基于SURF特征的图像与视频拼接技术的研究和实现(一)
一直有计划研究实时图像拼接,但是直到最近拜读西电2013年张亚娟的《基于SURF特征的图像与视频拼接技术的研究和实现》,条理清晰、内容完整、实现的技术具有市场价值。因此定下决心以这篇论文为基础脉络,结合实际情况,进行“基于SURF特征的图像与视频拼接技术的研究和实现”。
一、基于opencv的surf实现
3.0以后,surf被分到了"opencv_contrib-master"中去,操作起来不习惯,这里仍然选择一直在使用的opencv2.48,其surf的调用方式为:
// raw_surf.cpp : 本例是对opencv-2.48相关例子的实现
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector
int minHessian = 10000;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Draw keypoints
Mat img_keypoints_1; Mat img_keypoints_2;
drawKeypoints( img_1, keypoints_1, img_keypoints_1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
drawKeypoints( img_2, keypoints_2, img_keypoints_2, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
//-- Step 2: Calculate descriptors (feature vectors)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: Matching descriptor vectors with a brute force matcher
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_L2);
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//-- Draw matches
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2, matches, img_matches );
//-- Show detected (drawn) keypoints
imshow("Keypoints 1", img_keypoints_1 );
imshow("Keypoints 2", img_keypoints_2 );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow("Matches", img_matches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector
int minHessian = 10000;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Draw keypoints
Mat img_keypoints_1; Mat img_keypoints_2;
drawKeypoints( img_1, keypoints_1, img_keypoints_1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
drawKeypoints( img_2, keypoints_2, img_keypoints_2, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
//-- Step 2: Calculate descriptors (feature vectors)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: Matching descriptor vectors with a brute force matcher
BFMatcher matcher(NORM_L2);
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//-- Draw matches
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2, matches, img_matches );
//-- Show detected (drawn) keypoints
imshow("Keypoints 1", img_keypoints_1 );
imshow("Keypoints 2", img_keypoints_2 );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow("Matches", img_matches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
这里采用的是surffeaturedector的方法进行点的寻找,而后采用BFMatcher的方法进行数据比对。但这种方法错误的比较多,提供了FLANN的方法进行比对:
// raw_surf.cpp : 本例是对opencv-2.48相关例子的实现
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Draw keypoints
Mat img_keypoints_1; Mat img_keypoints_2;
drawKeypoints( img_1, keypoints_1, img_keypoints_1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
drawKeypoints( img_2, keypoints_2, img_keypoints_2, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
//-- Step 2: Calculate descriptors (feature vectors)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: Matching descriptor vectors using FLANN matcher
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
//-- Quick calculation of max and min distances between keypoints
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{ double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist );
printf("-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist );
//-- Draw only "good" matches (i.e. whose distance is less than 2*min_dist,
//-- or a small arbitary value ( 0.02 ) in the event that min_dist is very
//-- small)
//-- PS.- radiusMatch can also be used here.
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{ if( matches[i].distance <= max(2*min_dist, 0.02) )
{ good_matches.push_back( matches[i]); }
}
//-- Draw only "good" matches
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2,
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow( "Good Matches", img_matches );
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{ printf( "-- Good Match [%d] Keypoint 1: %d -- Keypoint 2: %d ", i, good_matches[i].queryIdx, good_matches[i].trainIdx ); }
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Draw keypoints
Mat img_keypoints_1; Mat img_keypoints_2;
drawKeypoints( img_1, keypoints_1, img_keypoints_1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
drawKeypoints( img_2, keypoints_2, img_keypoints_2, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
//-- Step 2: Calculate descriptors (feature vectors)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: Matching descriptor vectors using FLANN matcher
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
//-- Quick calculation of max and min distances between keypoints
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{ double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist );
printf("-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist );
//-- Draw only "good" matches (i.e. whose distance is less than 2*min_dist,
//-- or a small arbitary value ( 0.02 ) in the event that min_dist is very
//-- small)
//-- PS.- radiusMatch can also be used here.
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{ if( matches[i].distance <= max(2*min_dist, 0.02) )
{ good_matches.push_back( matches[i]); }
}
//-- Draw only "good" matches
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2,
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow( "Good Matches", img_matches );
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{ printf( "-- Good Match [%d] Keypoint 1: %d -- Keypoint 2: %d ", i, good_matches[i].queryIdx, good_matches[i].trainIdx ); }
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}

可以发现,除了错误一例,其他都是正确的。
继续来做,计算出单应矩阵
// raw_surf.cpp : 本例是对opencv-2.48相关例子的实现
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Draw keypoints
Mat img_keypoints_1; Mat img_keypoints_2;
drawKeypoints( img_1, keypoints_1, img_keypoints_1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
drawKeypoints( img_2, keypoints_2, img_keypoints_2, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
//-- Step 2: Calculate descriptors (feature vectors)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: Matching descriptor vectors using FLANN matcher
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
//-- Quick calculation of max and min distances between keypoints
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{ double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist );
printf("-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist );
//-- Draw only "good" matches (i.e. whose distance is less than 2*min_dist,
//-- or a small arbitary value ( 0.02 ) in the event that min_dist is very
//-- small)
//-- PS.- radiusMatch can also be used here.
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{ if( matches[i].distance <= /*max(2*min_dist, 0.02)*/3*min_dist )
{ good_matches.push_back( matches[i]); }
}
//-- Draw only "good" matches
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2,
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
obj.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
scene.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
printf( "-- Good Match [%d] Keypoint 1: %d -- Keypoint 2: %d ", i, good_matches[i].queryIdx, good_matches[i].trainIdx );
}
//直接调用ransac
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//-- Get the corners from the image_1 ( the object to be "detected" )
std::vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0,0); obj_corners[1] = Point( img_1.cols, 0 );
obj_corners[2] = Point( img_1.cols, img_1.rows ); obj_corners[3] = Point( 0, img_1.rows );
std::vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);
perspectiveTransform( obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
//-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )
Point2f offset( (float)img_1.cols, 0);
line( img_matches, scene_corners[0] + offset, scene_corners[1] + offset, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[1] + offset, scene_corners[2] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[2] + offset, scene_corners[3] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[3] + offset, scene_corners[0] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow( "Good Matches & Object detection", img_matches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: Detect the keypoints using SURF Detector
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Draw keypoints
Mat img_keypoints_1; Mat img_keypoints_2;
drawKeypoints( img_1, keypoints_1, img_keypoints_1, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
drawKeypoints( img_2, keypoints_2, img_keypoints_2, Scalar::all(-1), DrawMatchesFlags::DEFAULT );
//-- Step 2: Calculate descriptors (feature vectors)
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: Matching descriptor vectors using FLANN matcher
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
//-- Quick calculation of max and min distances between keypoints
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{ double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
printf("-- Max dist : %f ", max_dist );
printf("-- Min dist : %f ", min_dist );
//-- Draw only "good" matches (i.e. whose distance is less than 2*min_dist,
//-- or a small arbitary value ( 0.02 ) in the event that min_dist is very
//-- small)
//-- PS.- radiusMatch can also be used here.
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{ if( matches[i].distance <= /*max(2*min_dist, 0.02)*/3*min_dist )
{ good_matches.push_back( matches[i]); }
}
//-- Draw only "good" matches
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2,
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
obj.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
scene.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
printf( "-- Good Match [%d] Keypoint 1: %d -- Keypoint 2: %d ", i, good_matches[i].queryIdx, good_matches[i].trainIdx );
}
//直接调用ransac
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//-- Get the corners from the image_1 ( the object to be "detected" )
std::vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0,0); obj_corners[1] = Point( img_1.cols, 0 );
obj_corners[2] = Point( img_1.cols, img_1.rows ); obj_corners[3] = Point( 0, img_1.rows );
std::vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);
perspectiveTransform( obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
//-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )
Point2f offset( (float)img_1.cols, 0);
line( img_matches, scene_corners[0] + offset, scene_corners[1] + offset, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[1] + offset, scene_corners[2] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[2] + offset, scene_corners[3] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[3] + offset, scene_corners[0] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow( "Good Matches & Object detection", img_matches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}

简化后和注释后的版本
// raw_surf.cpp : 本例是对opencv-2.48相关例子的实现
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//画出"good match"
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2,
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
obj.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
scene.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//-- Get the corners from the image_1 ( the object to be "detected" )
std::vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0,0);
obj_corners[1] = Point( img_1.cols, 0 );
obj_corners[2] = Point( img_1.cols, img_1.rows );
obj_corners[3] = Point( 0, img_1.rows );
std::vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);
perspectiveTransform( obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
//-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )
Point2f offset( (float)img_1.cols, 0);
line( img_matches, scene_corners[0] + offset, scene_corners[1] + offset, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[1] + offset, scene_corners[2] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[2] + offset, scene_corners[3] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[3] + offset, scene_corners[0] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow( "Good Matches & Object detection", img_matches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
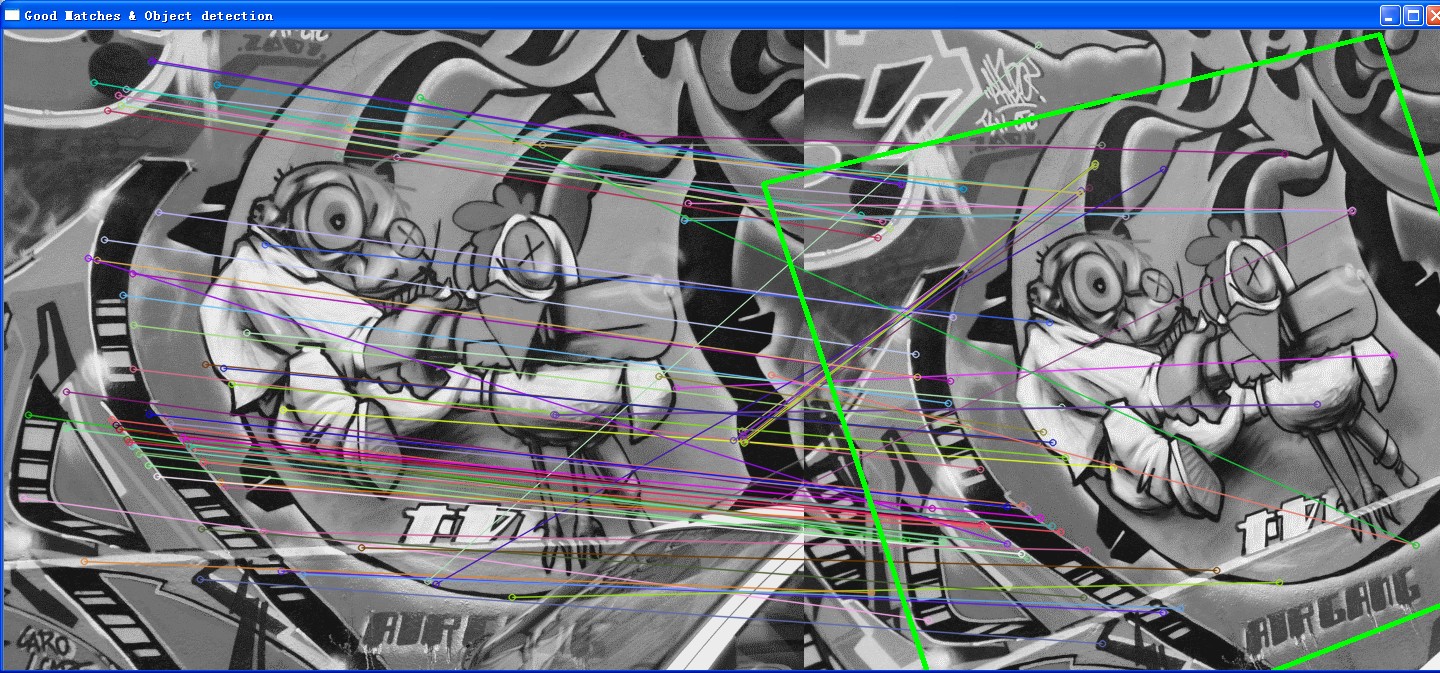

这里有两点需要注意,一个是除了FlannBasedMatcher之外,还有一种mathcer叫做BFMatcher,后者为强制匹配.
此外计算所谓GOODFEATURE的时候,采用了 3*min_dist的方法,我认为这里和论文中指出的“误差阈值设为3”是一致的,如果理解错误请指出,感谢!
同时测试了航拍图片和连铸图片,航拍图片是自然图片,特征丰富;
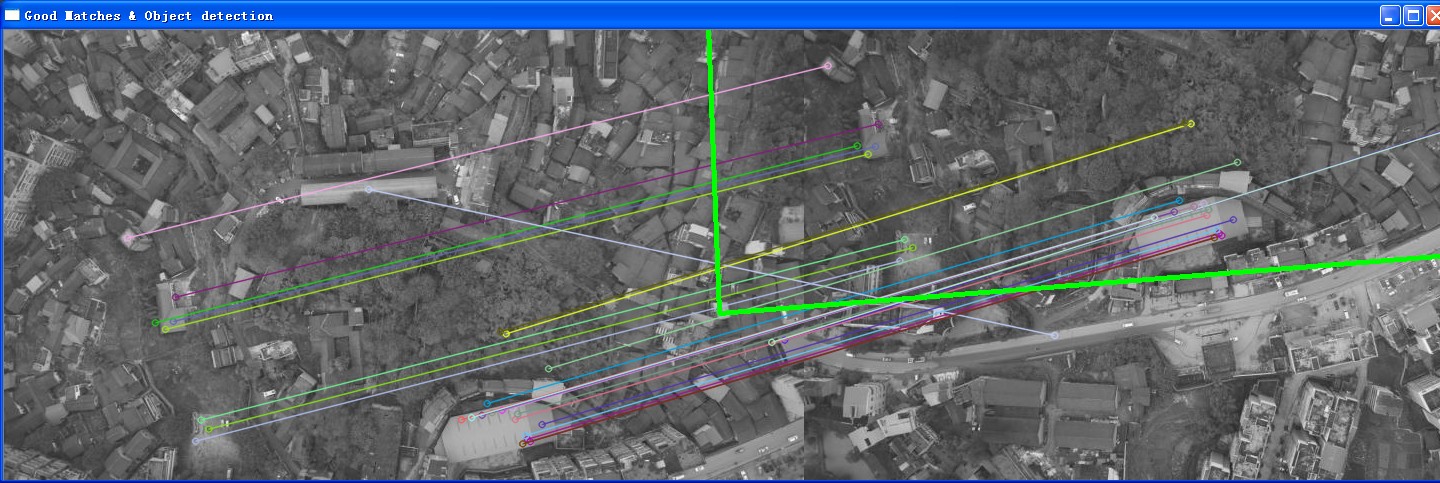
连铸图片由于表面干扰大于原始纹理,无法得到单应矩阵
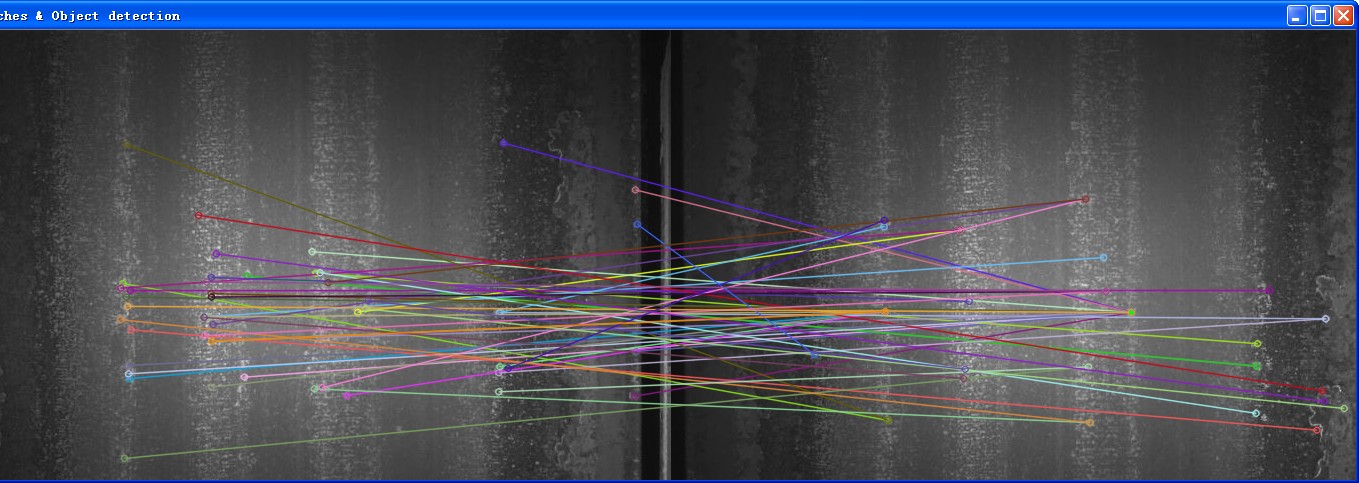
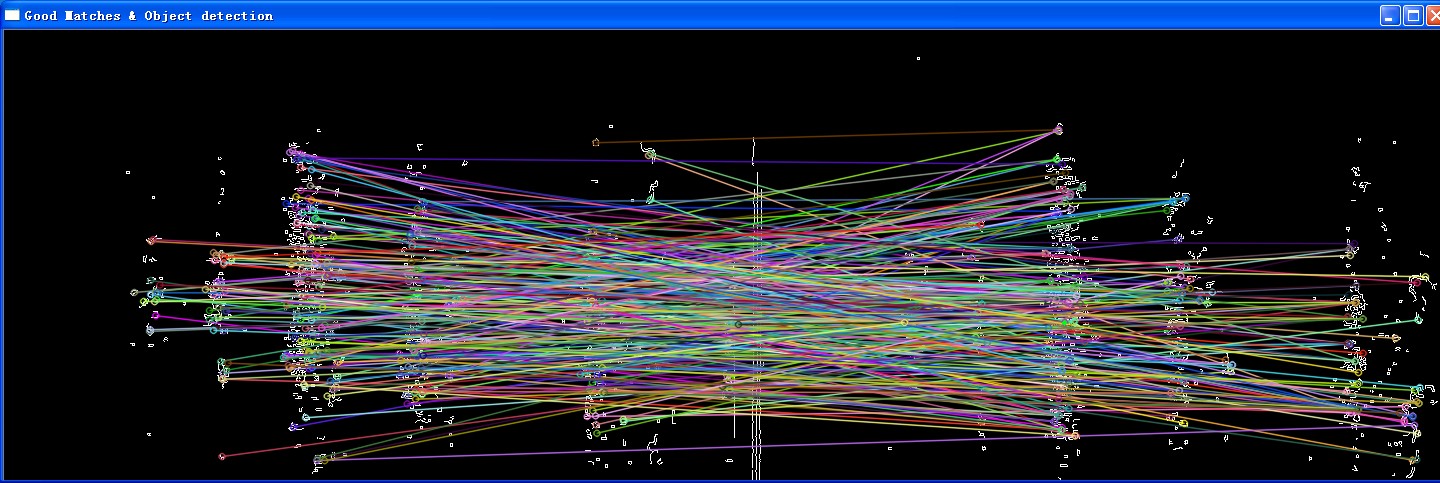
最后,添加计算RANSAC内点外点的相关代码,这里以3作为分界线
// raw_surf.cpp : 本例是对opencv-2.48相关例子的实现
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//获得两个pointf之间的距离
float fDistance(Point2f p1,Point2f p2)
{
float ftmp = (p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x) + (p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y);
ftmp = sqrt((float)ftmp);
return ftmp;
}
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
////添加于连铸图像
//img_1 = img_1(Rect(20,0,img_1.cols-40,img_1.rows));
//img_2 = img_2(Rect(20,0,img_1.cols-40,img_1.rows));
// cv::Canny(img_1,img_1,100,200);
// cv::Canny(img_2,img_2,100,200);
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//画出"good match"
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2,
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
obj.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
scene.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//-- Get the corners from the image_1 ( the object to be "detected" )
std::vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0,0);
obj_corners[1] = Point( img_1.cols, 0 );
obj_corners[2] = Point( img_1.cols, img_1.rows );
obj_corners[3] = Point( 0, img_1.rows );
std::vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);
perspectiveTransform( obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
//计算内点外点
std::vector<Point2f> scene_test(obj.size());
perspectiveTransform(obj,scene_test,H);
for (int i=0;i<scene_test.size();i++)
{
printf("%d is %f ",i+1,fDistance(scene[i],scene_test[i]));
}
//-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )
Point2f offset( (float)img_1.cols, 0);
line( img_matches, scene_corners[0] + offset, scene_corners[1] + offset, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[1] + offset, scene_corners[2] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[2] + offset, scene_corners[3] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[3] + offset, scene_corners[0] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow( "Good Matches & Object detection", img_matches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
//获得两个pointf之间的距离
float fDistance(Point2f p1,Point2f p2)
{
float ftmp = (p1.x-p2.x)*(p1.x-p2.x) + (p1.y-p2.y)*(p1.y-p2.y);
ftmp = sqrt((float)ftmp);
return ftmp;
}
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "img_opencv_1.png", 0 );
Mat img_2 = imread( "img_opencv_2.png", 0 );
////添加于连铸图像
//img_1 = img_1(Rect(20,0,img_1.cols-40,img_1.rows));
//img_2 = img_2(Rect(20,0,img_1.cols-40,img_1.rows));
// cv::Canny(img_1,img_1,100,200);
// cv::Canny(img_2,img_2,100,200);
if( !img_1.data || !img_2.data )
{ std::cout<< " --(!) Error reading images " << std::endl; return -1; }
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//画出"good match"
Mat img_matches;
drawMatches( img_1, keypoints_1, img_2, keypoints_2,
good_matches, img_matches, Scalar::all(-1), Scalar::all(-1),
vector<char>(), DrawMatchesFlags::NOT_DRAW_SINGLE_POINTS );
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
obj.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
scene.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//-- Get the corners from the image_1 ( the object to be "detected" )
std::vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4);
obj_corners[0] = Point(0,0);
obj_corners[1] = Point( img_1.cols, 0 );
obj_corners[2] = Point( img_1.cols, img_1.rows );
obj_corners[3] = Point( 0, img_1.rows );
std::vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4);
perspectiveTransform( obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
//计算内点外点
std::vector<Point2f> scene_test(obj.size());
perspectiveTransform(obj,scene_test,H);
for (int i=0;i<scene_test.size();i++)
{
printf("%d is %f ",i+1,fDistance(scene[i],scene_test[i]));
}
//-- Draw lines between the corners (the mapped object in the scene - image_2 )
Point2f offset( (float)img_1.cols, 0);
line( img_matches, scene_corners[0] + offset, scene_corners[1] + offset, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[1] + offset, scene_corners[2] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[2] + offset, scene_corners[3] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
line( img_matches, scene_corners[3] + offset, scene_corners[0] + offset, Scalar( 0, 255, 0), 4 );
//-- Show detected matches
imshow( "Good Matches & Object detection", img_matches );
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
结果显示
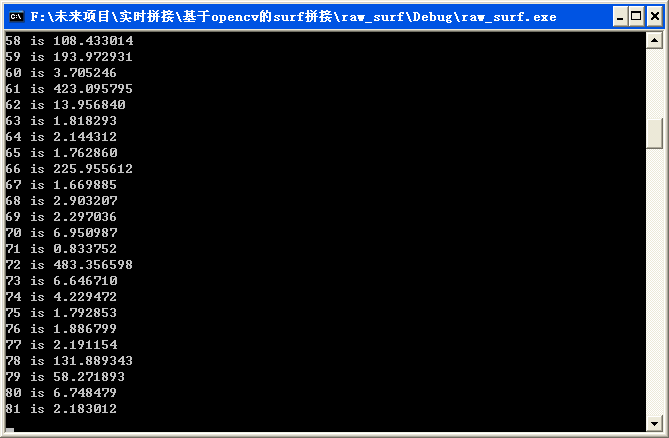
其中,有误差的点就很明显了。
小结一下,这里实现了使用opencv得到两幅图像之间的单应矩阵的方法。不是所有的图像都能够获得单应矩阵的,必须是两幅本身就有关系的图片才可以;而且最好是自然图像,像生产线上的这种图像,其拼接就需要采用其他方法。
二、拼接和融合
由于之前已经计算出了“单应矩阵”,所以这里直接利用这个矩阵就好。需要注意的一点是理清楚“帧”和拼接图像之间的关系。一般来说,我们采用的是“柱面坐标”或平面坐标。书中采用的是若干图像在水平方向上基本上是一字排开,是平面坐标。那么,如果按照文中的“帧到拼接图像”的方法,我们认为图像拼接的顺序就是由左到右,一幅一幅地计算误差,而后进行叠加。
为了方便说明算法,采用了《学习opencv》中提供的教堂图像
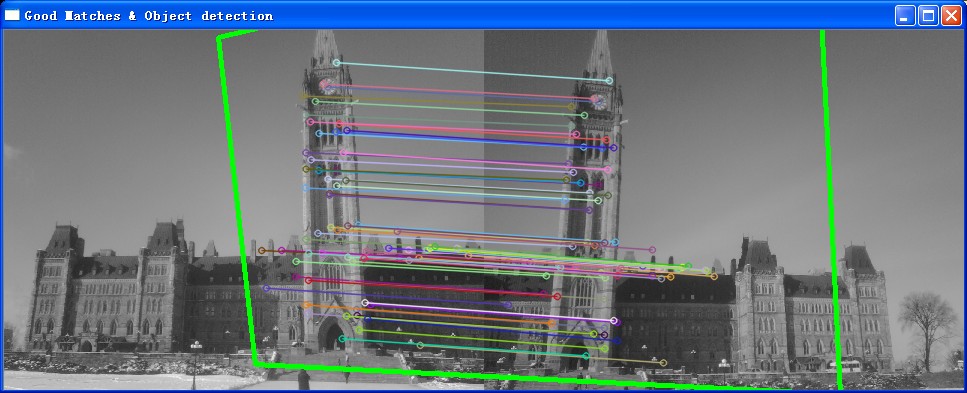

其结果就是经过surf匹配,而将右边的图像形变成为适合叠加的状态。
基于此,进行图像对准
// raw_surf.cpp : 本例是对opencv-2.48相关例子的实现
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 ;
Mat img_2 ;
Mat img_raw_1 = imread("c1.bmp");
Mat img_raw_2 = imread("c3.bmp");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
Mat result;
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(2*img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
Mat half(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half);
imshow("result",result);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 ;
Mat img_2 ;
Mat img_raw_1 = imread("c1.bmp");
Mat img_raw_2 = imread("c3.bmp");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
Mat result;
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(2*img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
Mat half(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half);
imshow("result",result);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}

依据论文中提到的3种方法进行融合
// raw_surf.cpp : 本例是对opencv-2.48相关例子的实现
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 ;
Mat img_2 ;
Mat img_raw_1 = imread("c1.bmp");
Mat img_raw_2 = imread("c3.bmp");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
Mat result;
Mat resultback; //保存的是新帧经过单应矩阵变换以后的图像
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(2*img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
result.copyTo(resultback);
Mat half(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half);
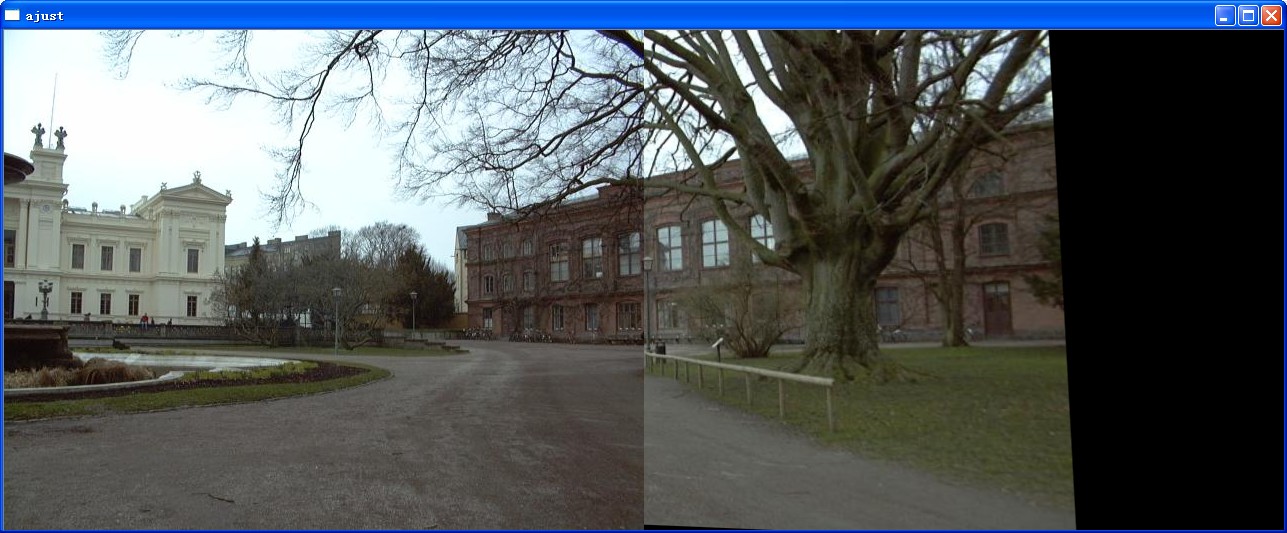
imshow("ajust",result);
//渐入渐出融合
Mat result_linerblend = result.clone();
double dblend = 0.0;
int ioffset =img_2.cols-100;
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++)
{
result_linerblend.col(ioffset+i) = result.col(ioffset+i)*(1-dblend) + resultback.col(ioffset+i)*dblend;
dblend = dblend +0.01;
}
imshow("result_linerblend",result_linerblend);
//最大值法融合
Mat result_maxvalue = result.clone();
for (int i = 0;i<img_2.rows;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<100;j++)
{
int iresult= result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int iresultback = resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
if (iresultback >iresult)
{
result_maxvalue.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
}
}
imshow("result_maxvalue",result_maxvalue);
//带阈值的加权平滑处理
Mat result_advance = result.clone();
for (int i = 0;i<img_2.rows;i++)
{
for (int j = 0;j<33;j++)
{
int iimg1= result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
//int iimg2= resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int ilinerblend = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
if (abs(iimg1 - ilinerblend)<3)
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0;i<img_2.rows;i++)
{
for (int j = 33;j<66;j++)
{
int iimg1= result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int iimg2= resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int ilinerblend = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
if (abs(max(iimg1,iimg2) - ilinerblend)<3)
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
else if (iimg2>iimg1)
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0;i<img_2.rows;i++)
{
for (int j = 66;j<100;j++)
{
//int iimg1= result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int iimg2= resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int ilinerblend = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
if (abs(iimg2 - ilinerblend)<3)
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
else
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
}
}
imshow("result_advance",result_advance);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 ;
Mat img_2 ;
Mat img_raw_1 = imread("c1.bmp");
Mat img_raw_2 = imread("c3.bmp");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
Mat result;
Mat resultback; //保存的是新帧经过单应矩阵变换以后的图像
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(2*img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
result.copyTo(resultback);
Mat half(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half);
imshow("ajust",result);
//渐入渐出融合
Mat result_linerblend = result.clone();
double dblend = 0.0;
int ioffset =img_2.cols-100;
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++)
{
result_linerblend.col(ioffset+i) = result.col(ioffset+i)*(1-dblend) + resultback.col(ioffset+i)*dblend;
dblend = dblend +0.01;
}
imshow("result_linerblend",result_linerblend);
//最大值法融合
Mat result_maxvalue = result.clone();
for (int i = 0;i<img_2.rows;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<100;j++)
{
int iresult= result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int iresultback = resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
if (iresultback >iresult)
{
result_maxvalue.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
}
}
imshow("result_maxvalue",result_maxvalue);
//带阈值的加权平滑处理
Mat result_advance = result.clone();
for (int i = 0;i<img_2.rows;i++)
{
for (int j = 0;j<33;j++)
{
int iimg1= result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
//int iimg2= resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int ilinerblend = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
if (abs(iimg1 - ilinerblend)<3)
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0;i<img_2.rows;i++)
{
for (int j = 33;j<66;j++)
{
int iimg1= result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int iimg2= resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int ilinerblend = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
if (abs(max(iimg1,iimg2) - ilinerblend)<3)
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
else if (iimg2>iimg1)
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0;i<img_2.rows;i++)
{
for (int j = 66;j<100;j++)
{
//int iimg1= result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int iimg2= resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
int ilinerblend = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[0]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[1]+ result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j)[2];
if (abs(iimg2 - ilinerblend)<3)
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = result_linerblend.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
else
{
result_advance.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j) = resultback.at<Vec3b>(i,ioffset+j);
}
}
}
imshow("result_advance",result_advance);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}




目前看来,maxvalue是最好的融合方法,但是和论文中提到的一样,此类图片不能很好地体现融合算法的特点,为此我也拍摄了和论文中类似的图片。发现想拍摄质量较好的图片,还是需要一定的硬件和技巧的。因此,软件和硬件,在使用的过程中应该结合起来。
此外,使用文中图片,效果如下
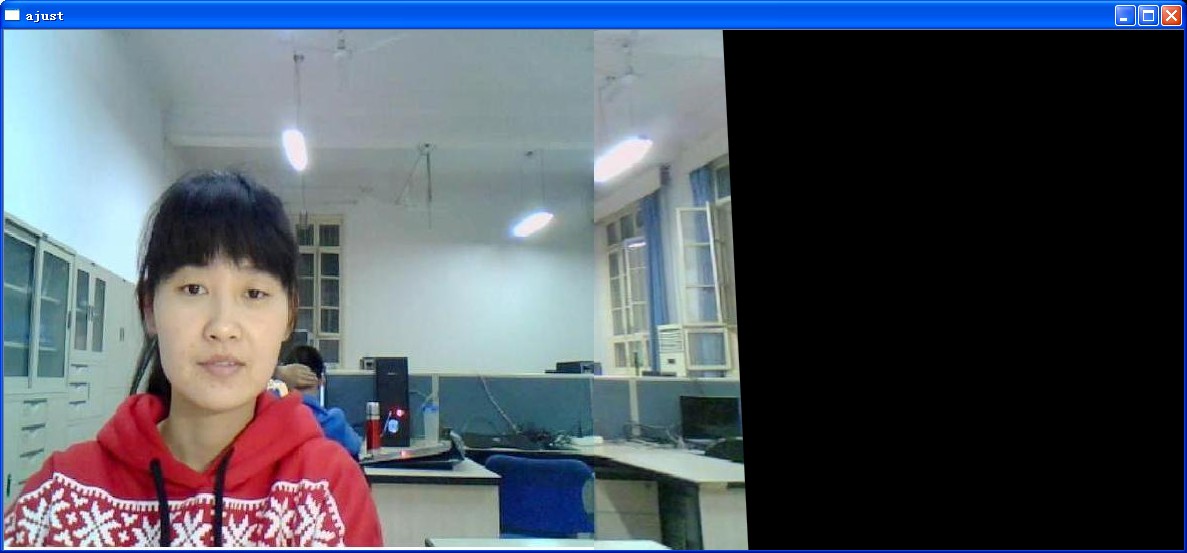
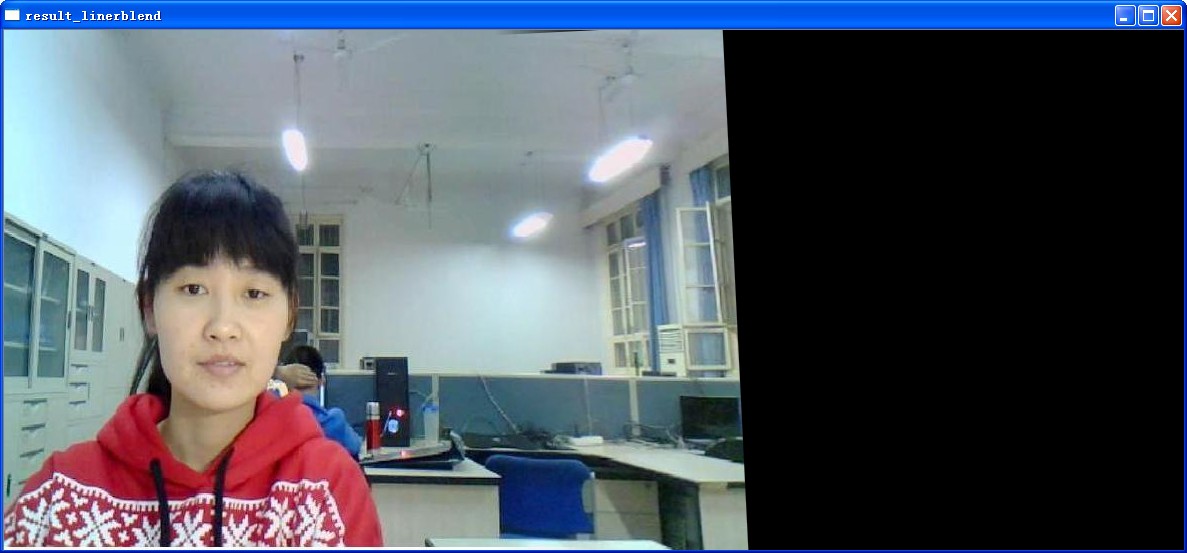

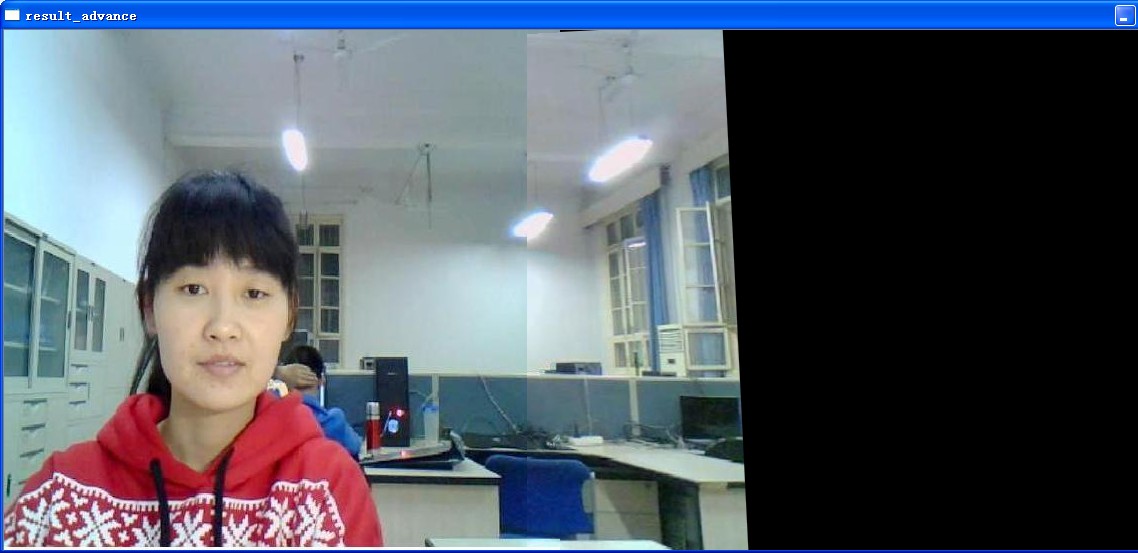
换一组图片,可以发现不同的结果
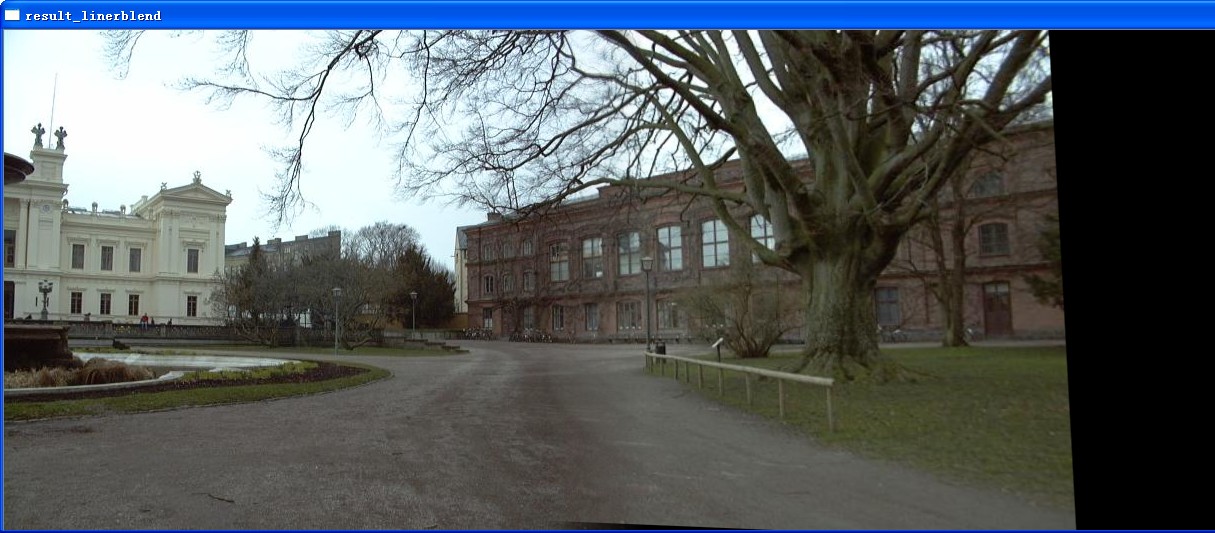
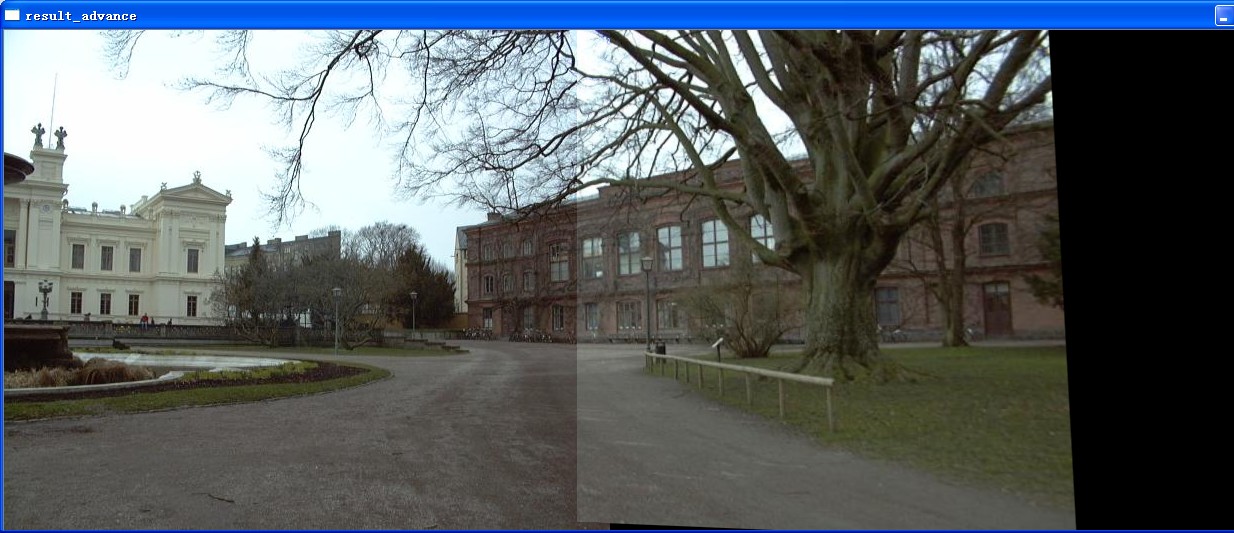




相比较而言,还是linerblend能够保持不错的质量,而具体到底采取哪种拼接的方式,必须根据实际情况来选择。
三、多图连续融合拼接
前面处理的是2图的例子,至少将这种情况推广到3图,这样才能够得到统一处理的经验。
连续图像处理,不仅仅是在已经处理好的图像上面再添加一幅图,其中比较关键的一点就是如何来处理已经拼接好的图像。
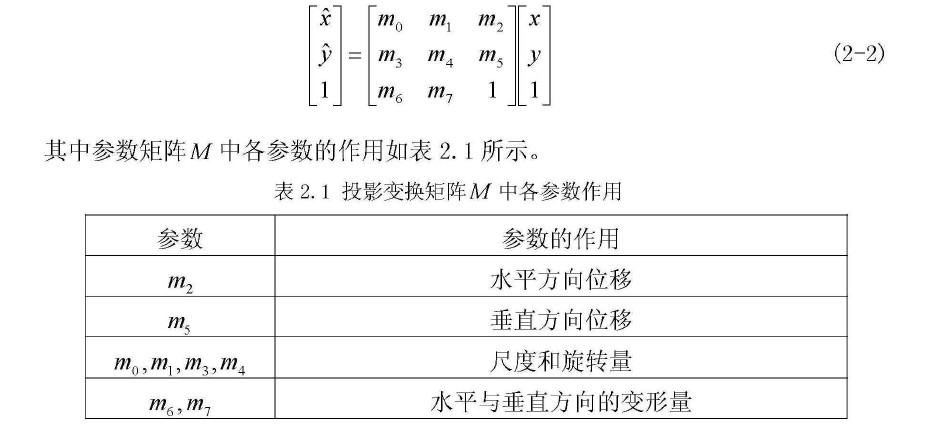
那么,m2也就是H.at<char>(0,2)就是水平位移。但是在实际使用中,始终无法正确取得这个值
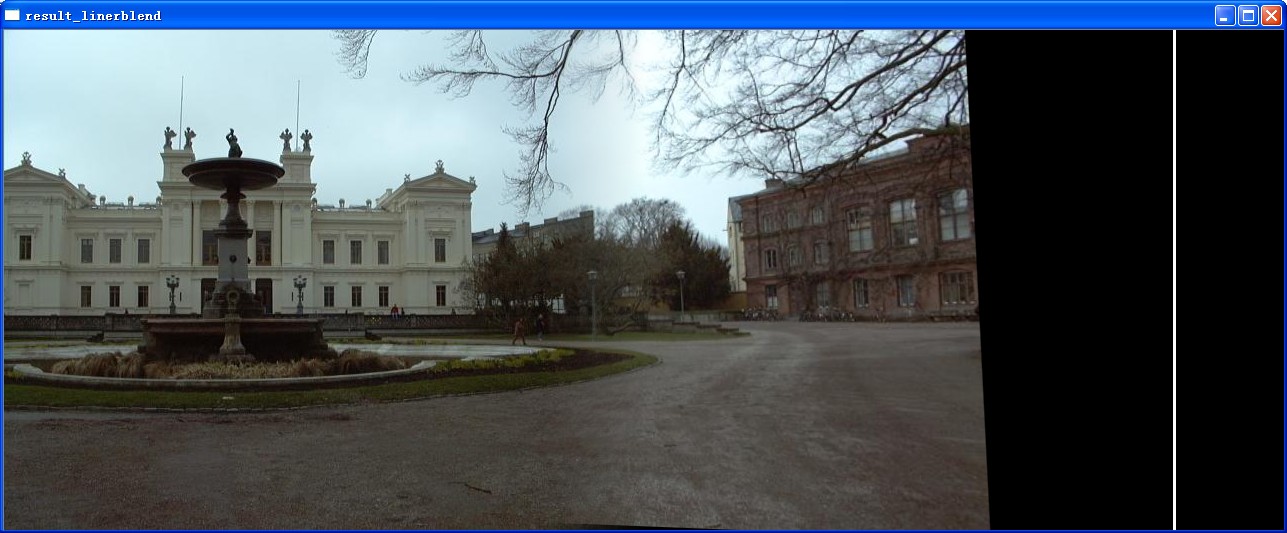

Mat outImage =H.clone();
uchar* outData=outImage.ptr<uchar>(0);
int itemp = outData[2]; //获得偏移
line(result_linerblend,Point(result_linerblend.cols-itemp,0),Point(result_linerblend.cols-itemp,img_2.rows),Scalar(255,255,255),2);
imshow("result_linerblend",result_linerblend);
uchar* outData=outImage.ptr<uchar>(0);
int itemp = outData[2]; //获得偏移
line(result_linerblend,Point(result_linerblend.cols-itemp,0),Point(result_linerblend.cols-itemp,img_2.rows),Scalar(255,255,255),2);
imshow("result_linerblend",result_linerblend);
只好采取编写专门代码的方法进行处理
//获取已经处理图像的边界
Mat matmask = result_linerblend.clone();
int idaterow0 = 0;int idaterowend = 0;//标识了最上面和最小面第一个不为0的树,这里采用的是宽度减去的算法
for(int j=matmask.cols-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (matmask.at<Vec3b>(0,j)[0]>0)
{
idaterow0 = j;
break;
}
}
for(int j=matmask.cols-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (matmask.at<Vec3b>(matmask.rows-1,j)[0]>0)
{
idaterowend = j;
break;
}
}
line(matmask,Point(min(idaterow0,idaterowend),0),Point(min(idaterow0,idaterowend),img_2.rows),Scalar(255,255,255),2);
imshow("result_linerblend",matmask);
Mat matmask = result_linerblend.clone();
int idaterow0 = 0;int idaterowend = 0;//标识了最上面和最小面第一个不为0的树,这里采用的是宽度减去的算法
for(int j=matmask.cols-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (matmask.at<Vec3b>(0,j)[0]>0)
{
idaterow0 = j;
break;
}
}
for(int j=matmask.cols-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (matmask.at<Vec3b>(matmask.rows-1,j)[0]>0)
{
idaterowend = j;
break;
}
}
line(matmask,Point(min(idaterow0,idaterowend),0),Point(min(idaterow0,idaterowend),img_2.rows),Scalar(255,255,255),2);
imshow("result_linerblend",matmask);
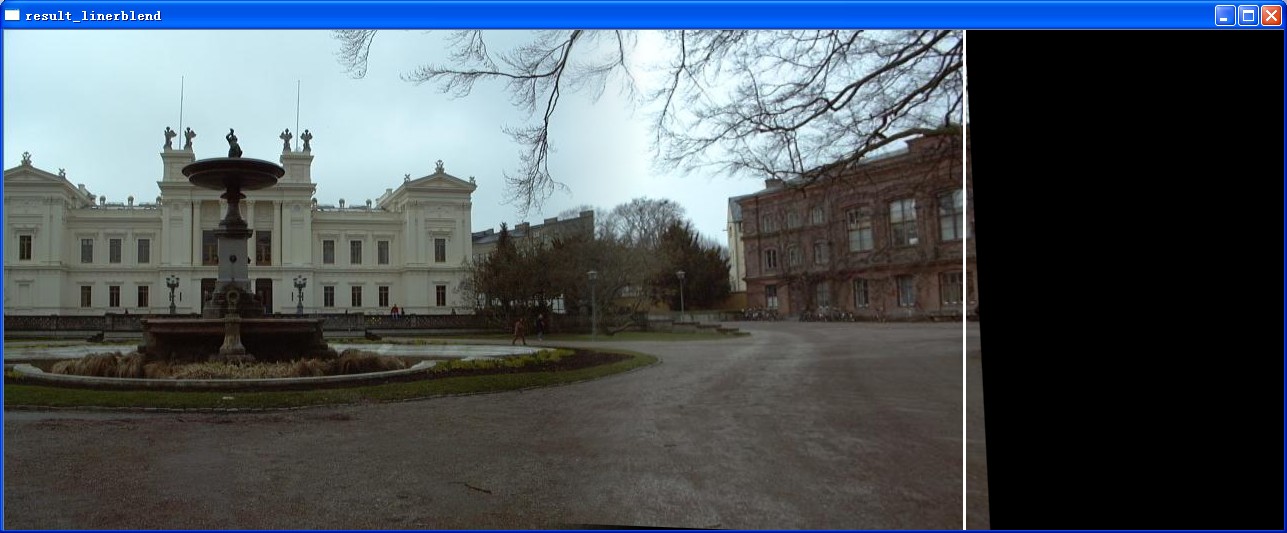

效果良好稳定.目前的实现是将白线以左的区域切割下来进行拼接。
基于此,编写3图拼接,效果如下。目前的图像质量,在差值上面可能还需要增强,下一步处理
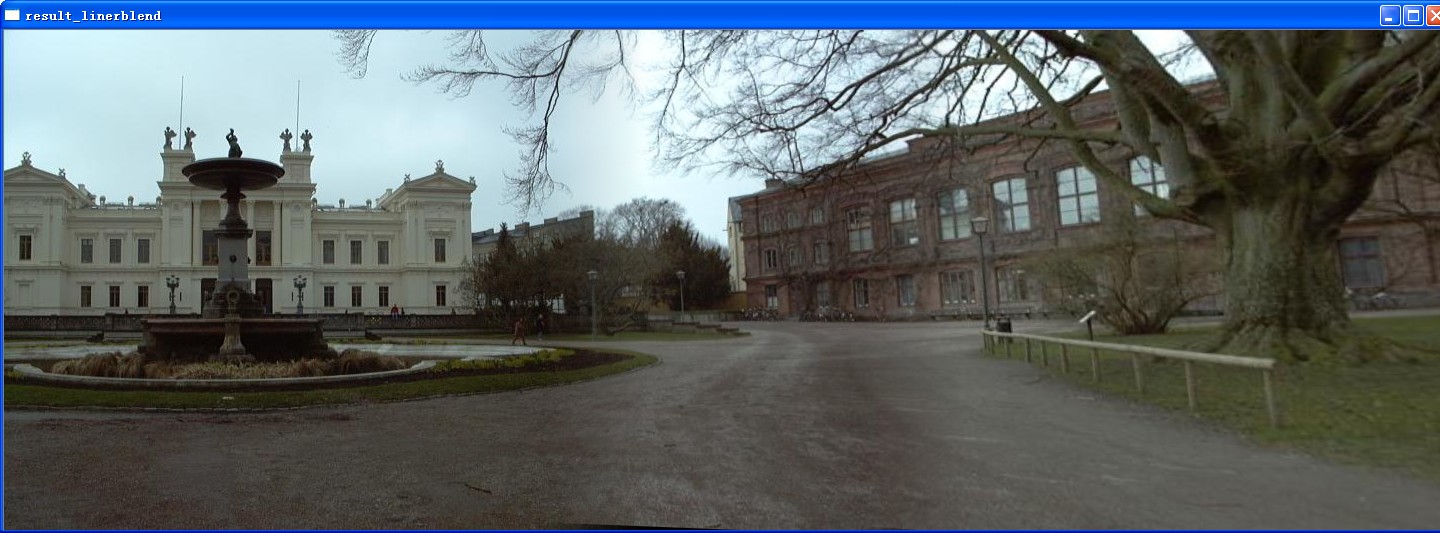

// blend_series.cpp : 多图拼接
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 ;
Mat img_2 ;
Mat img_raw_1 = imread("Univ3.jpg");
Mat img_raw_2 = imread("Univ2.jpg");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
Mat result;
Mat resultback; //保存的是新帧经过单应矩阵变换以后的图像
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(2*img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
result.copyTo(resultback);
Mat half(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half);
//imshow("ajust",result);
//渐入渐出融合
Mat result_linerblend = result.clone();
double dblend = 0.0;
int ioffset =img_2.cols-100;
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++)
{
result_linerblend.col(ioffset+i) = result.col(ioffset+i)*(1-dblend) + resultback.col(ioffset+i)*dblend;
dblend = dblend +0.01;
}
//获取已经处理图像的边界
Mat matmask = result_linerblend.clone();
int idaterow0 = 0;int idaterowend = 0;//标识了最上面和最小面第一个不为0的树,这里采用的是宽度减去的算法
for(int j=matmask.cols-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (matmask.at<Vec3b>(0,j)[0]>0)
{
idaterow0 = j;
break;
}
}
for(int j=matmask.cols-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (matmask.at<Vec3b>(matmask.rows-1,j)[0]>0)
{
idaterowend = j;
break;
}
}
line(matmask,Point(min(idaterow0,idaterowend),0),Point(min(idaterow0,idaterowend),img_2.rows),Scalar(255,255,255),2);
imshow("result_linerblend",matmask);
/////////////////---------------对结果图像继续处理---------------------------------/////////////////
img_raw_1 = result_linerblend(Rect(0,0,min(idaterow0,idaterowend),img_2.rows));
img_raw_2 = imread("Univ1.jpg");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
////-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
//
SurfFeatureDetector detector2( minHessian );
keypoints_1.clear();
keypoints_2.clear();
detector2.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector2.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor2;
extractor2.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor2.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher2;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
matcher2.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
max_dist = 0; min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
good_matches.clear();
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
obj.clear();
scene.clear();
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(img_1.cols+img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
result.copyTo(resultback);
Mat half2(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_1.cols,img_1.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half2);
imshow("ajust",result);
//渐入渐出融合
result_linerblend = result.clone();
dblend = 0.0;
ioffset =img_1.cols-100;
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++)
{
result_linerblend.col(ioffset+i) = result.col(ioffset+i)*(1-dblend) + resultback.col(ioffset+i)*dblend;
dblend = dblend +0.01;
}
imshow("result_linerblend",result_linerblend);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 ;
Mat img_2 ;
Mat img_raw_1 = imread("Univ3.jpg");
Mat img_raw_2 = imread("Univ2.jpg");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
//-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
int minHessian = 400;
SurfFeatureDetector detector( minHessian );
std::vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_1, keypoints_2;
detector.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor;
Mat descriptors_1, descriptors_2;
extractor.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
std::vector< DMatch > matches;
matcher.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
double max_dist = 0; double min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
std::vector< DMatch > good_matches;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
std::vector<Point2f> obj;
std::vector<Point2f> scene;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
Mat H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
Mat result;
Mat resultback; //保存的是新帧经过单应矩阵变换以后的图像
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(2*img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
result.copyTo(resultback);
Mat half(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half);
//imshow("ajust",result);
//渐入渐出融合
Mat result_linerblend = result.clone();
double dblend = 0.0;
int ioffset =img_2.cols-100;
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++)
{
result_linerblend.col(ioffset+i) = result.col(ioffset+i)*(1-dblend) + resultback.col(ioffset+i)*dblend;
dblend = dblend +0.01;
}
//获取已经处理图像的边界
Mat matmask = result_linerblend.clone();
int idaterow0 = 0;int idaterowend = 0;//标识了最上面和最小面第一个不为0的树,这里采用的是宽度减去的算法
for(int j=matmask.cols-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (matmask.at<Vec3b>(0,j)[0]>0)
{
idaterow0 = j;
break;
}
}
for(int j=matmask.cols-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (matmask.at<Vec3b>(matmask.rows-1,j)[0]>0)
{
idaterowend = j;
break;
}
}
line(matmask,Point(min(idaterow0,idaterowend),0),Point(min(idaterow0,idaterowend),img_2.rows),Scalar(255,255,255),2);
imshow("result_linerblend",matmask);
/////////////////---------------对结果图像继续处理---------------------------------/////////////////
img_raw_1 = result_linerblend(Rect(0,0,min(idaterow0,idaterowend),img_2.rows));
img_raw_2 = imread("Univ1.jpg");
cvtColor(img_raw_1,img_1,CV_BGR2GRAY);
cvtColor(img_raw_2,img_2,CV_BGR2GRAY);
////-- Step 1: 使用SURF识别出特征点
//
SurfFeatureDetector detector2( minHessian );
keypoints_1.clear();
keypoints_2.clear();
detector2.detect( img_1, keypoints_1 );
detector2.detect( img_2, keypoints_2 );
//-- Step 2: 描述SURF特征
SurfDescriptorExtractor extractor2;
extractor2.compute( img_1, keypoints_1, descriptors_1 );
extractor2.compute( img_2, keypoints_2, descriptors_2 );
//-- Step 3: 匹配
FlannBasedMatcher matcher2;//BFMatcher为强制匹配
matcher2.match( descriptors_1, descriptors_2, matches );
//取最大最小距离
max_dist = 0; min_dist = 100;
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
double dist = matches[i].distance;
if( dist < min_dist ) min_dist = dist;
if( dist > max_dist ) max_dist = dist;
}
good_matches.clear();
for( int i = 0; i < descriptors_1.rows; i++ )
{
if( matches[i].distance <= 3*min_dist )//这里的阈值选择了3倍的min_dist
{
good_matches.push_back( matches[i]);
}
}
//-- Localize the object from img_1 in img_2
obj.clear();
scene.clear();
for( int i = 0; i < (int)good_matches.size(); i++ )
{
//这里采用“帧向拼接图像中添加的方法”,因此左边的是scene,右边的是obj
scene.push_back( keypoints_1[ good_matches[i].queryIdx ].pt );
obj.push_back( keypoints_2[ good_matches[i].trainIdx ].pt );
}
//直接调用ransac,计算单应矩阵
H = findHomography( obj, scene, CV_RANSAC );
//图像对准
warpPerspective(img_raw_2,result,H,Size(img_1.cols+img_2.cols,img_2.rows));
result.copyTo(resultback);
Mat half2(result,cv::Rect(0,0,img_1.cols,img_1.rows));
img_raw_1.copyTo(half2);
imshow("ajust",result);
//渐入渐出融合
result_linerblend = result.clone();
dblend = 0.0;
ioffset =img_1.cols-100;
for (int i = 0;i<100;i++)
{
result_linerblend.col(ioffset+i) = result.col(ioffset+i)*(1-dblend) + resultback.col(ioffset+i)*dblend;
dblend = dblend +0.01;
}
imshow("result_linerblend",result_linerblend);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
复制粘贴,实现5图拼接。这个时候发现,3图往往是一个极限值(这也可能就是为什么opencv里面的例子提供的是3图),当第四图出现的时候,其单应效果非常差
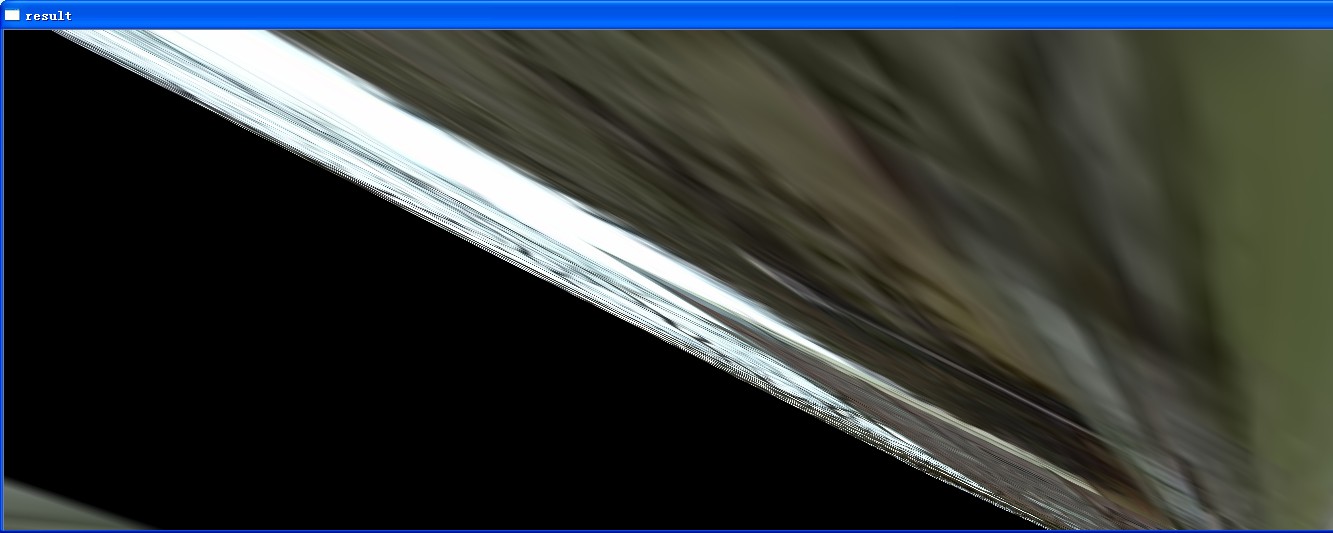
为什么会出现这种情况,反思后认识到,论文中采用的是平面坐标,也就是所有的图片都是基本位于一个平面上的,这一点特别通过她后面的那个罗技摄像头的部署能够看出来。但是在现实中,更常见的情况是人站在中间,360度地拍摄,这个时候需要采用柱面坐标系,也就是一开始对于图像要进行相关处理,也就是所谓的柱状投影。

可以得到这样的效果,这个效果是否正确还有待商榷,但是基于此的确可以更进一步地做东西了。
// column_transoform.cpp : 桶装投影
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
#define PI 3.14159
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "Univ1.jpg");
Mat img_result = img_1.clone();
for(int i=0;i<img_result.rows;i++)
{ for(int j=0;j<img_result.cols;j++)
{
img_result.at<Vec3b>(i,j)=0;
}
}
int W = img_1.cols;
int H = img_1.rows;
float r = W/(2*tan(PI/6));
float k = 0;
float fx=0;
float fy=0;
for(int i=0;i<img_1.rows;i++)
{ for(int j=0;j<img_1.cols;j++)
{
k = sqrt((float)(r*r+(W/2-j)*(W/2-j)));
fx = r*sin(PI/6)+r*sin(atan((j -W/2 )/r));
fy = H/2 +r*(i-H/2)/k;
int ix = (int)fx;
int iy = (int)fy;
if (ix<W&&ix>=0&&iy<H&&iy>=0)
{
img_result.at<Vec3b>(iy,ix)= img_1.at<Vec3b>(i,j);
}
}
}
imshow( "桶状投影", img_1 );
imshow("img_result",img_result);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/nonfree/features2d.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
#define PI 3.14159
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
Mat img_1 = imread( "Univ1.jpg");
Mat img_result = img_1.clone();
for(int i=0;i<img_result.rows;i++)
{ for(int j=0;j<img_result.cols;j++)
{
img_result.at<Vec3b>(i,j)=0;
}
}
int W = img_1.cols;
int H = img_1.rows;
float r = W/(2*tan(PI/6));
float k = 0;
float fx=0;
float fy=0;
for(int i=0;i<img_1.rows;i++)
{ for(int j=0;j<img_1.cols;j++)
{
k = sqrt((float)(r*r+(W/2-j)*(W/2-j)));
fx = r*sin(PI/6)+r*sin(atan((j -W/2 )/r));
fy = H/2 +r*(i-H/2)/k;
int ix = (int)fx;
int iy = (int)fy;
if (ix<W&&ix>=0&&iy<H&&iy>=0)
{
img_result.at<Vec3b>(iy,ix)= img_1.at<Vec3b>(i,j);
}
}
}
imshow( "桶状投影", img_1 );
imshow("img_result",img_result);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
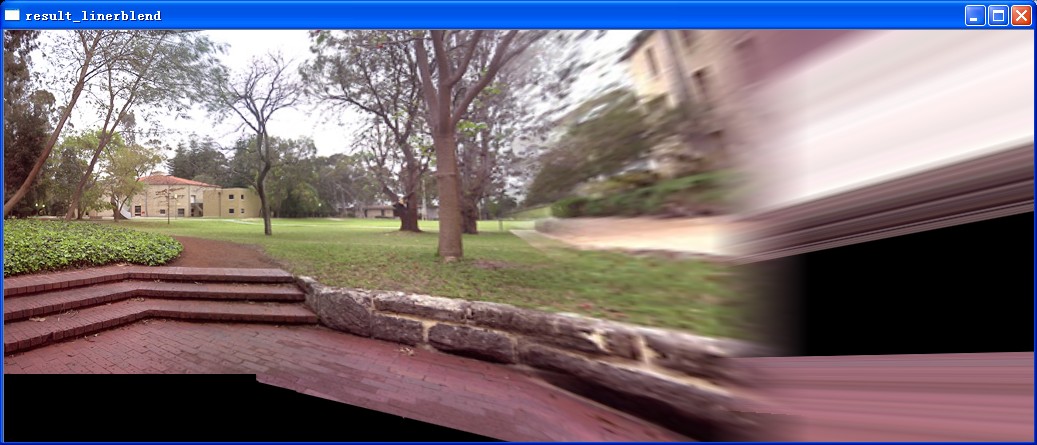

效果依然是不佳,看来在这个地方,不仅仅是做一个桶形变换那么简单,一定有定量的参数在里面,也可能是我的变换写错了。这个下一步研究。
【未完待续】