本文转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/weilu2/p/springsecurity_custom_decision_metadata.html
本文在SpringMVC和MyBatis项目框架的基础上整合Spring Security作为权限管理。并且完全实现一套自定义的权限管理规则。
1.权限管理
在本例中所使用的权限管理的思路如下图所示,在系统中存在着许多帐号,同时存在着许多资源,在一个Web系统中一个典型的资源就是访问页面的URL,控制了这个就能够直接控制用户的访问权。
由于资源非常多,直接针对资源与用户进行设置关系会比较繁琐,因此针对同一类或者同一组的资源打个包,称为一组权限,这样将权限分配给用户的时候,一组权限中的资源也就都分配给用户了。
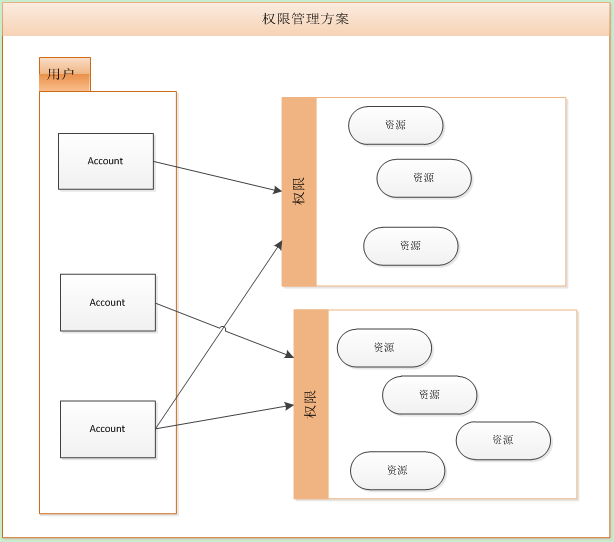
这个只是一个非常简单的权限管理方案,并且只能适用于较小的项目,因为此处给出这个只是为了便于理解自定义的Spring Security认证规则。
2.Spring Security的认证规则
要编写自定义的认证规则,首先需要对Spring Security中的认证规则有一定的了解,下面简单介绍下Spring Security的认证规则。
1)在Spring Security中每个URL都是一个资源,当系统启动的时候,Spring Security会根据配置将所有的URL与访问这个URL所需要的权限的映射数据加载到Spring Security中。
2)当一个请求访问一个资源时,Spring Security会判断这个URL是否需要权限验证,如果不需要,那么直接访问即可。
3)如果这个URL需要进行权限验证,那么Spring Security会检查当前请求来源所属用户是否登录,如果没有登录,则跳转到登录页面,进行登录操作,并加载这个用户的相关信息
4)如果登录,那么判断这个用户所拥有的权限是否包含访问这个URL所需要的权限,如果有则允许访问
5)如果没有权限,那么就给出相应的提示信息
3.自定义认证规则思路
根据上面一小节介绍的Spring Security认证的过程,我们相应的就能够分析出对于这个过程我们如果要修改的话,需要进行哪些方面的改动。
3.1.自定义SecurityMetadataSource
在Spring Security中的 SecurityMetadataSource 处于上面的步骤一中,也就是用于加载URL与权限对应关系的,对于这个我们需要自己进行定义
package com.oolong.customsecurity; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import org.apache.log4j.LogManager; import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute; import org.springframework.security.access.SecurityConfig; import org.springframework.security.web.FilterInvocation; import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 加载URL与权限资源,并提供根据URL匹配权限的方法 * @author weilu2 * @date 2016年12月17日 上午11:18:52 * */ @Component public class CustomSecurityMetadataSource implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource { private Map<String, List<ConfigAttribute>> resources; public CustomSecurityMetadataSource() { loadAuthorityResources(); } private void loadAuthorityResources() { // 此处在创建时从数据库中初始化权限数据 // 将权限与资源数据整理成 Map<resource, List<Authority>> 的形式 // 注意:加载URL资源时,需要对资源进行排序,要由精确到粗略进行排序,让精确的URL优先匹配 resources = new HashMap<>(); // 此处先伪造一些数据 List<ConfigAttribute> authorityList = new ArrayList<>(); ConfigAttribute auth = new SecurityConfig("AUTH_WELCOME"); authorityList.add(auth); resources.put("/welcome", authorityList); } @Override public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes(Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException { String url = ((FilterInvocation) object).getRequestUrl(); Set<String> keys = resources.keySet(); for (String k : keys) { if (url.indexOf(k) >= 0) { return resources.get(k); } } return null; } @Override public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return null; } @Override public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) { return true; } }
在这个类中,实现了FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource接口,这个接口中的 getAttributes(Object object)方法能够根据请求的URL,获取这个URL所需要的权限,那么我们就可以在这个类初始化的时候将所有需要的权限加载进来,然后根据我们的规则进行获取,因此这里还需要编写一个加载数据的方法 loadAuthorityResources(),并且在构造函数中调用。
此处加载资源为了简化,只是随意填充了一些数据,实际可以从数据库中获取。
3.2.自定义AccessDecisionManager
编写自定义的决策管理器,决策管理器是Spring Security用来决定对于一个用户的请求是否基于通过的中心控制。
package com.oolong.customsecurity; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; import org.apache.log4j.LogManager; import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDecisionManager; import org.springframework.security.access.AccessDeniedException; import org.springframework.security.access.ConfigAttribute; import org.springframework.security.authentication.InsufficientAuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication; import org.springframework.security.core.GrantedAuthority; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 进行决策,根据URL获得访问这个资源所需要的权限,然后在与当前用户所拥有的权限进行对比 * 如果当前用户拥有相关权限,就直接返回,否则抛出 AccessDeniedException异常 * @author weilu2 * @date 2016年12月17日 上午11:30:40 * */ @Component public class CustomAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager { @Override public void decide(Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException { LogManager.getLogger("CustomAccessDecisionManager").info("decide invoke"); if (configAttributes == null) { return; } if (configAttributes.size() <= 0) { return; } Iterator<ConfigAttribute> authorities = configAttributes.iterator(); String needAuthority = null; while(authorities.hasNext()) { ConfigAttribute authority = authorities.next(); if (authority == null || (needAuthority = authority.getAttribute()) == null) { continue; } LogManager.getLogger("CustomAccessDecisionManager").info("decide == " + needAuthority); for (GrantedAuthority ga : authentication.getAuthorities()) { if (needAuthority.equals(ga.getAuthority().trim())) { return; } } } throw new AccessDeniedException("No Authority"); } @Override public boolean supports(ConfigAttribute attribute) { return true; } @Override public boolean supports(Class<?> clazz) { return true; } }
决策管理器最重要的就是这个 decide()方法,Spring Security会将当前登录用户信息包装到一个 Authentication对象中,并传入这个方法;并且调用 SecurityMetadataSource.getAttributes() 方法获取这个URL相关的权限以参数 Collection<ConfigAttribute> 的形式传入这个方法。
然后这个decide方法获取到这两个信息之后就可以进行对比决策了。如果当前用户允许登录,那么直接return即可。如果当前用户不许运行登录,则抛出一个 AccessDeniedException异常。
3.3.自定义 UserDetailsService 和 AuthenticationProvider
前面说过,要进行验证,除了有URL与权限的映射关系,还需要有用户的权限信息。要编写自定义的用户数据加载,就需要实现这两个接口。
3.3.1.UserDetailsService
package com.oolong.customsecurity; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.apache.log4j.LogManager; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import com.oolong.model.AccountInfoModel; import com.oolong.model.AuthorityModel; @Component public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService { @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException { LogManager.getLogger("CustomUserDetailsService").info("loadUserByUsername invoke"); // 提供到数据库查询该用户的权限信息 // 关于角色和权限的转换关系在此处处理,根据用户与角色的关系、角色与权限的关系, // 将用户与权限的管理整理出来 // 此处伪造一些数据 // 伪造权限 AuthorityModel authority = new AuthorityModel("AUTH_WELCOME"); List<AuthorityModel> authorities = new ArrayList<>(); authorities.add(authority); AccountInfoModel account = new AccountInfoModel("oolong", "12345"); account.setAuthorities(authorities); return account; } }
3.3.2.AuthenticationProvider
AuthenticationProvider用于包装UserDetailsService,并将其提供给 Spring Security使用。这个接口中最重要的是实现 retrieveUser() 方法,这个请参考接口的说明进行实现,此处不再赘述。
package com.oolong.customsecurity; import org.apache.log4j.LogManager; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationServiceException; import org.springframework.security.authentication.BadCredentialsException; import org.springframework.security.authentication.UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken; import org.springframework.security.authentication.dao.AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider; import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetailsService; import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UsernameNotFoundException; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 这两个方法用于添加额外的检查功能,此处不需要添加,因此空着,直接实现这个抽象类即可。 * @author weilu2 * @date 2016年12月17日 下午12:20:27 * */ @Component public class CustomUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider extends AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider { @Autowired private UserDetailsService userDetailsService; public UserDetailsService getUserDetailService() { return this.userDetailsService; } public void setUserDetailService(UserDetailsService userDetailsService) { this.userDetailsService = userDetailsService; } @Override protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException { } @Override protected UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException { LogManager.getLogger("CustomUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider").info("retrieveUser invoke"); if (userDetailsService == null) { throw new AuthenticationServiceException(""); } UserDetails userDetails = userDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(username); if (userDetails == null) { throw new UsernameNotFoundException(username); } if (userDetails.getUsername().equals(authentication.getPrincipal().toString()) && userDetails.getPassword().equals(authentication.getCredentials().toString())) { return userDetails; } throw new BadCredentialsException(username + authentication.getCredentials()); } }
3.4.UserDetails和GrantedAuthority
这两个接口非常简单,请参考源码,此处不再赘述
4.配置
上面编写的这些自定义的实现都有了,但是仅仅这样是没有用的,如何配置能够让它们起作用呢?
package com.oolong.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter; import org.springframework.security.web.access.ExceptionTranslationFilter; import org.springframework.security.web.access.intercept.FilterSecurityInterceptor; import com.oolong.customsecurity.CustomAccessDecisionManager; import com.oolong.customsecurity.CustomSecurityMetadataSource; import com.oolong.customsecurity.CustomUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider; import com.oolong.customsecurity.TempHook; @Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackageClasses={TempHook.class}) @EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private CustomUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider customAuthenticationProvider; @Autowired private CustomAccessDecisionManager customAccessDecisionManager; @Autowired private CustomSecurityMetadataSource customSecurityMetadataSource; @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth.authenticationProvider(customAuthenticationProvider); } @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http.addFilterAfter(customFilterSecurityInterceptor(), ExceptionTranslationFilter.class); http.formLogin(); } @Bean public FilterSecurityInterceptor customFilterSecurityInterceptor() { FilterSecurityInterceptor fsi = new FilterSecurityInterceptor(); fsi.setAccessDecisionManager(customAccessDecisionManager); fsi.setSecurityMetadataSource(customSecurityMetadataSource); return fsi; } }
在Spring MVC中,Spring Security是通过过滤器发挥作用的,因此我们就爱那个决策管理器与数据加载放到一个过滤器中,然后将这个过滤器插入到系统的过滤器链中。
此外,我们向系统中提供了一个用于检索用户的 AuthenticationProvicer。
还有,别忘记了,告诉系统,如果用户没有权限应该怎么办,http.formLogin(),告诉Spring Security要跳转到表单登录页面。
参考