题目太长啦!文档下载【传送门】
第1题
简述:实现逻辑回归。
此处使用了minimize函数代替Matlab的fminunc函数,参考了该博客【传送门】。
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import scipy.optimize as op 4 5 #S函数 6 def sigmoid(z): 7 g = 1/(1+np.exp(-z)) 8 return g 9 10 #cost计算函数 11 def costFunction(theta, X, y): 12 theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta),1)) 13 m = np.size(y) 14 h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta)) 15 J = 1/m*(-np.dot(y.T, np.log(h)) - np.dot((1-y.T), np.log(1-h))) 16 return J.flatten() 17 18 def gradient(theta, X, y): 19 theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta), 1)) 20 m = np.size(y) 21 h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta)) 22 grad = 1/m*np.dot(X.T, h - y) 23 return grad.flatten() 24 25 26 #读取数据,第一列是成绩1,第二列是成绩2,第三列是yes/no 27 data = np.loadtxt('ex2data1.txt', delimiter=',', dtype='float') 28 m = np.size(data[:, 0]) 29 # print(data) 30 31 #绘制样本点 32 X = data[:, 0:2] 33 y = data[:, 2:3] 34 pos = np.where(y == 1)[0] 35 neg = np.where(y == 0)[0] 36 X1 = X[pos, 0:2] 37 X0 = X[neg, 0:2] 38 plt.plot(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], 'k+') 39 plt.plot(X0[:, 0], X0[:, 1], 'yo') 40 plt.xlabel('Exam 1 score') 41 plt.ylabel('Exam 2 score') 42 43 #求解最优解 44 one = np.ones(m) 45 X = np.insert(X, 0, values=one, axis=1) 46 initial_theta = np.zeros(np.size(X, 1)) 47 result = op.minimize(fun=costFunction, x0=initial_theta, args=(X, y), method='TNC', jac=gradient) 48 # print(result) 49 theta = result.x 50 cost = result.fun 51 print('theta:', theta) 52 print('cost:', cost) 53 54 #绘制决策边界 55 plot_x = np.array([np.min(X[:, 1]), np.max(X[:, 2])]) 56 # print(plot_x) 57 plot_y = (-1/theta[2])*(theta[1]*plot_x+theta[0]) 58 # print(plot_y) 59 plt.plot(plot_x,plot_y) 60 plt.legend(labels=['Admitted', 'Not admitted']) 61 plt.axis([30, 100, 30, 100]) 62 plt.show() 63 64 #预测[45 85]成绩的学生,并计算准确率 65 theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta),1)) 66 z = np.dot([1, 45, 85], theta) 67 prob = sigmoid(z) 68 print('For a student with scores 45 and 85, we predict an admission probability of ', prob) 69 p = np.round(sigmoid(np.dot(X,theta))) 70 acc = np.mean(p==y)*100 71 print('Train Accuracy: ',acc,'%')
运行结果:
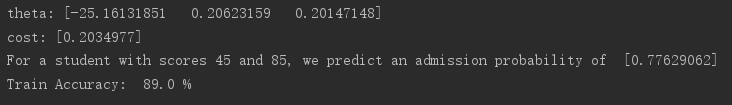
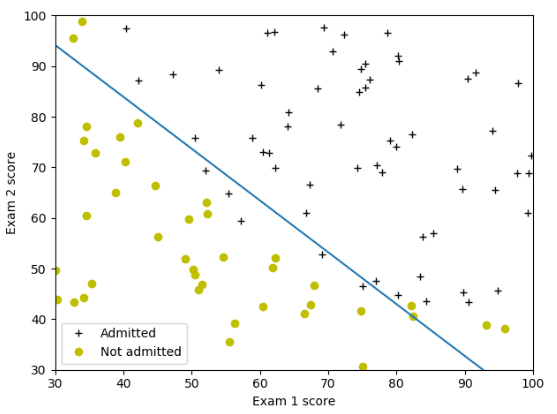
第2题
简述:通过正规化实现逻辑回归。
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import scipy.optimize as op 4 5 #S函数 6 def sigmoid(z): 7 g = 1/(1+np.exp(-z)) 8 return g 9 10 #cost计算函数 11 def costFunction(theta, X, y, lamb): 12 theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta), 1)) 13 m = np.size(y) 14 h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta)) 15 J = 1/m*(-np.dot(y.T, np.log(h)) - np.dot((1-y.T), np.log(1-h))) 16 # 添加项 17 theta2 = theta[1:, 0] 18 Jadd = lamb/(2*m)*np.sum(theta2**2) 19 J = J + Jadd 20 return J.flatten() 21 22 #求梯度 23 def gradient(theta, X, y, lamb): 24 theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta), 1)) 25 m = np.size(y) 26 h = sigmoid(np.dot(X, theta)) 27 grad = 1/m*np.dot(X.T, h - y) 28 #添加项 29 theta[0,0] = 0 30 gradadd = lamb/m*theta 31 grad = grad + gradadd 32 return grad.flatten() 33 34 #求特征矩阵 35 def mapFeature(X1, X2): 36 degree = 6 37 out = np.ones((np.size(X1),1)) 38 for i in range(1, degree+1): 39 for j in range(0, i+1): 40 res = np.multiply(np.power(X1, i-j), np.power(X2, j)) 41 out = np.insert(out, np.size(out[0, :]), values=res, axis=1) 42 return out 43 44 45 46 #读取数据,第一列是成绩1,第二列是成绩2,第三列是yes/no 47 data = np.loadtxt('ex2data2.txt', delimiter=',', dtype='float') 48 m = np.size(data[:, 0]) 49 50 #绘制样本点 51 X = data[:, 0:2] 52 y = data[:, 2:3] 53 pos = np.where(y == 1)[0] 54 neg = np.where(y == 0)[0] 55 X1 = X[pos, 0:2] 56 X0 = X[neg, 0:2] 57 plt.plot(X1[:, 0], X1[:, 1], 'k+') 58 plt.plot(X0[:, 0], X0[:, 1], 'yo') 59 plt.xlabel('Microchip Test 1') 60 plt.ylabel('Microchip Test 2') 61 plt.legend(labels=['y = 1', 'y = 0']) 62 63 #数据初始化 64 X = mapFeature(X[:, 0], X[:, 1]) 65 # print(X) 66 lamb = 1 67 initial_theta = np.zeros(np.size(X, 1)) 68 69 #求解最优解 70 result = op.minimize(fun=costFunction, x0=initial_theta, args=(X, y, lamb), method='TNC', jac=gradient) 71 # print(result) 72 cost = result.fun 73 theta = result.x 74 print('theta:', theta) 75 print('cost:', cost) 76 77 #绘制决策边界 78 u = np.linspace(-1, 1.5, 50) 79 v = np.linspace(-1, 1.5, 50) 80 z = np.zeros((np.size(u),np.size(v))) 81 theta = np.array(theta).reshape((np.size(theta), 1)) 82 for i in range(0, np.size(u)): 83 for j in range(0, np.size(v)): 84 z[i, j] = np.dot(mapFeature(u[i], v[j]), theta) 85 # print(z) 86 plt.contour(u, v, z.T, [0]) 87 plt.show() 88 89 #计算准确率 90 p = np.round(sigmoid(np.dot(X,theta))) 91 acc = np.mean(p==y)*100 92 print('Train Accuracy: ',acc,'%')
运行结果:

