简介
什么是grpc
grpc是一个由google推出的、高性能、开源、通用的rpc框架。它是基于HTTP2协议标准设计开发,默认采用Protocol Buffers数据序列化协议,支持多种开发语言。
什么是protobuf buffers
ProtoBuf buffer 是一种数据表达方式,以.proto结尾的数据文件,可以类比json、xml等。针对ProtoBuf buffer 数据源,可以利用protoc 工具来生成各种语言的访问类。其操作步骤:
- 定义数据元;
- 生成数据元的访问类。
优点:
- 编解码速度更快;
- 传输的数据更小。
protobuf buffers定义数据元的语法
一个.proto文件,主要包括以下部分:
syntax = "proto3";
package studentpb;
service Student {
rpc add (StudentReqs) returns (StudentReply) {} //新增学生接口
}
message StudentReqs {
repeated StudentReq s = 1;
}
message StudentReq{
string name= 1;
int32 age = 2;
}
message StudentReply {
int32 errno = 1;
string errmsg = 2;
}
- 关键字syntax:指定使用的proto3语法;
- 关键字package:定义一个包,需要注意避免命名冲突;
- 关键字message来定义请求或相应需要使用的消息格式,里面可以包含了不同类型的字段 。一个.proto文件中,可以包含多个message的定义。
- 关键字server来定一个服务。GRPC的服务是通过参数和返回类型来指定可以远程调用的方法。
字段的约束规则
- repeated:前置repeated关键词,声明该字段为数组类型。
- proto3不支持proto2中的required和optional关键字。
字段支持的类型
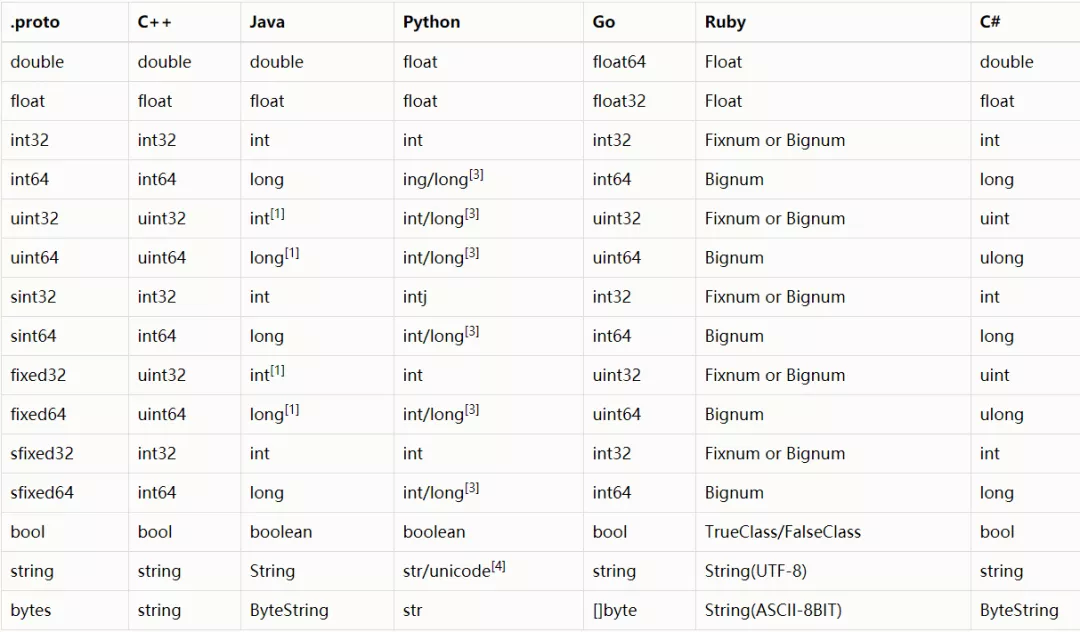
支持基础类型、枚举类型、map类型、数组类型、message类型等。
- 基础类型
- 枚举类型
syntax = "proto3";
message Student{
string name = 1;
// 定义enum类型
enum Sex {
BOY = 0;
GIRL = 1;
}
Sex sex = 1; // 使用Corpus作为字段类型
}
- message类型
syntax = "proto3";
message Students {
repeated Student s = 1;
}
message Student{
string name = 1;
// 定义enum类型
enum Sex {
BOY = 0;
GIRL = 1;
}
Sex sex = 4; // 使用Corpus作为字段类型
}
如何利用protoc 工具生成访问类
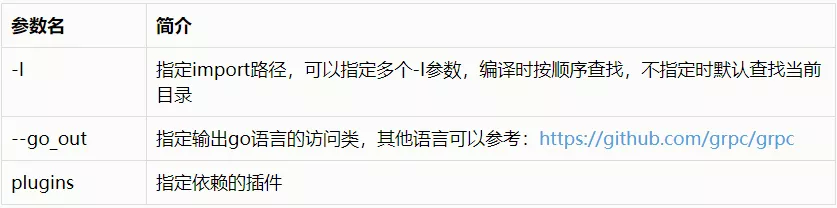
prooc常用参数
案例

其中“t.proto”内容如下:
syntax = "proto3";
package studentpb;
service Student {
rpc add (StudentReqs) returns (StudentReply) {} //新增学生接口
}
message StudentReqs {
repeated StudentReq s = 1;
}
message StudentReq{
string name= 1;
int32 age = 2;
}
message StudentReply {
int32 errno = 1;
string errmsg = 2;
}
生成go访问类的语句如下:
protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. protobuf/*.proto
GO如何利用GRPC通信
pb文件
syntax = "proto3";
package studentpb;
service Student {
rpc add (StudentReqs) returns (StudentReply) {} //新增学生接口
}
message StudentReqs {
repeated StudentReq s = 1;
}
message StudentReq{
string name= 1;
int32 age = 2;
}
message StudentReply {
int32 errno = 1;
string errmsg = 2;
}
执行如下命令,生成grpc访问类
protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. *.proto
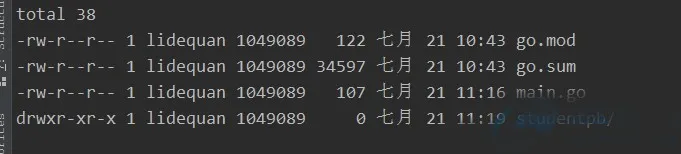
服务端
目录结构如下:
main.go内容如下:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"log"
"net"
"test/studentpb"
)
type Student struct {
}
// 新增students
func (r *Student) Add(ctx context.Context, in *studentpb.StudentReqs) (*studentpb.StudentReply, error) {
return &studentpb.StudentReply{
Errno: 0,
Errmsg: "ok",
}, nil
}
func main() {
// 建立server监听
rpcAddr := "127.0.0.1:8601"
server, err := net.Listen("tcp", rpcAddr)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("failed to listen", rpcAddr)
panic(err)
}
// 建立rpc server
var RpcServer = grpc.NewServer()
err = RpcServer.Serve(server)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
// 对外提供服务
r := new(Student)
studentpb.RegisterStudentServer(RpcServer, r)
select {
}
}
用户端
用户端的目录结构和服务端一样。main.go的内容如下:
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"test/studentpb"
"time"
)
func main() {
addr := "127.0.0.1:8601"
timeout := 10
//建立rpc通道
client, err := grpc.Dial(addr, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
panic("连接失败")
}
defer client.Close()
// 创建studentrpc对象
rpcClient := studentpb.NewStudentClient(client)
// 创建上线文
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), time.Duration(timeout)*time.Second)
defer cancel()
//封装请求参数
req := &studentpb.StudentReqs{}
req.S = append(req.S, &studentpb.StudentReq{Name:"张三", Age:12})
// 打印结果
res , err := rpcClient.Add(ctx, req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("请求错误", err)
} else {
fmt.Println(res.GetErrno(), res.GetErrmsg())
}
}