CRI - Container Runtime Interface(容器运行时接口)
CRI中定义了容器和镜像的服务的接口,因为容器运行时与镜像的生命周期是彼此隔离的,因此需要定义两个服务。该接口使用Protocol Buffer,基于gRPC,在Kubernetes v1.10+版本中是在pkg/kubelet/apis/cri/runtime/v1alpha2的api.proto中定义的。
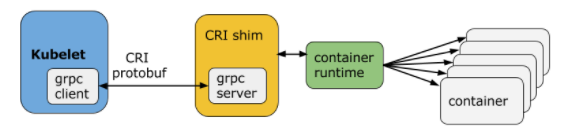
CRI架构
Container Runtime实现了CRI gRPC Server,包括RuntimeService和ImageService。该gRPC Server需要监听本地的Unix socket,而kubelet则作为gRPC Client运行。
启用CRI
除非集成了rktnetes,否则CRI都是被默认启用了,从Kubernetes1.7版本开始,旧的预集成的docker CRI已经被移除。
要想启用CRI只需要在kubelet的启动参数重传入此参数:--container-runtime-endpoint远程运行时服务的端点。当前Linux上支持unix socket,windows上支持tcp。例如:unix:///var/run/dockershim.sock、 tcp://localhost:373,默认是unix:///var/run/dockershim.sock,即默认使用本地的docker作为容器运行时。
CRI接口
Kubernetes 1.9中的CRI接口在api.proto中的定义如下:
// Runtime service defines the public APIs for remote container runtimes
service RuntimeService {
// Version returns the runtime name, runtime version, and runtime API version.
rpc Version(VersionRequest) returns (VersionResponse) {}
// RunPodSandbox creates and starts a pod-level sandbox. Runtimes must ensure
// the sandbox is in the ready state on success.
rpc RunPodSandbox(RunPodSandboxRequest) returns (RunPodSandboxResponse) {}
// StopPodSandbox stops any running process that is part of the sandbox and
// reclaims network resources (e.g., IP addresses) allocated to the sandbox.
// If there are any running containers in the sandbox, they must be forcibly
// terminated.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if all relevant
// resources have already been reclaimed. kubelet will call StopPodSandbox
// at least once before calling RemovePodSandbox. It will also attempt to
// reclaim resources eagerly, as soon as a sandbox is not needed. Hence,
// multiple StopPodSandbox calls are expected.
rpc StopPodSandbox(StopPodSandboxRequest) returns (StopPodSandboxResponse) {}
// RemovePodSandbox removes the sandbox. If there are any running containers
// in the sandbox, they must be forcibly terminated and removed.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the sandbox has
// already been removed.
rpc RemovePodSandbox(RemovePodSandboxRequest) returns (RemovePodSandboxResponse) {}
// PodSandboxStatus returns the status of the PodSandbox. If the PodSandbox is not
// present, returns an error.
rpc PodSandboxStatus(PodSandboxStatusRequest) returns (PodSandboxStatusResponse) {}
// ListPodSandbox returns a list of PodSandboxes.
rpc ListPodSandbox(ListPodSandboxRequest) returns (ListPodSandboxResponse) {}
// CreateContainer creates a new container in specified PodSandbox
rpc CreateContainer(CreateContainerRequest) returns (CreateContainerResponse) {}
// StartContainer starts the container.
rpc StartContainer(StartContainerRequest) returns (StartContainerResponse) {}
// StopContainer stops a running container with a grace period (i.e., timeout).
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the container has
// already been stopped.
// TODO: what must the runtime do after the grace period is reached?
rpc StopContainer(StopContainerRequest) returns (StopContainerResponse) {}
// RemoveContainer removes the container. If the container is running, the
// container must be forcibly removed.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the container has
// already been removed.
rpc RemoveContainer(RemoveContainerRequest) returns (RemoveContainerResponse) {}
// ListContainers lists all containers by filters.
rpc ListContainers(ListContainersRequest) returns (ListContainersResponse) {}
// ContainerStatus returns status of the container. If the container is not
// present, returns an error.
rpc ContainerStatus(ContainerStatusRequest) returns (ContainerStatusResponse) {}
// UpdateContainerResources updates ContainerConfig of the container.
rpc UpdateContainerResources(UpdateContainerResourcesRequest) returns (UpdateContainerResourcesResponse) {}
// ExecSync runs a command in a container synchronously.
rpc ExecSync(ExecSyncRequest) returns (ExecSyncResponse) {}
// Exec prepares a streaming endpoint to execute a command in the container.
rpc Exec(ExecRequest) returns (ExecResponse) {}
// Attach prepares a streaming endpoint to attach to a running container.
rpc Attach(AttachRequest) returns (AttachResponse) {}
// PortForward prepares a streaming endpoint to forward ports from a PodSandbox.
rpc PortForward(PortForwardRequest) returns (PortForwardResponse) {}
// ContainerStats returns stats of the container. If the container does not
// exist, the call returns an error.
rpc ContainerStats(ContainerStatsRequest) returns (ContainerStatsResponse) {}
// ListContainerStats returns stats of all running containers.
rpc ListContainerStats(ListContainerStatsRequest) returns (ListContainerStatsResponse) {}
// UpdateRuntimeConfig updates the runtime configuration based on the given request.
rpc UpdateRuntimeConfig(UpdateRuntimeConfigRequest) returns (UpdateRuntimeConfigResponse) {}
// Status returns the status of the runtime.
rpc Status(StatusRequest) returns (StatusResponse) {}
}
// ImageService defines the public APIs for managing images.
service ImageService {
// ListImages lists existing images.
rpc ListImages(ListImagesRequest) returns (ListImagesResponse) {}
// ImageStatus returns the status of the image. If the image is not
// present, returns a response with ImageStatusResponse.Image set to
// nil.
rpc ImageStatus(ImageStatusRequest) returns (ImageStatusResponse) {}
// PullImage pulls an image with authentication config.
rpc PullImage(PullImageRequest) returns (PullImageResponse) {}
// RemoveImage removes the image.
// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the image has
// already been removed.
rpc RemoveImage(RemoveImageRequest) returns (RemoveImageResponse) {}
// ImageFSInfo returns information of the filesystem that is used to store images.
rpc ImageFsInfo(ImageFsInfoRequest) returns (ImageFsInfoResponse) {}
}
这其中包含了两个gRPC服务:- RuntimeService:容器和Sandbox运行时管理。
- ImageService:提供了从镜像仓库拉取、查看、和移除镜像的RPC。
当前支持的CRI后端
我们最初在使用Kubernetes时通常会默认使用Docker作为容器运行时,其实从Kubernetes 1.5开始已经开始支持CRI,目前是处于Alpha版本,通过CRI接口可以指定使用其它容器运行时作为Pod的后端,目前支持 CRI 的后端有:
- cri-o:cri-o是Kubernetes的CRI标准的实现,并且允许Kubernetes间接使用OCI兼容的容器运行时,可以把cri-o看成Kubernetes使用OCI兼容的容器运行时的中间层。
- cri-containerd:基于Containerd的Kubernetes CRI 实现
- rkt:由CoreOS主推的用来跟docker抗衡的容器运行时
- frakti:基于hypervisor的CRI
- docker:kuberentes最初就开始支持的容器运行时,目前还没完全从kubelet中解耦,docker公司同时推广了OCI标准
CRI是由SIG-Node来维护的。
当前通过CRI-O间接支持CRI的后端
当前同样存在一些只实现了OCI标准的容器,但是它们可以通过CRI-O来作为Kubernetes的容器运行时。CRI-O是Kubernetes的CRI标准的实现,并且允许Kubernetes间接使用OCI兼容的容器运行时。
- Clear Containers:由Intel推出的兼容OCI容器运行时,可以通过CRI-O来兼容CRI。
- Kata Containers:符合OCI规范,可以通过CRI-O或Containerd CRI Plugin来兼容CRI。。
- gVisor:由谷歌推出的容器运行时沙箱(Experimental),可以通过CRI-O来兼容CRI。