简介
List、Deque接口的双链列表实现。实现所有可选的列表操作,并允许null元素。
此实现非线程安全,如果多个线程同时访问链表,并且至少一个线程在结构上修改了链表,则它必须从外部同步。
可以这样构造同步集合:Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList(…))
所谓结构上修改链表,就是会影响链表长度的操作,比如添加,删除,像set修改就不会影响结构。
迭代器支持快速失败,而不是在将来的不确定时间内冒着不确定的行为风险。
类继承关系
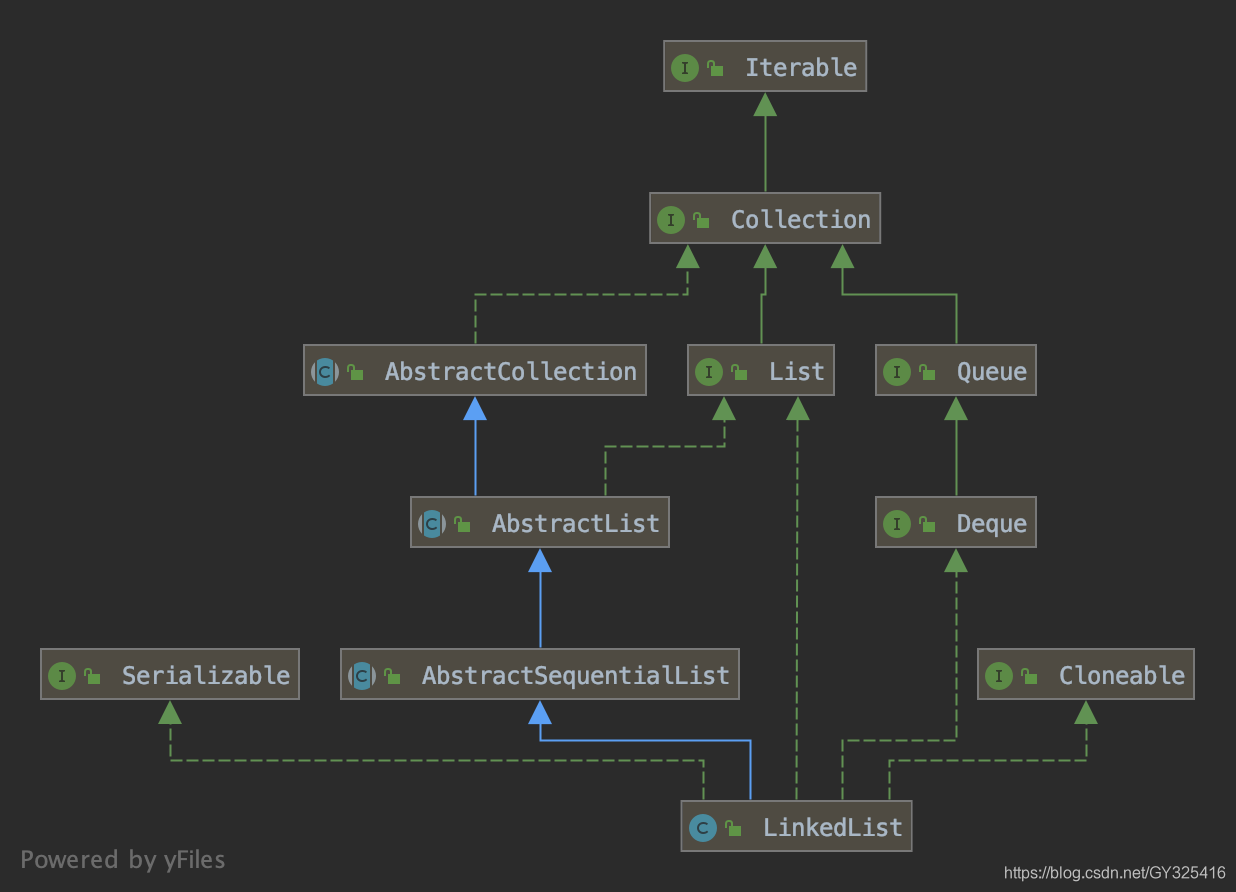
Serializable 标志可被序列化
Cloneable 标志能被复制
实现Deque(双端队列)接口 能够在头和尾操作元素
继承AbstractSequentialList类 提供了顺序访问的基本实现
属性
transient int size = 0; //元素个数
transient Node<E> first; //指向第一个节点的指针
transient Node<E> last; //指向最后一个节点的指针
构造方法
//构造一个空集合
public LinkedList() {
}
//构造一个包含指定数据的集合
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
内部类
private static class Node<E> {
E item; //当前节点
Node<E> next; //下一个节点指针
Node<E> prev; //前一个节点指针
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
private class ListItr implements ListIterator<E> {
...... //实现了hasnext next hasPrevious previous等迭代器方法
}
主要方法
// 将元素e作为第一个节点
// 这里指针操作值得仔细品味
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first; //f指向第一个节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);//构造节点
first = newNode;//first指针指向新构造节点 注意:此时f仍然指向原来的第一个节点
//如果原来的节点为空 说明集合为空 随即将尾节点指向新构造节点
//否则就将原来的头节点前驱指向新节点
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
f.prev = newNode;
size++;//容量加一
modCount++;//修改次数加一
}
//将元素e作为最后的节点
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
// 将元素e插入非空节点succ前面
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//移除非空的第一个节点f
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
//取出来当前元素和下一个节点
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
//将当前元素的指针置空 以使gc回收
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next; //first指向下一个节点
//如果下一个节点为空 说明集合原本就一个元素 随即将尾节点置空
//否则将下一个节点(也即是将来的手节点)的前驱置空
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
//取消链接非空的最后一个节点l
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
final E element = l.item;
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
// 取消链接非空节点x
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
删除
// 循环找到第一个元素删除
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//循环将每个节点的元素置空
public void clear() {
//先清除中间元素
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) {
Node<E> next = x.next;
x.item = null;
x.next = null;
x.prev = null;
x = next;
}
first = last = null;//首尾节点清空
size = 0;//容量置零
modCount++;
}
查找元素
//循环比对找到第一个相同的元素位置
public int indexOf(Object o) {
int index = 0;
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null)
return index;
index++;
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item))
return index;
index++;
}
}
return -1;
}
栈操作
//
//入栈
public void push(E e) {
addFirst(e);
}
//出栈
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
// 还有很多其他队列操作
总结
LinkedList是一个双向链表,还是一个双端队列,队列,栈
在首尾插入删除效率高,复杂度O(1)
在链表中间删除查找效率低,平均复杂度O(n)
没有下标,不能随机访问,访问除了首尾元素外比较低效