Reference: http://jermmy.xyz/2017/08/25/2017-8-25-learn-tensorflow-shared-variables/
Tensorflow doesn't know what nodes should be grouped together, unless you tell it to.



name scope VS variable scope tf.name_scope() VS tf.variable_scope() variable scope facilitates variable sharing
tf.variable_scope() implicitly creates a name scope.
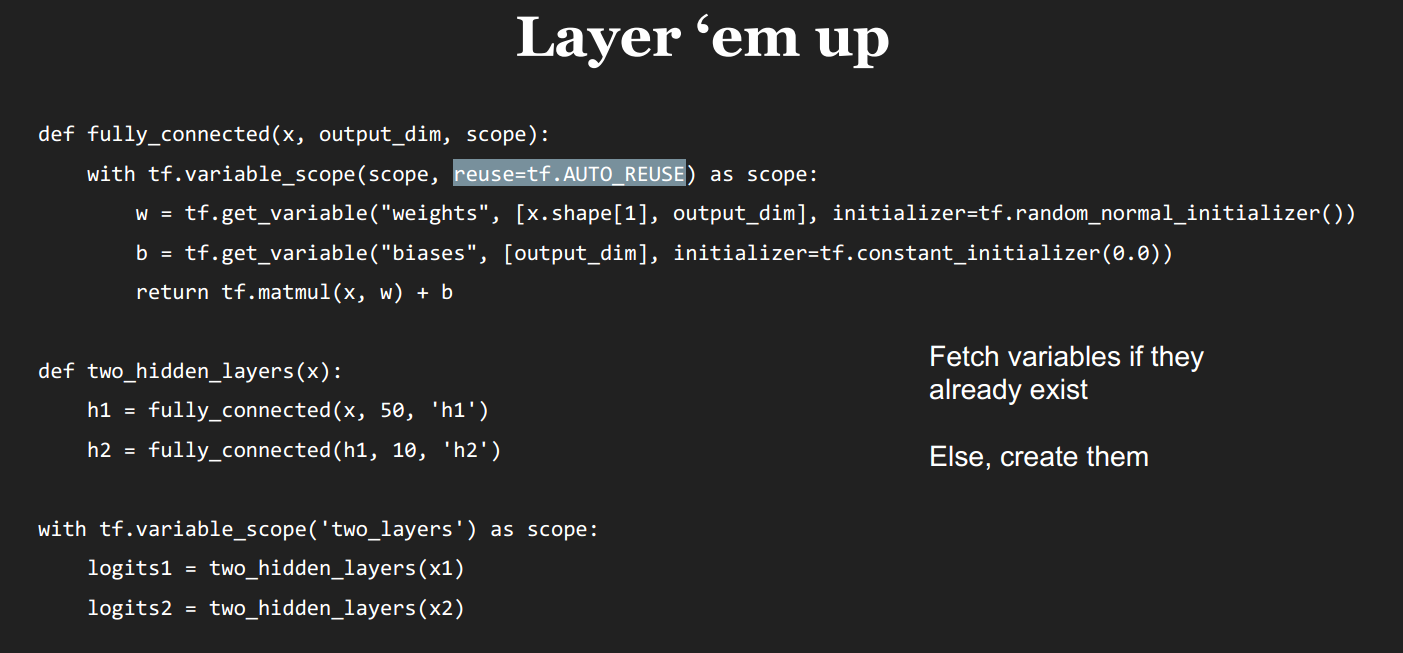
1 """ Examples to demonstrate variable sharing 2 CS 20: 'TensorFlow for Deep Learning Research' 3 cs20.stanford.edu 4 Chip Huyen (chiphuyen@cs.stanford.edu) 5 Lecture 05 6 """ 7 import os 8 os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL']='2' 9 10 import tensorflow as tf 11 12 x1 = tf.truncated_normal([200, 100], name='x1') 13 x2 = tf.truncated_normal([200, 100], name='x2') 14 15 def two_hidden_layers(x): 16 assert x.shape.as_list() == [200, 100] 17 w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([100, 50]), name='h1_weights') 18 b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([50]), name='h1_biases') 19 h1 = tf.matmul(x, w1) + b1 20 assert h1.shape.as_list() == [200, 50] 21 w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([50, 10]), name='h2_weights') 22 b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]), name='2_biases') 23 logits = tf.matmul(h1, w2) + b2 24 return logits 25 26 def two_hidden_layers_2(x): 27 assert x.shape.as_list() == [200, 100] 28 w1 = tf.get_variable('h1_weights', [100, 50], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer()) 29 b1 = tf.get_variable('h1_biases', [50], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0)) 30 h1 = tf.matmul(x, w1) + b1 31 assert h1.shape.as_list() == [200, 50] 32 w2 = tf.get_variable('h2_weights', [50, 10], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer()) 33 b2 = tf.get_variable('h2_biases', [10], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0)) 34 logits = tf.matmul(h1, w2) + b2 35 return logits 36 37 # logits1 = two_hidden_layers(x1) 38 # logits2 = two_hidden_layers(x2)
#### Two sets of variables are created. You want all your inputs to use the same weights and biases!
40 # logits1 = two_hidden_layers_2(x1) 41 # logits2 = two_hidden_layers_2(x2)
####ValueError: Variable h1_weights already exists,disallowed.Did you mean to set reuse=True in VarScope?
42 43 # with tf.variable_scope('two_layers') as scope: 44 # logits1 = two_hidden_layers_2(x1) 45 # scope.reuse_variables() 46 # logits2 = two_hidden_layers_2(x2) 47 48 # with tf.variable_scope('two_layers') as scope: 49 # logits1 = two_hidden_layers_2(x1) 50 # scope.reuse_variables() 51 # logits2 = two_hidden_layers_2(x2) 52 53 def fully_connected(x, output_dim, scope): 54 with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE) as scope: 55 w = tf.get_variable('weights', [x.shape[1], output_dim], initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer()) 56 b = tf.get_variable('biases', [output_dim], initializer=tf.constant_initializer(0.0)) 57 return tf.matmul(x, w) + b 58 59 def two_hidden_layers(x): 60 h1 = fully_connected(x, 50, 'h1') 61 h2 = fully_connected(h1, 10, 'h2') 62 63 with tf.variable_scope('two_layers') as scope: 64 logits1 = two_hidden_layers(x1) 65 # scope.reuse_variables() 66 logits2 = two_hidden_layers(x2) 67 68 writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('./graphs/cool_variables', tf.get_default_graph()) 69 writer.close()