参考: https://golangcode.com/checking-if-date-has-been-set/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/20924303/date-time-comparison-in-golang
// utc life
loc, _ := time.LoadLocation("UTC")
// setup a start and end time
createdAt := time.Now().In(loc).Add(1 * time.Hour)
expiresAt := time.Now().In(loc).Add(4 * time.Hour)
// get the diff
diff := expiresAt.Sub(createdAt)
fmt.Printf("Lifespan is %+v", diff)---------------------------------------------------------------
Check If a Date/Time Has Been Set with IsZero
In Go, we can store and use dates using the time package and although a date in Go cannot be saved as null (because there’s no such thing) there is an unset state. This unset state can be shown as 0001-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 UTC and there’s a simple way we can check if a date variable has been populated, as demonstrated below. It’s also important to note that these are not unix timestamps, which go back as far as 1970, but can handle a large spectrum of dates.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func main() {
var myDate time.Time
// IsZero returns a bool of whether a date has been set, but as the printf shows it will
// still print a zero-based date if it hasn't been set.
if myDate.IsZero() {
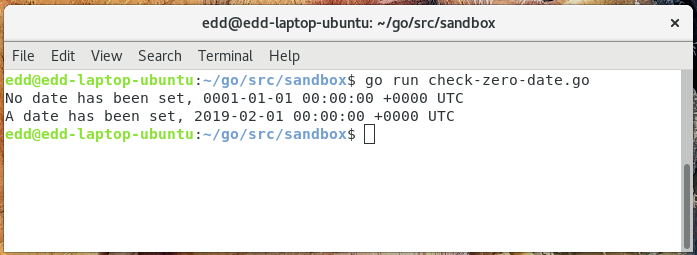
fmt.Printf("No date has been set, %s
", myDate)
}
// Demonstrating that by setting a date, IsZero now returns false
myDate = time.Date(2019, time.February, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, time.UTC)
if !myDate.IsZero() {
fmt.Printf("A date has been set, %s
", myDate)
}
}
Use the time package to work with time information in Go.
Time instants can be compared using the Before, After, and Equal methods. The Sub method subtracts two instants, producing a Duration. The Add method adds a Time and a Duration, producing a Time.
Play example:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
)
func inTimeSpan(start, end, check time.Time) bool {
return check.After(start) && check.Before(end)
}
func main() {
start, _ := time.Parse(time.RFC822, "01 Jan 15 10:00 UTC")
end, _ := time.Parse(time.RFC822, "01 Jan 16 10:00 UTC")
in, _ := time.Parse(time.RFC822, "01 Jan 15 20:00 UTC")
out, _ := time.Parse(time.RFC822, "01 Jan 17 10:00 UTC")
if inTimeSpan(start, end, in) {
fmt.Println(in, "is between", start, "and", end, ".")
}
if !inTimeSpan(start, end, out) {
fmt.Println(out, "is not between", start, "and", end, ".")
}
}