插入节点
在链表中插入节点有以下三种情形:
1、在链表头部
2、在特定节点
3、在链表尾部
1)在头部添加(4步操作)
新节点添加到头部,将成为新的头节点,以下将节点添加到链表头部的函数是push,push接收指向链表头部的指针,然后将指针修改

指向新的节点:
c语言:
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list
and an int, inserts a new node on the front of the list. */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* 1. allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* 2. put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* 3. Make next of new node as head */
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
/* 4. move the head to point to the new node */
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
Java:
/* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a
new Node at front of the list. This method is
defined inside LinkedList class shown above */
public void push(int new_data)
{
/* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node &
Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 3. Make next of new Node as head */
new_node.next = head;
/* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */
head = new_node;
}
push时间复杂度O(1)
2)在特定节点(5步操作)
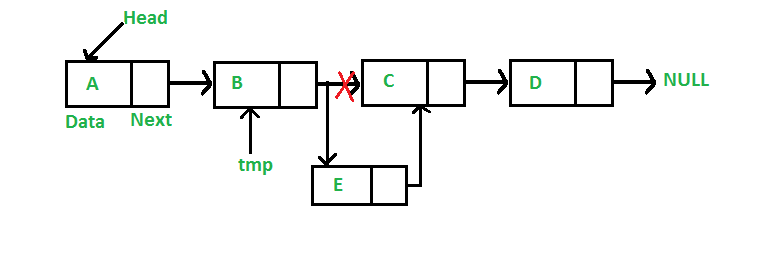
c语言:
/* Given a node prev_node, insert a new node after the given
prev_node */
void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node, int new_data)
{
/*1. check if the given prev_node is NULL */
if (prev_node == NULL)
{
printf("the given previous node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
/* 2. allocate new node */
struct Node* new_node =(struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
/* 3. put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* 4. Make next of new node as next of prev_node */
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
/* 5. move the next of prev_node as new_node */
prev_node->next = new_node;
}
java:
/* This function is in LinkedList class.
Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. This method is
defined inside LinkedList class shown above */
public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data)
{
/* 1. Check if the given Node is null */
if (prev_node == null)
{
System.out.println("The given previous node cannot be null");
return;
}
/* 2. Allocate the Node &
3. Put in the data*/
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */
new_node.next = prev_node.next;
/* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */
prev_node.next = new_node;
}
因为已经给定了节点,所以insertAfter时间复杂为O(1)
3)在链表尾部(6个步骤)
我们需要遍历链表,得到最后一个节点,然后把新节点追加到最后,然后让他成为新的尾部节点

c语言:
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head
of a list and an int, appends a new node at the end */
void append(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
/* 1. allocate node */
struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
struct Node *last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/
/* 2. put in the data */
new_node->data = new_data;
/* 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next
of it as NULL*/
new_node->next = NULL;
/* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */
if (*head_ref == NULL)
{
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
/* 5. Else traverse till the last node */
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
/* 6. Change the next of last node */
last->next = new_node;
return;
}
java:
/* Appends a new node at the end. This method is
defined inside LinkedList class shown above */
public void append(int new_data)
{
/* 1. Allocate the Node &
2. Put in the data
3. Set next as null */
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
/* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the
new node as head */
if (head == null)
{
head = new Node(new_data);
return;
}
/* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so
make next of it as null */
new_node.next = null;
/* 5. Else traverse till the last node */
Node last = head;
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
/* 6. Change the next of last node */
last.next = new_node;
return;
}
因为需要从头到尾循环,所以append时间复杂度为O(n),其中n是节点的个数。
当然你可以修改结构,保存尾节点,使其复杂度降为O(1)
来源:https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/linked-list-set-2-inserting-a-node/