原文: https://blog.mrfrontend.org/2017/10/2-ways-get-child-elements-javascript/
Along the lines of other frameworks such as jQuery or Prototype, shortening the "querySelector" name can be convenient:
function $ (selector, el) {
if (!el) {el = document;}
return el.querySelector(selector);
}
function $$ (selector, el) {
if (!el) {el = document;}
return el.querySelectorAll(selector);
// Note: the returned object is a NodeList.
// If you'd like to convert it to a Array for convenience, use this instead:
// return Array.prototype.slice.call(el.querySelectorAll(selector));
}
alert($('#myID').id);
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In jQuery, it is super easy to get the child elements of a parent HTML element. But do you know how it works with Vanilla JavaScript?
Today I want to show you 2 ways how you can use Vanilla JavaScript to get the child elements, even when you don’t know what’s in the parent element.
If you like reading instead of watching a video? Please scroll down to continue reading.
Looking for the video resources? Scroll to the bottom!
Let’s start with a simple webshop page.
HTML
<header class="product__list-header">
<h2>Webshop</h2>
</header>
<section class="product__list">
<div class="product__item">
<img src="http://lorempixel.com/400/200/food" class="product__image" alt="Food">
<span class="product__price">500</span>
</div>
<div class="product__item fun__class">
<img src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/food" class="product__image" alt="Food">
<span class="product__price">500</span>
</div>
<div class="product__item">
<img src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/food" class="product__image" alt="Food">
<span class="product__price">500</span>
</div>
<div class="product__item">
<img src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/food" class="product__image" alt="Food">
<span class="product__price">500</span>
</div>
<div class="product__item">
<img src="https://lorempixel.com/400/200/food" class="product__image" alt="Food">
<span class="product__price">500</span>
</div>
</section>
As you noticed, I used BEM as naming convention for my webshop example page.
#1 element.children
The first way to get the child elements is with the element.children. If you want to check out what kind of properties the DOM Element Object has for you, check it on W3schools. That is btw one of my favorite websites to check JavaScript example’s & documentation.
JavaScript
var productList = document.querySelector('.product__list').children;
console.log('productList: ', productList);
In the console log, you will find a.HTMLCollection Check the property__proto__, you will find out that he is not an Array.
Loop over the children
The children property will return a.HTMLCollection So you can loop over it with the plain-old For-loop.
for (i = 0; i < productList.length; i++) {
console.log('productList[i]: ', productList[i]);
}
Check my element.children jsbin example.
#2 document.querySelectorAll
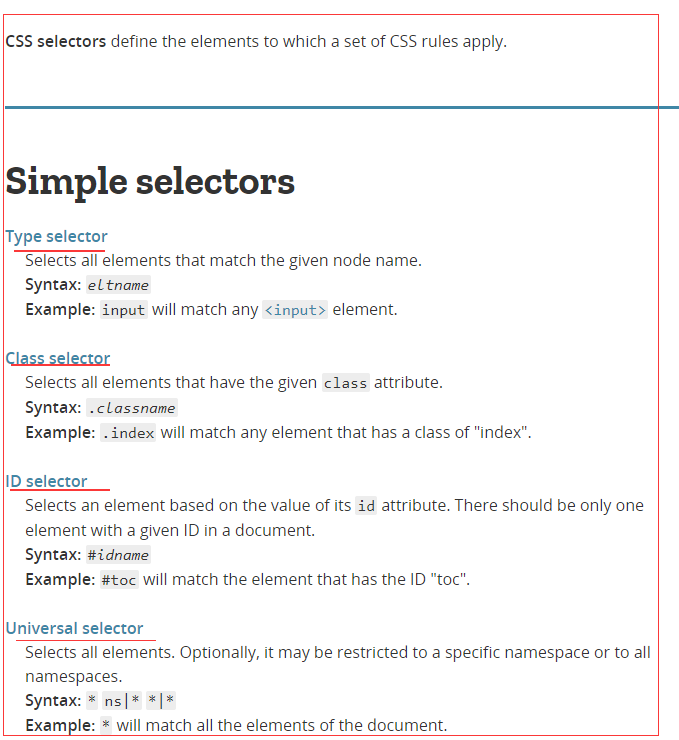
If you know which elements are in a parent element, you can adjust the selector to:..product__list .product__item With this selector, you target al the product items inside the product list.
If you don’t know which elements are in the parent element, I would recommend the element.children way. Because then you will definitely get all the children back.
Maybe you remind the querySelectorAll from my previous blog post, but I don’t mind to show it again .
JavaScript
var productList = document.querySelectorAll('.product__list .product__item');
console.log('productList: ', productList);
In the console log, you will find a NodeList. If you check the __proto__ you will find out that he is not an Array.
Just like the HTMLCollection, you can use the For-loop to loop over each element in the NodeList.
for (i = 0; i < productList.length; i++) {
console.log('product: ', productList[i]);
}
Check my querySelectorAll jsbin example.
Conclusion: element.children VS querySelectorAll
But now is the question, which one do you use?
You know the child elements
In the case you know what child elements there are in the parent element, it is good to use the document.querySelectorAll method.
This a much faster way to target them with the CSS selector. And because of the, querySelectorAll it doesn’t matter how much elements there are.
You don’t know the child elements
In the case you don’t know what child elements you can expect, you need the. element.children All the elements inside the parent element will come back with the DOM Element Object.