1.投影模型和BA代价函数

这个流程就是观测方程
之前抽象的记为: (z = h(x, y))
现在给出具体的参数话过程,x指此时相机的位姿R,t,它对应的李代数为(xi)。路标y即为这里的三维点p,而观测数据则是像素坐标(u,v)。
此次观测的误差为: (e = z - h(xi, p))
如果把其他时刻的观测量也考虑进来,则整体的代价函数为:
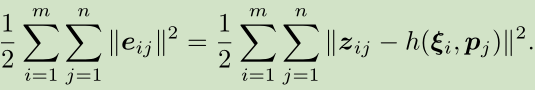
相当于对位姿和3D路标点同时进行优化,也就是所谓的BA。
2.BA的求解
在BA的目标函数上,把自变量定义成所有待优化的变量:
(x = [xi_{1}, ..., xi_{m}, p_{1}, ..., p_{n}]^{T})
相应的,增量方程中的(Delta x)则是对整体自变量的增量,在这个意义下,当给一个增量时,目标函数为:
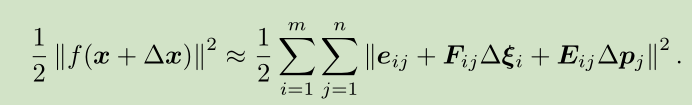
其中F表示整个代价函数在当前状态下对相机姿态的偏导数,而E代表该函数对路标点位置的偏导。
无论是使用G-N还是L-M方法,最后都将面对增量线性方程: (HDelta x = g)
主要区别是H取 (J^{T}J)还是取 (J^{T}J + lambda I)的形式。
以G-N为例,H矩阵为:
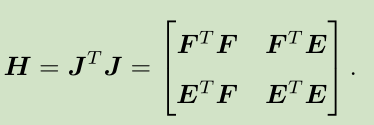
3.H矩阵的稀疏性
H的稀疏性是有雅可比矩阵J引起的。考虑其中一个e,这个误差项只描述了在(xi_{i})看到(p_{j})这件事,只涉及到第i个相机位姿和第j个路标点,其余都是0
故: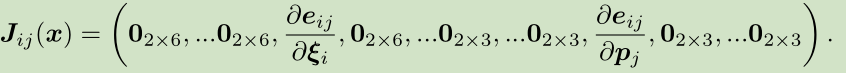
假设一个场景有2个相机位姿(C1,C2)和6个路标点(P1,P2,P3,P4,P5,P6)观测过程为:
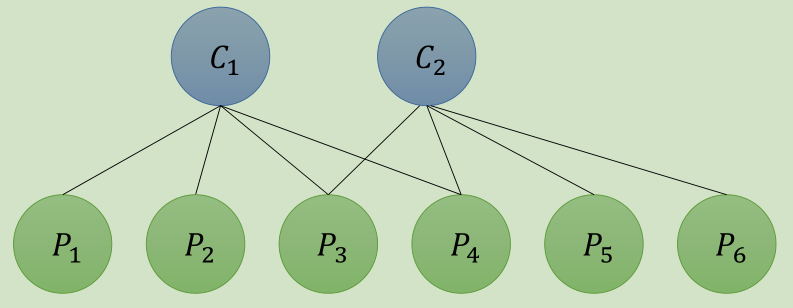
J为: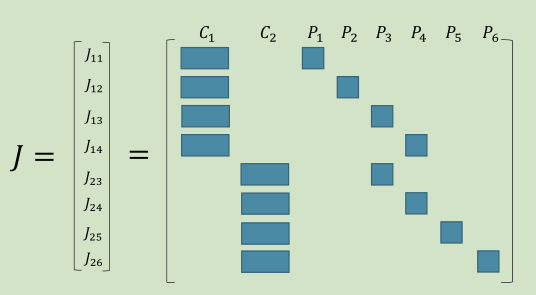
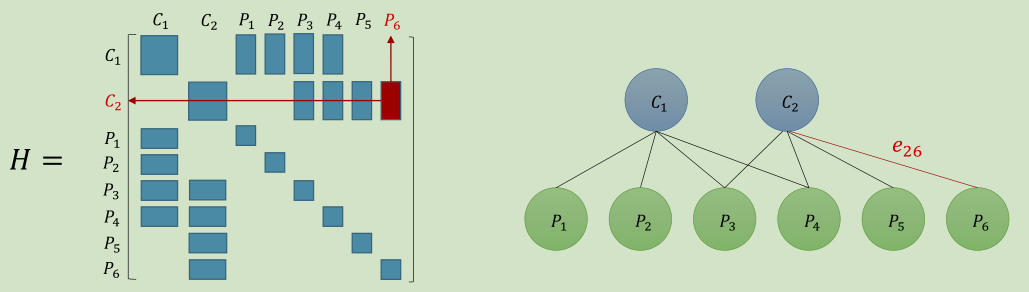
由上面的结构,我们把H分为4个矩阵块B,E,C:
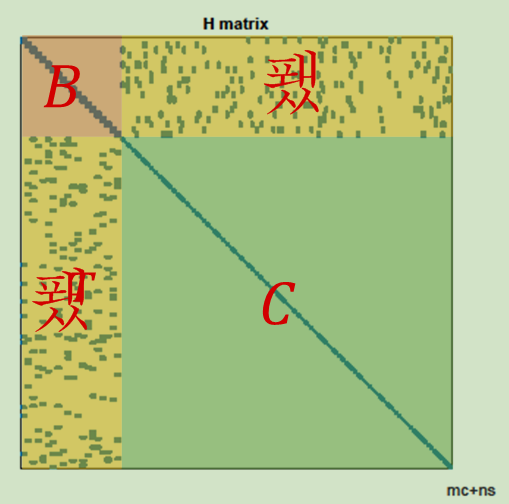
于是,对应的线性方程组也可以变为如下形式:
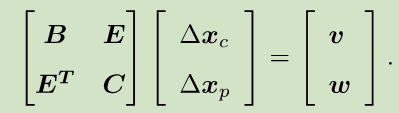
4.G2O实践
1.开始前,先讲一下BAL数据集的数据格式

第一行表示有16个相机,22106个3D路标点 83718个观测点
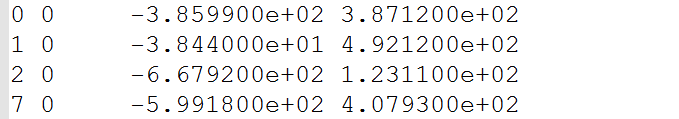
第一列是代表第几个相机,第二列代表第几个路标点,后面是观测到的像素坐标。
该组数据一共是83718行。
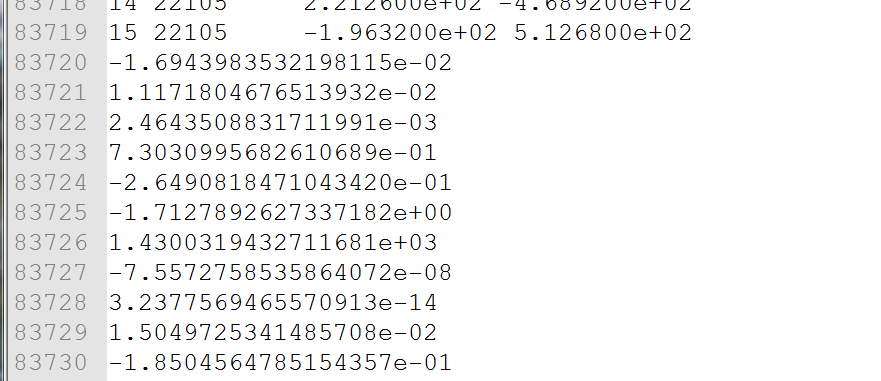
后面的数据是16个相机的参数,9维,分别是-R(3维),t(3维),f(焦距),k1,k2畸变参数
一共16组数据。
再后面的数据,就是22106个路标点的3D坐标(3维)
2.bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp
#include <g2o/core/base_vertex.h>
#include <g2o/core/base_binary_edge.h>
#include <g2o/core/block_solver.h>
#include <g2o/core/optimization_algorithm_levenberg.h>
#include <g2o/solvers/csparse/linear_solver_csparse.h>
#include <g2o/core/robust_kernel_impl.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "common.h"
#include "sophus/se3.hpp"
using namespace Sophus;
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace std;
/// 姿态和内参的结构
struct PoseAndIntrinsics {
PoseAndIntrinsics() {}
/// set from given data address
explicit PoseAndIntrinsics(double *data_addr) {
rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(data_addr[0], data_addr[1], data_addr[2]));
translation = Vector3d(data_addr[3], data_addr[4], data_addr[5]);
focal = data_addr[6];
k1 = data_addr[7];
k2 = data_addr[8];
}
/// 将估计值放入内存
void set_to(double *data_addr) {
auto r = rotation.log();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i] = r[i];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) data_addr[i + 3] = translation[i];
data_addr[6] = focal;
data_addr[7] = k1;
data_addr[8] = k2;
}
SO3d rotation;
Vector3d translation = Vector3d::Zero();
double focal = 0;
double k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
};
/// 位姿加相机内参的顶点,9维,前三维为so3,接下去为t, f, k1, k2
class VertexPoseAndIntrinsics : public g2o::BaseVertex<9, PoseAndIntrinsics> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics() {}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = PoseAndIntrinsics();
}
//更新估计值
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate.rotation = SO3d::exp(Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2])) * _estimate.rotation;
_estimate.translation += Vector3d(update[3], update[4], update[5]);
_estimate.focal += update[6];
_estimate.k1 += update[7];
_estimate.k2 += update[8];
}
/// 根据估计值投影一个点,
Vector2d project(const Vector3d &point) {
//把一个世界的3D点变换到当前相机点
Vector3d pc = _estimate.rotation * point + _estimate.translation;
pc = -pc / pc[2]; //投影到前方的距离1的相机平面
double r2 = pc.squaredNorm(); //r2
//去畸变 1 + k1*r2 + k2*r2*r2
double distortion = 1.0 + r2 * (_estimate.k1 + _estimate.k2 * r2);
//得到投影的像素坐标
return Vector2d(_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[0],
_estimate.focal * distortion * pc[1]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
//路标3D点的顶点
class VertexPoint : public g2o::BaseVertex<3, Vector3d> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
VertexPoint() {}
virtual void setToOriginImpl() override {
_estimate = Vector3d(0, 0, 0);
}
//更新估计值
virtual void oplusImpl(const double *update) override {
_estimate += Vector3d(update[0], update[1], update[2]);
}
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
//误差模型 观测维度2,类型为2d, 连接2个顶点类型
class EdgeProjection :
public g2o::BaseBinaryEdge<2, Vector2d, VertexPoseAndIntrinsics, VertexPoint> {
public:
EIGEN_MAKE_ALIGNED_OPERATOR_NEW;
//计算模型误差 ,投影-观测
virtual void computeError() override {
auto v0 = (VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *) _vertices[0]; //位姿
auto v1 = (VertexPoint *) _vertices[1]; //路标
auto proj = v0->project(v1->estimate());//观测路标投影一个像素点
_error = proj - _measurement; //误差
}
// use numeric derivatives
virtual bool read(istream &in) {}
virtual bool write(ostream &out) const {}
};
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem);
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
cout << "usage: bundle_adjustment_g2o bal_data.txt" << endl;
return 1;
}
BALProblem bal_problem(argv[1]); //读取BAL数据集
bal_problem.Normalize(); //对相机参数和路标点3D数据进行处理
bal_problem.Perturb(0.1, 0.5, 0.5); //给路标3D点添加噪声
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("initial.ply"); //生成噪声ply文件
SolveBA(bal_problem); //BA优化
bal_problem.WriteToPLYFile("final.ply"); //生成优化后的ply文件
return 0;
}
void SolveBA(BALProblem &bal_problem) {
const int point_block_size = bal_problem.point_block_size();
const int camera_block_size = bal_problem.camera_block_size();
double *points = bal_problem.mutable_points(); //3D点
double *cameras = bal_problem.mutable_cameras();//相机
// pose dimension 9, landmark is 3
typedef g2o::BlockSolver<g2o::BlockSolverTraits<9, 3>> BlockSolverType;
typedef g2o::LinearSolverCSparse<BlockSolverType::PoseMatrixType> LinearSolverType; //线性求解器
// use LM
auto solver = new g2o::OptimizationAlgorithmLevenberg(
g2o::make_unique<BlockSolverType>(g2o::make_unique<LinearSolverType>()));
g2o::SparseOptimizer optimizer; //图模型
optimizer.setAlgorithm(solver); //设置求解器
optimizer.setVerbose(true); //打开调试输出
/// build g2o problem
const double *observations = bal_problem.observations(); //获取观测数据
// vertex
vector<VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *> vertex_pose_intrinsics;
vector<VertexPoint *> vertex_points;
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) { //16个相机位姿
VertexPoseAndIntrinsics *v = new VertexPoseAndIntrinsics();
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
v->setId(i); //顶点设置ID,
v->setEstimate(PoseAndIntrinsics(camera)); //往图里增加顶点位姿,相机的位姿数据9维
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_pose_intrinsics.push_back(v);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) { //22106个路标点
VertexPoint *v = new VertexPoint();
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
v->setId(i + bal_problem.num_cameras()); //设置ID,不能和上面重复,直接往后排
v->setEstimate(Vector3d(point[0], point[1], point[2])); //路标点 3维
// g2o在BA中需要手动设置待Marg的顶点
v->setMarginalized(true); //路标要被边缘化计算,所以设置边缘化属性为true
optimizer.addVertex(v);
vertex_points.push_back(v);
}
// edge
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_observations(); ++i) { //增加边,总共83718个观测数据
EdgeProjection *edge = new EdgeProjection;
edge->setVertex(0, vertex_pose_intrinsics[bal_problem.camera_index()[i]]); //设置链接的顶点,取出标号,对应数据
edge->setVertex(1, vertex_points[bal_problem.point_index()[i]]); //设置链接的顶点
edge->setMeasurement(Vector2d(observations[2 * i + 0], observations[2 * i + 1])); //观测数据
edge->setInformation(Matrix2d::Identity()); //信息矩阵:协方差矩阵之逆
edge->setRobustKernel(new g2o::RobustKernelHuber());
optimizer.addEdge(edge);
}
optimizer.initializeOptimization();
optimizer.optimize(40); //迭代40次
// set to bal problem
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_cameras(); ++i) {
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_pose_intrinsics[i];
auto estimate = vertex->estimate(); //获取位姿的最优值9维
estimate.set_to(camera);
}
for (int i = 0; i < bal_problem.num_points(); ++i) {
double *point = points + point_block_size * i;
auto vertex = vertex_points[i]; //获取3D路标的最优值3维
for (int k = 0; k < 3; ++k) point[k] = vertex->estimate()[k]; //路标覆盖保存
}
}
3.common.cpp
#include <cstdio>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include "common.h"
#include "rotation.h"
#include "random.h"
typedef Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd> VectorRef;
typedef Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd> ConstVectorRef;
//这个函数从fptr文件中读出一个format类型的值,赋值给参数value,从开头开始,找到一个合适的就停止。
//这个函数主要是给BALProblem()构造函数读取txt数据文件用的,比较简陋
template<typename T>
void FscanfOrDie(FILE *fptr, const char *format, T *value) {
int num_scanned = fscanf(fptr, format, value);
if (num_scanned != 1)
std::cerr << "Invalid UW data file. ";
}
//给一个三维向量加入噪声,很简单xyz依次加入随机值就好了。定义这个的目的是为了后面的Perturb()函数在增加噪声时,
// 是分开对路标点,相机的旋转,相机的平移分别加入噪声的,并且这三个量都是三维的,所以定义一个三维向量添加噪声的函数
void PerturbPoint3(const double sigma, double *point) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
point[i] += RandNormal() * sigma;
}
double Median(std::vector<double> *data) {
int n = data->size();
std::vector<double>::iterator mid_point = data->begin() + n / 2;
std::nth_element(data->begin(), mid_point, data->end());
return *mid_point;
}
BALProblem::BALProblem(const std::string &filename, bool use_quaternions) {
FILE *fptr = fopen(filename.c_str(), "r");
if (fptr == NULL) {
std::cerr << "Error: unable to open file " << filename;
return;
};
// This wil die horribly on invalid files. Them's the breaks.
FscanfOrDie(fptr, "%d", &num_cameras_); //读取总的相机数
FscanfOrDie(fptr, "%d", &num_points_); //读取总的路标数
FscanfOrDie(fptr, "%d", &num_observations_);//读取总的观测数据个数
std::cout << "Header: " << num_cameras_
<< " " << num_points_
<< " " << num_observations_;
point_index_ = new int[num_observations_]; //取出3D路标点的标号
camera_index_ = new int[num_observations_]; //相机的标号
observations_ = new double[2 * num_observations_]; //观测的像素点
num_parameters_ = 9 * num_cameras_ + 3 * num_points_;//每个相机9个参数,每个路标3个参数
parameters_ = new double[num_parameters_]; //参数的总大小
for (int i = 0; i < num_observations_; ++i) { //拷贝数据
FscanfOrDie(fptr, "%d", camera_index_ + i); //第几个相机
FscanfOrDie(fptr, "%d", point_index_ + i); //第几个路标
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) {
FscanfOrDie(fptr, "%lf", observations_ + 2 * i + j);//观测到的像素坐标
}
}
//每个相机是一组9个参数,-R:3维(罗德里格斯向量) t:3维 f,k1,k2。后面是3D路标的数据3维
for (int i = 0; i < num_parameters_; ++i) {
FscanfOrDie(fptr, "%lf", parameters_ + i);
}
fclose(fptr);
use_quaternions_ = use_quaternions;
if (use_quaternions) {
// Switch the angle-axis rotations to quaternions.
num_parameters_ = 10 * num_cameras_ + 3 * num_points_;
double *quaternion_parameters = new double[num_parameters_];//指针指向一个新的四元数数组
double *original_cursor = parameters_; //指针指向原始数据参数数组
double *quaternion_cursor = quaternion_parameters;//指针指向指向四元数数组的指针
for (int i = 0; i < num_cameras_; ++i) {
AngleAxisToQuaternion(original_cursor, quaternion_cursor); //R转换为四元数
quaternion_cursor += 4;
original_cursor += 3;
for (int j = 4; j < 10; ++j) {
*quaternion_cursor++ = *original_cursor++;
}
}
// Copy the rest of the points.
for (int i = 0; i < 3 * num_points_; ++i) {
*quaternion_cursor++ = *original_cursor++;
}
// Swap in the quaternion parameters.
delete[]parameters_;
parameters_ = quaternion_parameters;
}
}
//构造函数读入数据txt,将数据存入类成员中。猜测这里是反向过程,由类成员中存储的数据,生成一个待优化数据.txt。
void BALProblem::WriteToFile(const std::string &filename) const {
FILE *fptr = fopen(filename.c_str(), "w");
if (fptr == NULL) {
std::cerr << "Error: unable to open file " << filename;
return;
}
fprintf(fptr, "%d %d %d %d
", num_cameras_, num_cameras_, num_points_, num_observations_);
for (int i = 0; i < num_observations_; ++i) {
fprintf(fptr, "%d %d", camera_index_[i], point_index_[i]);
for (int j = 0; j < 2; ++j) {
fprintf(fptr, " %g", observations_[2 * i + j]);
}
fprintf(fptr, "
");
}
for (int i = 0; i < num_cameras(); ++i) {
double angleaxis[9];
if (use_quaternions_) {
//OutPut in angle-axis format.
QuaternionToAngleAxis(parameters_ + 10 * i, angleaxis);
memcpy(angleaxis + 3, parameters_ + 10 * i + 4, 6 * sizeof(double));
} else {
memcpy(angleaxis, parameters_ + 9 * i, 9 * sizeof(double));
}
for (int j = 0; j < 9; ++j) {
fprintf(fptr, "%.16g
", angleaxis[j]);
}
}
const double *points = parameters_ + camera_block_size() * num_cameras_;
for (int i = 0; i < num_points(); ++i) {
const double *point = points + i * point_block_size();
for (int j = 0; j < point_block_size(); ++j) {
fprintf(fptr, "%.16g
", point[j]);
}
}
fclose(fptr);
}
//将相机的世界坐标位移和3D路标点写入文件
// Write the problem to a PLY file for inspection in Meshlab or CloudCompare
void BALProblem::WriteToPLYFile(const std::string &filename) const {
std::ofstream of(filename.c_str());
of << "ply"
<< '
' << "format ascii 1.0"
<< '
' << "element vertex " << num_cameras_ + num_points_
<< '
' << "property float x"
<< '
' << "property float y"
<< '
' << "property float z"
<< '
' << "property uchar red"
<< '
' << "property uchar green"
<< '
' << "property uchar blue"
<< '
' << "end_header" << std::endl;
// Export extrinsic data (i.e. camera centers) as green points.
double angle_axis[3];
double center[3];
for (int i = 0; i < num_cameras(); ++i) {
const double *camera = cameras() + camera_block_size() * i;
CameraToAngelAxisAndCenter(camera, angle_axis, center);
of << center[0] << ' ' << center[1] << ' ' << center[2]
<< "0 255 0" << '
';
}
// Export the structure (i.e. 3D Points) as white points.
const double *points = parameters_ + camera_block_size() * num_cameras_;
for (int i = 0; i < num_points(); ++i) {
const double *point = points + i * point_block_size();
for (int j = 0; j < point_block_size(); ++j) {
of << point[j] << ' ';
}
of << "255 255 255
";
}
of.close();
}
/**
*
* 由camera数据中的旋转向量和平移向量解析出相机世界坐标系下的姿态(依旧是旋转向量)和位置(世界坐标系下的xyz),也是用于生成点云用的
* @param camera 要解析的相机参数,前三维旋转,接着三维平移,这里指用到这6维
* @param angle_axis 解析出的相机姿态承接数组,也是旋转向量形式
* @param center 解析出来的相机原点在世界坐标系下的坐标承接数组,XYZ
*/
void BALProblem::CameraToAngelAxisAndCenter(const double *camera,
double *angle_axis,
double *center) const {
VectorRef angle_axis_ref(angle_axis, 3);
if (use_quaternions_) {
QuaternionToAngleAxis(camera, angle_axis);
} else {
angle_axis_ref = ConstVectorRef(camera, 3); //读取R
}
Eigen::VectorXd inverse_rotation = -angle_axis_ref; //-R,BAL文件定义,取负号
/**
* 这里解释一下center的计算逻辑:
* center是指相机原点在世界坐标系下的坐标,那么定义一下:
* PW_center, 世界坐标系下相机原点的坐标
* PC_center, 相机坐标系下的相机原点坐标
* 它俩的关系是什么呢?
* PW_center*R+t = PC_center
* 反向过程就是
* PC_center * T^(-1) = PW_center
* 那么相机坐标系的原点,在世界坐标系下的坐标就可以求出来了
* [R^(T) -R^(T)*t ] * [相机原点也就是000]
* [0 1 ] [ 1 ]
* 结果就是 -R^(T) * t
*由旋转向量形式表示的旋转,反向过程(也就是求逆)就是旋转向量取负即可。
* 所以结果就是cos(theta) * t + ( 1 - cos(theta) ) (n 点乘 t) n + sin(theta) ( n 叉乘 t )
*/
AngleAxisRotatePoint(inverse_rotation.data(), //R
camera + camera_block_size() - 6, //平移t的数据
center); //结果
//最后加上负号。记住,map类型构造的是引用,能直接对原构造数组进行操作的。
//说一下这句,这句还是,用center数组的前3维,去构造一个无名的map类型矩阵,并且后面直接跟上*-1操作。
//VectorRef是Map的一个define。
//记住Map构造出来是引用,能对原始值直接操作。
VectorRef(center, 3) *= -1.0;
}
/**
* 由世界坐标系下的相机姿态和原点位置,生成一个camera数据
* @param angle_axis 世界坐标到相机坐标变化的旋转向量数据
* @param center 相机中心在世界坐标系下的位置坐标
* @param camera 承接数据的camera数组,由于这里只是生成旋转和平移,所以是camera的前6维
*/
void BALProblem::AngleAxisAndCenterToCamera(const double *angle_axis,
const double *center,
double *camera) const {
ConstVectorRef angle_axis_ref(angle_axis, 3);
if (use_quaternions_) {
AngleAxisToQuaternion(angle_axis, camera);
} else {
VectorRef(camera, 3) = angle_axis_ref;
}
//这里相机姿态R没有取反,原始数据是-R,代表是相机坐标系对世界坐标系的变换
/* 和上面类似
* 结果就是 -R^(T) * t
*
* 所以结果就是cos(theta) * t + ( 1 - cos(theta) ) (n 点乘 t) n + sin(theta) ( n 叉乘 t )
*/
//该函数直接修改了储存相机平移数据的数据
AngleAxisRotatePoint(angle_axis, center, camera + camera_block_size() - 6);
//最后再取个反
VectorRef(camera + camera_block_size() - 6, 3) *= -1.0;
}
void BALProblem::Normalize() {
// Compute the marginal median of the geometry
std::vector<double> tmp(num_points_);
Eigen::Vector3d median;
double *points = mutable_points();//获取路标3D点的位置
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < num_points_; ++j) {
tmp[j] = points[3 * j + i];
}
median(i) = Median(&tmp); //返回中位数,如果是偶数,取平均值
}
for (int i = 0; i < num_points_; ++i) {
VectorRef point(points + 3 * i, 3);
tmp[i] = (point - median).lpNorm<1>(); //每个点 - 中位数 的LP范数
}
const double median_absolute_deviation = Median(&tmp); //再取中位数
// Scale so that the median absolute deviation of the resulting
// reconstruction is 100
const double scale = 100.0 / median_absolute_deviation;
// X = scale * (X - median)
for (int i = 0; i < num_points_; ++i) {
VectorRef point(points + 3 * i, 3); //
point = scale * (point - median); //对每个3D点进行处理,MAP是引用,会改变原数据
}
double *cameras = mutable_cameras(); //相机参数
double angle_axis[3];
double center[3];
for (int i = 0; i < num_cameras_; ++i) {
double *camera = cameras + camera_block_size() * i;
//angle_axis赋值了R,center为结果
CameraToAngelAxisAndCenter(camera, angle_axis, center); //求解世界坐标系下的相机中心坐标
// center = scale * (center - median)
VectorRef(center, 3) = scale * (VectorRef(center, 3) - median); //因为世界路标3D点做了处理,所以这个也要处理
//最终,修改了*camera指向储存的数据的平移数据
AngleAxisAndCenterToCamera(angle_axis, center, camera); //因为世界坐标进行处理了,所以将处理后的数据转到相机坐标去
}
}
//添加噪声
void BALProblem::Perturb(const double rotation_sigma,
const double translation_sigma,
const double point_sigma) {
assert(point_sigma >= 0.0);
assert(rotation_sigma >= 0.0);
assert(translation_sigma >= 0.0);
double *points = mutable_points();
if (point_sigma > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < num_points_; ++i) {
PerturbPoint3(point_sigma, points + 3 * i);
}
}
//这里相机是被分成两块,旋转和平移,
//旋转是考虑到四元数形式,增加了一步用CameraToAngelAxisAndCenter()从camera中取出三维的angle_axis,
//然后添加噪声,添加完后再用AngleAxisAndCenterToCamera()重构camera参数
//平移部分就直接用PerturbPoint3()添加了
for (int i = 0; i < num_cameras_; ++i) {
double *camera = mutable_cameras() + camera_block_size() * i;
double angle_axis[3];
double center[3];
// Perturb in the rotation of the camera in the angle-axis
// representation
CameraToAngelAxisAndCenter(camera, angle_axis, center);
if (rotation_sigma > 0.0) {
PerturbPoint3(rotation_sigma, angle_axis);
}
AngleAxisAndCenterToCamera(angle_axis, center, camera);
if (translation_sigma > 0.0)
PerturbPoint3(translation_sigma, camera + camera_block_size() - 6);
}
}
common.h
#pragma once
/// 从文件读入BAL dataset原始数据,然后进行分割储存
class BALProblem {
public:
/// load bal data from text file
explicit BALProblem(const std::string &filename, bool use_quaternions = false);
~BALProblem() {
delete[] point_index_;
delete[] camera_index_;
delete[] observations_;
delete[] parameters_;
}
/// save results to text file
void WriteToFile(const std::string &filename) const;
/// save results to ply pointcloud
void WriteToPLYFile(const std::string &filename) const;
void Normalize();
void Perturb(const double rotation_sigma,
const double translation_sigma,
const double point_sigma);
int camera_block_size() const { return use_quaternions_ ? 10 : 9; }
int point_block_size() const { return 3; }
int num_cameras() const { return num_cameras_; }
int num_points() const { return num_points_; }
int num_observations() const { return num_observations_; }
int num_parameters() const { return num_parameters_; }
const int *point_index() const { return point_index_; }
const int *camera_index() const { return camera_index_; }
const double *observations() const { return observations_; }
const double *parameters() const { return parameters_; }
const double *cameras() const { return parameters_; }
const double *points() const { return parameters_ + camera_block_size() * num_cameras_; }
/// camera参数的起始地址
double *mutable_cameras() { return parameters_; }
double *mutable_points() { return parameters_ + camera_block_size() * num_cameras_; }
double *mutable_camera_for_observation(int i) {
return mutable_cameras() + camera_index_[i] * camera_block_size();
}
double *mutable_point_for_observation(int i) {
return mutable_points() + point_index_[i] * point_block_size();
}
const double *camera_for_observation(int i) const {
return cameras() + camera_index_[i] * camera_block_size();
}
const double *point_for_observation(int i) const {
return points() + point_index_[i] * point_block_size();
}
private:
void CameraToAngelAxisAndCenter(const double *camera,
double *angle_axis,
double *center) const;
void AngleAxisAndCenterToCamera(const double *angle_axis,
const double *center,
double *camera) const;
int num_cameras_;
int num_points_;
int num_observations_;
int num_parameters_;
bool use_quaternions_;
int *point_index_; // 每个observation对应的point index
int *camera_index_; // 每个observation对应的camera index
double *observations_;
double *parameters_;
};
4.random.h
#ifndef RAND_H
#define RAND_H
#include <math.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
inline double RandDouble()
{
double r = static_cast<double>(rand());
return r / RAND_MAX;
}
inline double RandNormal()
{
double x1, x2, w;
do{
x1 = 2.0 * RandDouble() - 1.0;
x2 = 2.0 * RandDouble() - 1.0;
w = x1 * x1 + x2 * x2;
}while( w >= 1.0 || w == 0.0);
w = sqrt((-2.0 * log(w))/w);
return x1 * w;
}
#endif // random.h
rotation.h
#ifndef ROTATION_H
#define ROTATION_H
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <limits>
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// math functions needed for rotation conversion.
// dot and cross production
template<typename T>
inline T DotProduct(const T x[3], const T y[3]) {
return (x[0] * y[0] + x[1] * y[1] + x[2] * y[2]);
}
template<typename T>
inline void CrossProduct(const T x[3], const T y[3], T result[3]) {
result[0] = x[1] * y[2] - x[2] * y[1];
result[1] = x[2] * y[0] - x[0] * y[2];
result[2] = x[0] * y[1] - x[1] * y[0];
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Converts from a angle anxis to quaternion :
template<typename T>
inline void AngleAxisToQuaternion(const T *angle_axis, T *quaternion) {
const T &a0 = angle_axis[0];
const T &a1 = angle_axis[1];
const T &a2 = angle_axis[2];
const T theta_squared = a0 * a0 + a1 * a1 + a2 * a2;
if (theta_squared > T(std::numeric_limits<double>::epsilon())) {
const T theta = sqrt(theta_squared);
const T half_theta = theta * T(0.5);
const T k = sin(half_theta) / theta;
quaternion[0] = cos(half_theta);
quaternion[1] = a0 * k;
quaternion[2] = a1 * k;
quaternion[3] = a2 * k;
} else { // in case if theta_squared is zero
const T k(0.5);
quaternion[0] = T(1.0);
quaternion[1] = a0 * k;
quaternion[2] = a1 * k;
quaternion[3] = a2 * k;
}
}
template<typename T>
inline void QuaternionToAngleAxis(const T *quaternion, T *angle_axis) {
const T &q1 = quaternion[1];
const T &q2 = quaternion[2];
const T &q3 = quaternion[3];
const T sin_squared_theta = q1 * q1 + q2 * q2 + q3 * q3;
// For quaternions representing non-zero rotation, the conversion
// is numercially stable
if (sin_squared_theta > T(std::numeric_limits<double>::epsilon())) {
const T sin_theta = sqrt(sin_squared_theta);
const T &cos_theta = quaternion[0];
// If cos_theta is negative, theta is greater than pi/2, which
// means that angle for the angle_axis vector which is 2 * theta
// would be greater than pi...
const T two_theta = T(2.0) * ((cos_theta < 0.0)
? atan2(-sin_theta, -cos_theta)
: atan2(sin_theta, cos_theta));
const T k = two_theta / sin_theta;
angle_axis[0] = q1 * k;
angle_axis[1] = q2 * k;
angle_axis[2] = q3 * k;
} else {
// For zero rotation, sqrt() will produce NaN in derivative since
// the argument is zero. By approximating with a Taylor series,
// and truncating at one term, the value and first derivatives will be
// computed correctly when Jets are used..
const T k(2.0);
angle_axis[0] = q1 * k;
angle_axis[1] = q2 * k;
angle_axis[2] = q3 * k;
}
}
template<typename T>
inline void AngleAxisRotatePoint(const T angle_axis[3], const T pt[3], T result[3]) {
const T theta2 = DotProduct(angle_axis, angle_axis);
if (theta2 > T(std::numeric_limits<double>::epsilon())) {
// Away from zero, use the rodriguez formula
//
// result = pt costheta +
// (w x pt) * sintheta +
// w (w . pt) (1 - costheta)
//
// We want to be careful to only evaluate the square root if the
// norm of the angle_axis vector is greater than zero. Otherwise
// we get a division by zero.
//
const T theta = sqrt(theta2); //旋转角度,单位弧度
const T costheta = cos(theta);
const T sintheta = sin(theta);
const T theta_inverse = 1.0 / theta;
const T w[3] = {angle_axis[0] * theta_inverse, //归一化
angle_axis[1] * theta_inverse,
angle_axis[2] * theta_inverse};
// Explicitly inlined evaluation of the cross product for
// performance reasons.
/*const T w_cross_pt[3] = { w[1] * pt[2] - w[2] * pt[1],
w[2] * pt[0] - w[0] * pt[2],
w[0] * pt[1] - w[1] * pt[0] };*/
T w_cross_pt[3];
CrossProduct(w, pt, w_cross_pt); //t 叉乘 n
const T tmp = DotProduct(w, pt) * (T(1.0) - costheta); //t 点乘 n
// (w[0] * pt[0] + w[1] * pt[1] + w[2] * pt[2]) * (T(1.0) - costheta);
result[0] = pt[0] * costheta + w_cross_pt[0] * sintheta + w[0] * tmp;
result[1] = pt[1] * costheta + w_cross_pt[1] * sintheta + w[1] * tmp;
result[2] = pt[2] * costheta + w_cross_pt[2] * sintheta + w[2] * tmp;
} else {
// Near zero, the first order Taylor approximation of the rotation
// matrix R corresponding to a vector w and angle w is
//
// R = I + hat(w) * sin(theta)
//
// But sintheta ~ theta and theta * w = angle_axis, which gives us
//
// R = I + hat(w)
//
// and actually performing multiplication with the point pt, gives us
// R * pt = pt + w x pt.
//
// Switching to the Taylor expansion near zero provides meaningful
// derivatives when evaluated using Jets.
//
// Explicitly inlined evaluation of the cross product for
// performance reasons.
/*const T w_cross_pt[3] = { angle_axis[1] * pt[2] - angle_axis[2] * pt[1],
angle_axis[2] * pt[0] - angle_axis[0] * pt[2],
angle_axis[0] * pt[1] - angle_axis[1] * pt[0] };*/
T w_cross_pt[3];
CrossProduct(angle_axis, pt, w_cross_pt);
result[0] = pt[0] + w_cross_pt[0];
result[1] = pt[1] + w_cross_pt[1];
result[2] = pt[2] + w_cross_pt[2];
}
}
#endif // rotation.h
5.CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(bundle_adjustment)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE "Release")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "-O3 -std=c++11")
LIST(APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake)
Find_Package(G2O REQUIRED)
Find_Package(Eigen3 REQUIRED)
Find_Package(Ceres REQUIRED)
Find_Package(Sophus REQUIRED)
Find_Package(CSparse REQUIRED)
SET(G2O_LIBS g2o_csparse_extension g2o_stuff g2o_core cxsparse)
include_directories(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR} ${EIGEN3_INCLUDE_DIR} ${CSPARSE_INCLUDE_DIR})
add_library(bal_common common.cpp)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_g2o bundle_adjustment_g2o.cpp)
add_executable(bundle_adjustment_ceres bundle_adjustment_ceres.cpp)
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_ceres ${CERES_LIBRARIES} bal_common)
target_link_libraries(bundle_adjustment_g2o ${G2O_LIBS} bal_common)