一、概述
一般问题:数据集合固定,而遍历方式多变。
核心方案:提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中的各种元素,而又不暴露该对象的内部表示。
设计意图:从学习编程的循环语句以来,每次说到遍历,满脑子只会想到for和while,我们都有面向过程编程的基因。然而在面向对象编程里,一切皆为对象;在设计模式里,一切变化的都应当分离,一起能拆散的都是假耦合!客户端遍历集合,如果使用for或while就必须知道集合的内部数据结构,这就带来了耦合,而且是没有必要的。所以遍历要对象化,从而保证集合独立解耦。而且这种思维已经渗入到各大语言内部。比如,java提供了工具类Iterator,专门来做集合遍历。
迭代器模式类图:
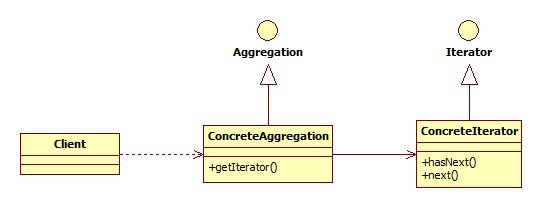
- Aggregation是集合接口,声明了getIterator()方法,返回一个Iterator对象;
- Iterator是遍历器接口,声明hasNext()和next()两个遍历相关方法。
二、应用实战
我们以Android中的ArrayList为例,来讲一下它用到的遍历模式,先看它的相关类图:
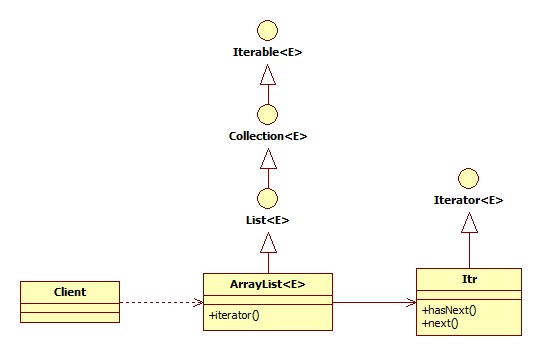
其中ArrayList间接实现Iterable<E>接口,Iterable<E>接口主要声明集合支持iterator()和forEach()两种遍历方式。
/** * Implementing this interface allows an object to be the target of * the "for-each loop" statement. See */ public interface Iterable<T> { /** * Returns an iterator over elements of type {@code T}. * * @return an Iterator. */ Iterator<T> iterator(); /** * Performs the given action for each element of the {@code Iterable} * until all elements have been processed or the action throws an * exception. Unless otherwise specified by the implementing class, * actions are performed in the order of iteration (if an iteration order * is specified). Exceptions thrown by the action are relayed to the * caller. */ default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) { Objects.requireNonNull(action); for (T t : this) { action.accept(t); } } }
Iterator遍历器接口,主要声明hasNext()和next()两个遍历方法:
/** * An iterator over a collection. {@code Iterator} takes the place of * {@link Enumeration} in the Java Collections Framework. Iterators * differ from enumerations in two ways: */ public interface Iterator<E> { /** * Returns {@code true} if the iteration has more elements. * (In other words, returns {@code true} if {@link #next} would * return an element rather than throwing an exception.) * * @return {@code true} if the iteration has more elements */ boolean hasNext(); /** * Returns the next element in the iteration. * * @return the next element in the iteration * @throws NoSuchElementException if the iteration has no more elements */ E next(); }
ArrayList的遍历器Itr实现Iterator接口,实现了hasNext()和next()两个遍历方法:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { // Android-changed: Add "limit" field to detect end of iteration. // The "limit" of this iterator. This is the size of the list at the time the // iterator was created. Adding & removing elements will invalidate the iteration // anyway (and cause next() to throw) so saving this value will guarantee that the // value of hasNext() remains stable and won't flap between true and false when elements // are added and removed from the list. protected int limit = ArrayList.this.size; int cursor; // index of next element to return int lastRet = -1; // index of last element returned; -1 if no such int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor < limit; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public E next() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); int i = cursor; if (i >= limit) throw new NoSuchElementException(); Object[] elementData = ArrayList.this.elementData; if (i >= elementData.length) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); cursor = i + 1; return (E) elementData[lastRet = i]; } }
三、总结
总结:迭代器模式是一种行为型设计模式,这种模式用于顺序访问集合对象的元素,不需要知道集合对象的底层表示,实现了数据与遍历的解耦。
优点:
- 它支持以不同的方式遍历一个聚合对象。
- 在迭代器模式中,增加新的聚合类和迭代器类都很方便,无须修改原有代码。
缺点:增加新的聚合类需要对应增加新的迭代器类,类的个数成对增加,这在一定程度上增加了系统的复杂性。