceOne(){ return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } @Bean @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.two") DataSource dataSourceTwo(){ return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build(); } }
mybatis模板配置类1:
@Configuration @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.ph.demo.mapper1", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "sessionFactory1") public class MybatisConfigOne { @Resource(name = "dataSourceOne") DataSource dataSource; @Bean SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory1(){ SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); try { bean.setDataSource(dataSource); return bean.getObject(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } @Bean SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate1(){ return new SqlSessionTemplate(sessionFactory1()); } }
mybatis模板配置类2:
@Configuration @MapperScan(value = "com.ph.demo.mapper2", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "sqlSessionFactory2") public class MybatisConfigTwo { @Resource(name = "dataSourceTwo") DataSource dataSourceTwo; @Bean SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory2(){ SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); try{ sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSourceTwo); return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject(); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } @Bean SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate2(){ return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory2()); } }
测试类:
@SpringBootTest class MybatistestApplicationTests { @Autowired UserInfoMapper1 userInfoMapper1; @Autowired UserInfoMapper2 userInfoMapper2; @Test void contextLoads() { List<UserInfo>list = userInfoMapper1.selectAllUser(); List<UserInfo>list2 = userInfoMapper2.selectAllUser2(); System.out.println(list); System.out.println(list2); } }