概念
线程池(ThreadPool)是一种多线程处理形式,处理过程中将任务添加到队列,然后在创建线程后自动启动这些任务。线程池线程都是后台线程。每个线程都使用默认的堆栈大小,以默认的优先级运行,并处于多线程单元中。如果某个线程在托管代码中空闲(如正在等待某个事件),则线程池将插入另一个辅助线程来使所有处理器保持繁忙。如果所有线程池线程都始终保持繁忙,但队列中包含挂起的工作,则线程池将在一段时间后创建另一个辅助线程但线程的数目永远不会超过最大值。超过最大值的线程可以排队,但他们要等到其他线程完成后才启动。
默认线程池
1.newFixedThreadPool(),这个线程池创建后会包含固定数量的线程,空闲线程会一直被保留。
// 线程池中5个工作线程,类似银行有5个受理窗口 ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
newFixedThreadPool是创建指定线程,而且通过0L可以看出长期保持
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }
2.newSingleThreadExecutor(),这个线程池中只有一个线程,该线程是顺序执行,每执行完一个线程后,才会执行下一个线程。
// 线程池中,每次只处理1个请求,类似一个银行有1个受理窗口 ExecutorService threadPool1 = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
newSingleThreadExecutor()验证线程池中有且仅有一个线程
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }
3.newCachedThreadPool(),必要时创建新线程;空闲线程会保留60秒
// 一池N个工作线程,类似银行有N个受理窗口,自动调节的。 ExecutorService threadPool2 = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
验证newCachedThreadPool()空闲线程保留60秒,我们可以通过查看源码来验证
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }
测试
try { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { threadPool.execute(()-> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 办理业务");}); threadPool1.execute(()-> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 办理业务");}); threadPool2.execute(()-> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 办理业务");}); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { threadPool.shutdown();// 回收线程 threadPool1.shutdown();// 回收线程 threadPool2.shutdown();// 回收线程 }
在开发中是否会用Executors去创建线程池呢?
我们看一下阿里java开发手册中明确强调不允许使用Executors来创建线程池。
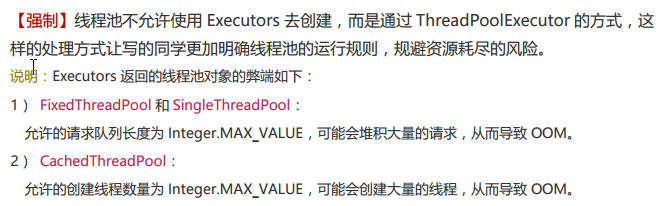
通过阅读源码我们可以看到newFixedThreadPool()和newSingleThreadExecutor()中阻塞队列都是用了new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(),它的构造函数为
public LinkedBlockingQueue() { this(Integer.MAX_VALUE); }
通过阅读源码我们可以看到newCachedThreadPool()的底层实现时将参赛 maximumPoolSize 设为Integer.MAX_VALUE,也就印证了阿里所说的最大线程数。
又通过源码可以看出newFixedThreadPool()、newSingleThreadExecutor()以及newCachedThreadPool()都是调用了new ThreadPoolExecutor()来创建线程池,
所以我们要想做到对线程池的掌控,也就是创建我们想要的线程池就需要通过new ThreadPoolExecutor()来进行创建,也就是阿里建议我们的做法。
ThreadPoolExecutor()的7大参数
很多时候说道ThreadPoolExecutor的参数,通常很多人会说线程池的5个参数 int corePoolSize 核心线程数也就是初始线程数, int maximumPoolSize
最大线程数也就是同时可以拥有的线程数量, long keepAliveTime 线程存活时间它结合 TimeUnit unit 也就是时间单位 形成最终的线程存活时间,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue 阻塞队列长度也就是当线程池满负荷运行时,在等候区待执行的任务数。
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) { this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler); }
标题说是7大参数,那么上边一直在介绍的是5个参数,那么其余的两个参数是什么,依照源码往下看,this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler); this的前5个参数就不需要过多解释,那么后边的Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler
分别是什么?接着查看源码
/** * Creates a new {@code ThreadPoolExecutor} with the given initial * parameters. * * @param corePoolSize the number of threads to keep in the pool, even * if they are idle, unless {@code allowCoreThreadTimeOut} is set * @param maximumPoolSize the maximum number of threads to allow in the * pool * @param keepAliveTime when the number of threads is greater than * the core, this is the maximum time that excess idle threads * will wait for new tasks before terminating. * @param unit the time unit for the {@code keepAliveTime} argument * @param workQueue the queue to use for holding tasks before they are * executed. This queue will hold only the {@code Runnable} * tasks submitted by the {@code execute} method. * @param threadFactory the factory to use when the executor * creates a new thread * @param handler the handler to use when execution is blocked * because the thread bounds and queue capacities are reached * @throws IllegalArgumentException if one of the following holds:<br> * {@code corePoolSize < 0}<br> * {@code keepAliveTime < 0}<br> * {@code maximumPoolSize <= 0}<br> * {@code maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize} * @throws NullPointerException if {@code workQueue} * or {@code threadFactory} or {@code handler} is null */ public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { if (corePoolSize < 0 || maximumPoolSize <= 0 || maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize || keepAliveTime < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException(); if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null) throw new NullPointerException(); this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize; this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize; this.workQueue = workQueue; this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime); this.threadFactory = threadFactory; this.handler = handler; }
ThreadFactory threadFactory的注释中解释道:
threadFactory the factory to use when the executor creates a new thread 线程工厂是用于创建一个新的线程,
我们看到系统提供的线程池使用的是默认线程工厂Executors.defaultThreadFactory()
RejectedExecutionHandler handler 的注释中解释道 :
handler the handler to use when execution is blocked because the thread bounds and queue capacities are
reached
大致意思是当线程和队列到达最大值时,又被分配的任务怎么执行。简单说就是阻塞策略,系统提供的线程池使用的是
默认阻塞策略new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy(),
这个策略是遇当线程池满负荷运行且等候队列也满时,直接抛出异常。系统提供了以下几种阻塞策略:
1.AbortPolicy(默认):直接抛出RejectedExecutionException异常阻止系统正常运行.
public static void main(String[] args) { // 自定义线程 ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 5, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() ); try { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { threadPool.execute(()-> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 办理业务");}); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { threadPool.shutdown();// 回收线程 }
控制台输出: pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-2 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-3 办理业务 pool-1-thread-4 办理业务 pool-1-thread-5 办理业务 java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException:
执行到第9个线程时抛出异常。
2.CallerRunsPolicy:“调用者运行”一种调节机制,该策略既不会抛弃任务,也不会抛出异常,
而是将某些任务回退到调用者,从而降低新任务的流量。
// 自定义线程 ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 5, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() ); try { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { threadPool.execute(()-> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 办理业务");}); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { threadPool.shutdown();// 回收线程 }
控制台输出: main 办理业务 main 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-2 办理业务 pool-1-thread-3 办理业务 pool-1-thread-4 办理业务 pool-1-thread-5 办理业务 Process finished with exit code 0
3.DiscardOldestPolicy:抛弃队列中等待最久的任务,然后把当前任务加人队列中尝试再次提交当前任务。
// 自定义线程 ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 5, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() ); try { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { threadPool.execute(()-> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 办理业务");}); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { threadPool.shutdown();// 回收线程 }
控制台输出: pool-1-thread-2 办理业务 pool-1-thread-3 办理业务 pool-1-thread-2 办理业务 pool-1-thread-3 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-2 办理业务 pool-1-thread-4 办理业务 pool-1-thread-5 办理业务 Process finished with exit code 0 直接丢弃了两个线程的任务,并且没有报错。
4.DiscardPolicy:该策略默默地丢弃无法处理的任务,不予任何处理也不抛出异常。如果允许任务丢失,
这是最好的一种策略。
// 自定义线程 ExecutorService threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor( 2, 5, 2L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() ); try { for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { threadPool.execute(()-> {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 办理业务");}); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { threadPool.shutdown();// 回收线程 }
pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-1 办理业务 pool-1-thread-2 办理业务 pool-1-thread-3 办理业务 pool-1-thread-4 办理业务 pool-1-thread-5 办理业务 Process finished with exit code 0