一:二叉树的基本知识:
二叉树是每个节点最多有两个子树的树结构。通常子树被称作“左子树”(left subtree)和“右子树”(right subtree)。二叉树常被用于实现二叉查找树和二叉堆。
二叉树的每个结点至多只有二棵子树(不存在度大于2的结点),二叉树的子树有左右之分,次序不能颠倒。二叉树的第i层至多有 个结点;深度为k的二叉树至多有
个结点;深度为k的二叉树至多有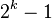 个结点;对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为
个结点;对任何一棵二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为 ,度为2的结点数为
,度为2的结点数为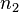 ,则
,则 。
。
满二叉树:在一棵二叉树中,如果所有的分支结点都存在左子树和右子树,并且所有的叶子结点都在同一层上。
完全二叉树:一棵深度为K的n个结点的二叉树,对树中的结点从上到下,从左到右编号,如果编号为i的结点与满二叉树中的编号为i的结点在二叉树中的位置相同,称这颗树为完全二叉树。
二:二叉树的构建及遍历:
顺序树:abd,,e,,cf,,g,,
先序遍历打印:abdecfg
中序遍历打印:dbeafcg
后序遍历打印:dbefcga
已知一个按先序序列输入的字符序列,如abc,,de,g,,f,,,(其中逗号表示空节点)。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> struct tree { char data; struct tree *l,*r; }; //构建二叉树 tree *build(tree *t) { char ch; if((ch=getchar())==',') //如果输入为',' 则指针悬空 { t=NULL; } else { t=(struct tree *)malloc(sizeof(struct tree)); t->data=ch; t->l =build(t->l);//建立左子树 t->r =build(t->r);//建立右子树 } return t; } //访问根 按照先序遍历访问左子树 按照先序遍历访问右子树 void pre(tree *t) { if(t!=NULL) { printf("%c",t->data); pre(t->l); pre(t->r); } } //按中序遍历左子树;访问根;按中序遍历右子树 void inprime(tree *t) { if(t!=NULL) { inprime(t->l); printf("%c",t->data); inprime(t->r); } } //按后序遍历左子树;按后序遍历右子树;访问根 void outprime(tree *t) { if(t!=NULL) { outprime(t->l); outprime(t->r); printf("%c",t->data); } } //计算树叶数 int count=0; void leaves (tree *t) { if(t!=NULL) { if(t->l==NULL && t->r==NULL) { count ++; } leaves(t->l); leaves(t->r); } } // 计算树的深度 int deep(tree *t) { int lch,rch; if(!t)//t为空时返回值0 { return 0; } else { lch = deep(t->l); rch = deep(t->r); if(lch>rch) { return lch+1; } else return rch+1; } } int main () { int n; struct tree *t; t=build(t);//构建二叉树 pre(t);//按先序遍历 printf(" "); inprime(t);//按中序遍历 printf(" "); outprime(t);//按后序遍历 printf(" "); leaves(t);//计算树叶数 printf("%d ",count); n=deep(t);//计算树的深度 printf("%d ",n); return 0; }
三:二叉树的层次遍历:(参考http://www.cnblogs.com/pony1993/archive/2012/02/28/2371900.html)
当输入ABC,,DE G,,F,,结果是ABCDEFG “ ,”代表空
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostream> struct tree { char data; struct tree *l,*r; }; //构建二叉树 tree *build(tree *t) { char ch; if((ch=getchar())==',') //如果输入为',' 则指针悬空 { t=NULL; } else { t=(struct tree *)malloc(sizeof(struct tree)); t->data=ch; t->l =build(t->l);//建立左子树 t->r =build(t->r);//建立右子树 } return t; } //用队列 实现层次遍历 void cheep(tree *t) { int front=0,rear=1;//front下标跟踪输出 rear记录子树 tree *q[100];//建立队列 q[0]=t; while(front <rear) { if(q[front]) { printf("%c",q[front]->data); q[rear++]=q[front]->l;//如果存在右子树,右子树进队列 q[rear++]=q[front]->r;//如果存在左子树,左子树进队列 front++; } else front++; } } int main () { int n; struct tree *t; t=build(t);//构建二叉树 cheep(t); return 0; }
四:如何由先序遍历,中序遍历还原二叉树:
tree *creat(char *pre,char *in,int len) { int k; if(len<=0) return NULL; tree*head; head=(tree*)malloc(sizeof(tree)); head->data=*pre; char *p; for(p=in;p!=NULL;p++) if(*p==*pre) break;// 在中序遍历的序列中得到与先序相同的节点 k=p-in; head->l=creat(pre+1,in,k);//递归得到左子树 head->r=creat(pre+k+1,p+1,len-k-1);//得到右子树 return head; }