1.can和could表示可能性
It can't be Mary. She's in hospital.
He said the news could be true. 这个消息有可能是真的
well,you could be right I suppose. 我觉得你可能讲的是真的
can表可能行比could强烈一些
2.can和could表示惊讶,要看说话者本身的语境
How can this be true? I can't belive my eyes.这怎么是真的?
How could you say such a insulting thing to her? 隐含一种责备的语气,你怎么能对她说这种侮辱性的语言呢?
3.may和might表示可能性
may表示可能性比can要小
might比may更小
Watch out when strangers are nice to you. They may want something for themselves.当陌生人和你示好的时候你要小心了
we tend not to choose the unkonwn which may be a shock or disappoint.我们往往不选择未知的,因为它可能使我们震惊或失望
Thinking it might rain.I decided to go in a car. 我当时觉得会下雨,决定开车去。(might是may的过去时,和may一个意思)
4.表示地点方位的介词
- 表示在某个事物的正上方或者正下方over/under
The bridge over the river has a long history.河正上方这座桥有悠久的历史了。
The cats is sitting under your feet. 小猫在你的脚下
- 表示在上面或者下方 above/below
The plane flew above the clouds. 飞机在云上飞。不一定是正上方
I live below the mountains. 我住在山脚下。不一定是正下方
- 表示在事物的前面或者事物的前部分(事物里面的前方)in front of/in the front of
In front of my house run the small river.房子前面有条小河
Don't sit in the front of the car.不要坐在汽车的前部
- 两个事物之间或者多个事物之间between/among
The house stands betewwn two farms. 房子在两个农场之间
my village lies among mountains. 我们村坐落在群山之间
- 表示穿过一个平面/穿过一个空间的内部/从事物旁边经过 across/through/pass
Cross the street.穿过街道
Though the gate. 穿过这道门
The bus just pass the Great Hall of the people.公交车刚刚经过人民大会堂
5.副词:一般用来修饰形容词,动词或者其他副词甚至有时候可以修饰整个句子。
- 时间副词
- then,ago,soon很快,just now刚才
- 地点副词
- here,there,in,out
- 方式副词
- well,kindly,carefully,slowly
- 程度副词
- much,little,almost几乎,hardly几乎不
- 频度副词
- often,usually,always,sometimes
- 评论副词(带有个人感情色彩)
- luckily,happily,honestly,briefly简洁地
- 疑问副词(关系副词)
- where,when,how,why
- 连接副词
- therefore因此,besides除此之外还有,otherwise否则,though虽然
6.常用介词的用法:可以用来表示时间、空间、方位或者手段等等。
- 时间介词
- at表示在具体的某一刻,节假日也可以
- at seven o'clock/at time在那个时候/at Christmas
- in 在一个时间段内,或者表示将来的一个时间段
- in the evening/in August在八月份/in the future/in one's life在人的一生中
- on 表示具体的某一天
- on Monday/on May 1st/on the rainy day在一个下雨天
- during 表示一个时间过程
- during the meeting /meal/the fire火灾
- before 在什么时间之前
- I will be back before supper time 在晚饭之前回来
- after 在什么时间之后
- After supper I will take a short walk
- since 从某个时间段开始
- I have lived here since last year
- for 后面接一段时间
- I have lived here for 2 years.
- at表示在具体的某一刻,节假日也可以
- 空间介词
- 方位介词
- 上面的4
- 手段介词
7.反身代词的用法,你自己,我自己,她自己
- myself,youself,himself,herself,itself
- ourselves,yourselves,themselves
- 1.非强调用法:在非强调用法里面,通常反身代词是语句中的主语,指的是同一个人,但是在剧中一般作宾语。
- Jane is too young to look after herself. 珍妮太年轻了以至于不能照顾自己
2.强调的用法:用来加强某个名词或者某个代词的语气比如:本人,亲自,相当于省略了同谓语成分
- you must do it yourself.你必须亲自去做
- 3.会跟by搭配,表示单独的,没人帮助
- We must finish it all by ourselves.
8.冠词:是一种虚词,名词的一种标识
- 定冠词:the,
- 特指某一个或某一类
- Shut the windows before you leave the room.关窗户。说话人一定是知道哪一个的
- 表示宇宙中独一无二的事物,比如天体太阳,地球
- Men is now studenting and using the sun. 研究和利用太阳
- 当表示地点和方位的时候
- on the left/in the East
- 用在比较级和最高级的前面
- Math is the most difficult subject I think.
- 用在乐器前面用定冠词the
- Shall we dance to the guitar? 随着吉他声跳舞
- by the +计量名次单位的时候
- I pay the rent by the month .我每个月付房租。month这里是一个计量单位,按月。
- 用在定语或者组织单位前面
- the Great Wall 长城/The Yangtse River长江
- 特指某一个或某一类
- 不定冠词:a 、an(元音前用an)
- 同类中的任何一个,用a或an
- A doctor is a person who save people's life
- 表示数量的一个
- I would like a cup of juice and a tomota. 我想要一杯果汁和一个西红柿
- 表示相同的
- We are all of an age. 我们都是同龄人
- 表示不特指
- In a sense,what you said is true.在某种意义上来说,你说的是对的。
- 表示单位量词的每一个
- We have a music class once a week.
- 表示物质n或者抽象n或者集体n前面
- a heavy rain 一场大雨,rain是物质名词
- have a try
- a happy family
- 同类中的任何一个,用a或an
9.名词
- 可数名词的规则变化
- 当单数变成复数,直接在后面加s,bag-bags,coat-coats
- 当单词的结尾是下面的:buses,classes,boxes,
- 以字母f或者fe结尾的,直接去掉f或者fe,变成v再加es。leaf-leaves树叶,self-selves自己,knife-knives
- 以辅音y结尾的名词,变成i+es,factory-factories,city-cities
- 以o以为的名词,加上es,如hero-heroes,potato-potatoes
- 可数名词的不规则变化
- 单复数同型,词形一样。sheep绵阳,deer鹿
- 当单数变成复数,元音变了 foot-feet,man-men,woman-women,tooth-teeth,goose-geest 鹅
- 单数变复数,词尾发生了变化。但是不规则的child-children,ox-oxen公牛,phenomenon-phenomena 现象
- 复数有两种 peny-pence 价值peny-pennies 便士,work-works著作 work-work工作,people-people人,people-peoples民族
- 只有复数,没有单数trousers 裤子,clothes,shorts短裤,goods商品,glasses眼镜
10.名词所有格的用法
-
- 用’s
- My father's wish.
- 如果是词尾已经有s,那么加上’就可以
- The United States' policy. 美国的政策
- 在复合名词最后加’s,
- My brother-in-law's new flat。我姐夫的新公寓
- 当名词后面有同谓语的时候,将同谓语变成所有格.
- This is my sister,Marry's bicycle.
- 当由and构成的2个或者多个
- 如果是多者都共同拥有,那么直接在最后一个名词后面加’s
- John and Marry's school.
如果不是共同拥有,是各自拥有的话,需要在每一个名词后面都加’s
- Henry's,John' and Robert's cars.
- 如果是多者都共同拥有,那么直接在最后一个名词后面加’s
- 用’s
- 用介词of来表示
- 双从所有格: of+名词的所有格
- 特定人的不特定所有关系,但是不可以在不特指的前面加定冠词
- A latest work of my father's. 我父亲最近的一部作品,不指定是哪一部,特定的人
- another friend of George's. 乔治的另外一个朋友,另外一个朋友不特指,乔治特指
- 当表示特殊的情感的时候
- The dog of Tom's is very fierce. 凶狠。带着一种厌恶不赞赏的语气在里面,特定的人,特定的东西
- The sweet eyes of Marry's shock all of us. 赞赏的语气
- 特定人的不特定所有关系,但是不可以在不特指的前面加定冠词
11.人称代词的使用:
- 主格:做主语使用
- I, we,you,he, she,it,they,
- I am a teacher
- you are a student
- 单数人称顺序是2,3,1: You, he and I are all student.
- 复数人称顺序是1,2,3: We, you and they are all Chinese.
- 当承担责任的时候把自己放前面: I and he are to balme for the accident.都要尾这次事故负责任
- I, we,you,he, she,it,they,
- 宾格:作宾语使用
- me,us,you,him,her,it,them,
- buy it for me.
- let us go.
- me,us,you,him,her,it,them,
12.省略的使用:为了是句子更简单方便,突出重点内容,可以是省略单个词或者短语的省略甚至是整个句子的省略
- 省略某个词
- 一般是对介词省略
- Follow me (in) this way please
- 口语中对助动词和系动词进行省略
- you better have another try.最好再试一次 you have'd better
- you doing this on purpose? 口语中可以省略,书面语中不可以 you are
- 一般是对介词省略
- 对整个句子的省略
- 在前面不影响意思的情况下可以省略
- I'll say a word about your composition.我想对你的作文说几句话
- 习惯上的省略
- if only I could speak Japanese.如果我可以说日语就好了
- 在前面不影响意思的情况下可以省略
13.时态的用法:表示谓语动词发生的时间的一种变化形式
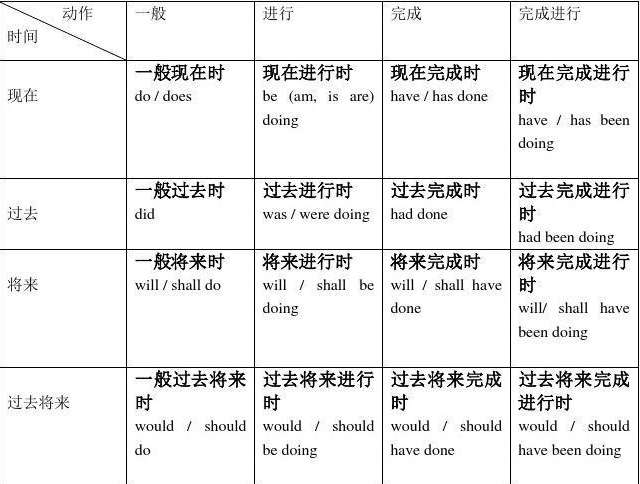
- 一般现在时:用来描述现在或者经常性的一种性质,动作或者状态的一种时态
- 表示客观真理的和客观存在,自然规律
- Knowledge is power.知识就是力量
- 习惯,经常性的
- where do you live and where do you work?你现在住哪里在哪里工作?
- 用于从句中的时候,表示将要发生的动作
- if it doesn't rain,we will go for a picnic as planned. 按计划去野餐(if 从句)
- 表示时间表已经拟定好的事情或者安排好的事情
- The final exam takes places next week. 期末考试下周举行
- 现在正在发生的动作或者状态
- Here comes the bus.公车来了
- 表示客观真理的和客观存在,自然规律
- 一般过去时:表示过去完成的事情,或者动作和状态
- She looked very well when I last saw her.
- 表示过去经常反复发生
- I always got up too late and never had enough time for breakfast.
- 当追溯逝去的人或者物
- The book was written by Mr.Liang Shiqiu.
- 表示过去将来发生的动作
- She said she would come if I promised to wait for her. 她那个时候说她要来
- 在since从句中,一般用一般过去时
- It's long time since she was ill. 病了很长一段时间
- 一般将来时
- will和shall这样的表示一般将来时
- I will see you tomorrow about the new plan.
be going to
- I am going to get some materials about Picasso. 我要去搜集一些毕加索的资料
- The Amerian president is to visit China next week.
- Don't go out ,we're about to have a dinner.
- We shouldn't quit, we are on the point of making it. 马上就要成功了
一般过去将来时:表示从过去的某一个时间点看来,将要发生的动作或者将要存在的一种状态。一般用在宾语从句或者间接引语。直接把will变成would再加v原型 - will和shall这样的表示一般将来时
- <----------A-------------B-------------现在-----------将来>
- 过去某时 过去将来时发生的动作
- 或存在的一种状态
- 直接把will变成would再加v原型
- Last week he promised that he would come, but he hasn't arrived until now. 上星期他说,是一般过去时,他要来是做过去的基础上说的将来要来。还没有来是现在完成时。promise后面接的时宾语从句
- 把上面的全部换成过去式就好 be going to
- You were going to give me your address, but you didn't. 你那个时候说会给我地址,但是你没有
- be about to
- I was about to turn on the power of the computer when the electricity was cut off. 准备打开电脑的时候电源断了
- Quncy told me that he would be seeing his parents next month.下周会去看他的父母。told表示是过去告诉我的,that引导的是told动词的宾语,宾语从句
- The interview that I would be going to made me nervours.将要去参加的面试让我觉得很紧张,made叙述过去的事实,什么样的面试呢?是我要去参加的面试,that从句做interview的定语
- 用在状语从句中
- Because Mara would be leaving soon,many of her friends feel very unwilling to live her. beacase引导的原因状语从句
- I can't make it at 9 o'clock, I'll be having a meeting.
- The president will be visiting us next week. 表示按照时间表这样走下去,到时候会发生的事情
- what will you be doing this evening? 今晚你做什么呢?(隐藏含义就是如果没什么事的话,就怎么怎么样)
- 跟一般将来时连用,表示在将来动作之后会做的事情
- My summer vacation will end very soon.I'll be having a classes. 假期快结束了,将要上课
- 过去进行时:相对于现在进行时,直接把系动词变成过去式,表示过去的某一段时间内正在进行的动作
- 表示过去的某一段时间内正在进行的动作
- What were you doing last year besides interviewing people?你除了采访人还做过什么
- 表示一个动作发生时,另一个动作正在进行
- When you called yesterday I was playing computer chess.
- 描述一个故事的情景
- It was a dark night, and it was snowing heavily. 那是一个很黑的夜晚,下的雪很大。
- 过去将要发生的一个动作
- He told me he was leaving for Shanghai tomorrow. 明天离开去上海
- 礼貌用语,不表示时态
- I was wondering if you could help me look up the word.不知道你能不能帮我查一下这个词呢
- 表示过去的某一段时间内正在进行的动作
- 现在完成时:是现在时和过去时的一种混合时态,它总和现在有密切关系,因此不能与表示确定的过去时间的状语如yesterday,last week等连用,。have/has+动词的过去分词
- 表示从过去某时开始,并且一直延续到现在,甚至还可以继续延续下去。常和表示持续时间的状语如for three years,since,so far,until now,这时谓语动词要求使用持续性动词
- Saturday he caught cold and has been in bed ever since. 周六感冒,直到现在还躺床上
- 表示到目前为止已经完成或刚完成,而其结果或影响保留到现在,通常使用非延续性v如arrive,become,begin,break,give,go,meet,recover,see等,有时可以带有表示起讫意义的时间状语如so far,up to now等和表示从过去直到包括现在在内的时间状语如:now,just,today,three few days,this morning等。
- She has arrived in China。她已经到了中国(指现在还在中国)
- 非持续性动词如arrive,become,begin,close,come,die,fall,hit,go,join,jump,knock,leave,meet,open,return,see,start等不能和表示一段时间的状语如for four days,since 2014等连用,但是由于v的否定形式可以和表示持续时间的状语连用。
- She has been here for two years,不可以说She had come here for two years。
- I haven't seen her for long time,不可以说 I have seen her for long time。
- 表示从过去直到包括现在在内的这段时间中的动作或者状态,如果反复发生或者多次出现,常和表示频度的时间状语如always,often,frequently,usually,regularly,repeatedly,sometimes,twice,every week,on Fridays,time and again等连用。可以不带时间状语,或和表示不确切过去时间的状语如already,ever,never,yet,recently,lately,of late,before等连用
- I've often wondered why I get such a poor reception on my radio.我常常感到纳闷,为什么我的收音机接受性能这么差。
- Twice he has tried and twice he has faild.他试了两次,两次都失败了
- Has she finished reading the novel yet? 她读完这本小说了吗?
- He's never been late before.他以前从未迟到过
- 在时间或条件状语从句中,现在完成时代替将来完成时,表示将来某一时间已经完成的动作。
- I'll let you konw when I've got an answer from him.我得到他答复后会通知你
- He'll go there as soon as he has finished his breakfast. 他吃完早饭立刻去那里
- I'll have to go back if the train has left.如果火车已经开走了,我只好回去。
- 表示从过去某时开始,并且一直延续到现在,甚至还可以继续延续下去。常和表示持续时间的状语如for three years,since,so far,until now,这时谓语动词要求使用持续性动词
- 过去完成时:表示在过去某一动作发生之前或某一时刻之前已经发生或已经结束的动作,所以可以说,它是一个相对的时态,不能离开过去某一时间而独立存在。使用过去完成时,就必须现有一个过去的某一时间才行,即“过去的过去”。 |---过去完成时态A-----|
- 图示: <过去-------------------B(过去某一时刻)---------现在-------------将来>
- 形式:had+动词的过去分词
- 用法:
- 1.表示过去某一时刻,某一动作之前已经发生的动作。如果动作已经完成,常和by,before等介词短语或者时间状语从句连用;如果动作已经开始,一直延续到过去某一时刻,通常和表示一段时间的状语(如since引导的从句或短语或for引出的短语)连用。这类句子多用于宾语从句,主句中的谓语如know,think,find,decide,remember等用了一般过去时,如果宾语从句的谓语所表示的动作先发生,则用过去完成时,例如:
- The young man felt he had acted foolishly.这个年轻人觉得自己已经干了傻事。
- Her father was more difficult. He didn't believe that Tess had married at all. 她父亲就更难对付了。他根本就不相信苔丝是结了婚的。
- 2.用来追述以前发生的事情,并说明原因。例如
- He looked rather pale.He had been ill for some time. 他的脸色相当苍白,因为他曾经病了一段时间。
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 1.表示过去某一时刻,某一动作之前已经发生的动作。如果动作已经完成,常和by,before等介词短语或者时间状语从句连用;如果动作已经开始,一直延续到过去某一时刻,通常和表示一段时间的状语(如since引导的从句或短语或for引出的短语)连用。这类句子多用于宾语从句,主句中的谓语如know,think,find,decide,remember等用了一般过去时,如果宾语从句的谓语所表示的动作先发生,则用过去完成时,例如:
- 将来完成时
- 过去将来完成时
- 现在完成进行时
- 过去完成进行时
- 将来完成进行时
- 过去将来完成进行时