一、Spring中实现异步执行
在这里我先以事件的机制举例,注意默认情况下事件的发布与监听都是同步执行的。那么我们来看一看基于异步事件的例子该怎么写
首先还是定义事件:
package com.bdqn.lyrk.ssm.study.app.entity.event; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; /** * 定义一个饥饿的事件 * * @author chen.nie * @date 2018/6/26 **/ public class HungryEvent extends ApplicationEvent { /** * Create a new ApplicationEvent. * * @param source the object on which the event initially occurred (never {@code null}) */ public HungryEvent(Object source) { super(source); } }
定义一个Person类,该类主要发布相关事件
package com.bdqn.lyrk.ssm.study.app.entity.event; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import static com.bdqn.lyrk.ssm.study.app.utils.Printer.print; @Component public class Person implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware { private int hungry; private String name = "admin"; public String getName() { return name; } private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher; public void setHungry(int hungry) { this.hungry = hungry; } public void work(){ if (hungry < 10) { print("饿了,谁来帮我做做饭.."); applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new HungryEvent(this)); } print("继续工作...."); } @Override public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) { this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher; } }
定义事件的监听者
package com.bdqn.lyrk.ssm.study.app.entity; import com.bdqn.lyrk.ssm.study.app.entity.event.HungryEvent; import com.bdqn.lyrk.ssm.study.app.entity.event.Person; import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import static com.bdqn.lyrk.ssm.study.app.utils.Printer.print; @Component public class TeacherEntity { @Async @EventListener(HungryEvent.class) public void cook(HungryEvent hungryEvent) throws InterruptedException { Person person = (Person) hungryEvent.getSource(); print(person.getName() + "饿了开始做饭"); Thread.sleep(5000); print("饭做好了..."); } }
在这里@Async表明调用该方法时,会开启一个线程进行异步执行。@EventListener表明该方法会监听对应的事件
AppConfig的配置
@Configuration
@ComponentScan @EnableAsync public class AppConfig{ /** * 定义异步线程任务 * * @author chen.nie * @date 2018/6/27 **/ @Bean public Executor taskExecutor() { ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor(); return executorService; } }
在这里顺便用Printer方法打印出线程名称
public class Printer { public static void print(String content) { System.out.printf("[%s]--%s%n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), content); } }
main方法:
public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext appApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); Person person = appApplicationContext.getBean(Person.class); person.setHungry(1); person.work(); appApplicationContext.close(); }
执行结果:
[main]--饿了,谁来帮我做做饭.. [main]--继续工作.... [pool-1-thread-1]--admin饿了开始做饭 [pool-1-thread-1]--饭做好了...
二、Async的原理分析
2.1 @EnableAsync
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(AsyncConfigurationSelector.class) public @interface EnableAsync { /** * Indicate the 'async' annotation type to be detected at either class * or method level. * <p>By default, both Spring's @{@link Async} annotation and the EJB 3.1 * {@code @javax.ejb.Asynchronous} annotation will be detected. * <p>This attribute exists so that developers can provide their own * custom annotation type to indicate that a method (or all methods of * a given class) should be invoked asynchronously. */ Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class; /** * Indicate whether subclass-based (CGLIB) proxies are to be created as opposed * to standard Java interface-based proxies. * <p><strong>Applicable only if the {@link #mode} is set to {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}</strong>. * <p>The default is {@code false}. * <p>Note that setting this attribute to {@code true} will affect <em>all</em> * Spring-managed beans requiring proxying, not just those marked with {@code @Async}. * For example, other beans marked with Spring's {@code @Transactional} annotation * will be upgraded to subclass proxying at the same time. This approach has no * negative impact in practice unless one is explicitly expecting one type of proxy * vs. another — for example, in tests. */ boolean proxyTargetClass() default false; /** * Indicate how async advice should be applied. * <p>The default is {@link AdviceMode#PROXY}. * @see AdviceMode */ AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY; /** * Indicate the order in which the {@link AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor} * should be applied. * <p>The default is {@link Ordered#LOWEST_PRECEDENCE} in order to run * after all other post-processors, so that it can add an advisor to * existing proxies rather than double-proxy. */ int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; }
绝大多数的特性注解@EnableXXX都有个特性使用@Import进行导入操作,那么我们不妨在看一下AsyncConfigurationSelector这个类
public class AsyncConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableAsync> { private static final String ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME = "org.springframework.scheduling.aspectj.AspectJAsyncConfiguration"; /** * {@inheritDoc} * @return {@link ProxyAsyncConfiguration} or {@code AspectJAsyncConfiguration} for * {@code PROXY} and {@code ASPECTJ} values of {@link EnableAsync#mode()}, respectively */ @Override public String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) { switch (adviceMode) { case PROXY: return new String[] { ProxyAsyncConfiguration.class.getName() }; case ASPECTJ: return new String[] { ASYNC_EXECUTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME }; default: return null; } } }
看到这里我们已经能猜到Spring中的Async是基于AOP实现的,毕竟我们看到了AspectJ与Proxy了嘛
2.2、ProxyAsyncConfiguration
/* * Copyright 2002-2015 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.scheduling.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Role; import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils; import org.springframework.scheduling.config.TaskManagementConfigUtils; import org.springframework.util.Assert; /** * {@code @Configuration} class that registers the Spring infrastructure beans necessary * to enable proxy-based asynchronous method execution. * * @author Chris Beams * @author Stephane Nicoll * @since 3.1 * @see EnableAsync * @see AsyncConfigurationSelector */ @Configuration @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public class ProxyAsyncConfiguration extends AbstractAsyncConfiguration { @Bean(name = TaskManagementConfigUtils.ASYNC_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME) @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor asyncAdvisor() { Assert.notNull(this.enableAsync, "@EnableAsync annotation metadata was not injected"); AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor bpp = new AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(); Class<? extends Annotation> customAsyncAnnotation = this.enableAsync.getClass("annotation"); if (customAsyncAnnotation != AnnotationUtils.getDefaultValue(EnableAsync.class, "annotation")) { bpp.setAsyncAnnotationType(customAsyncAnnotation); } if (this.executor != null) { bpp.setExecutor(this.executor); } if (this.exceptionHandler != null) { bpp.setExceptionHandler(this.exceptionHandler); } bpp.setProxyTargetClass(this.enableAsync.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")); bpp.setOrder(this.enableAsync.<Integer>getNumber("order")); return bpp; } }
在这里我们可以看到此类是一个Spring的配置类,主要用于创建AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的Bean
2.3、AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
首先我先贴一下这个类图:
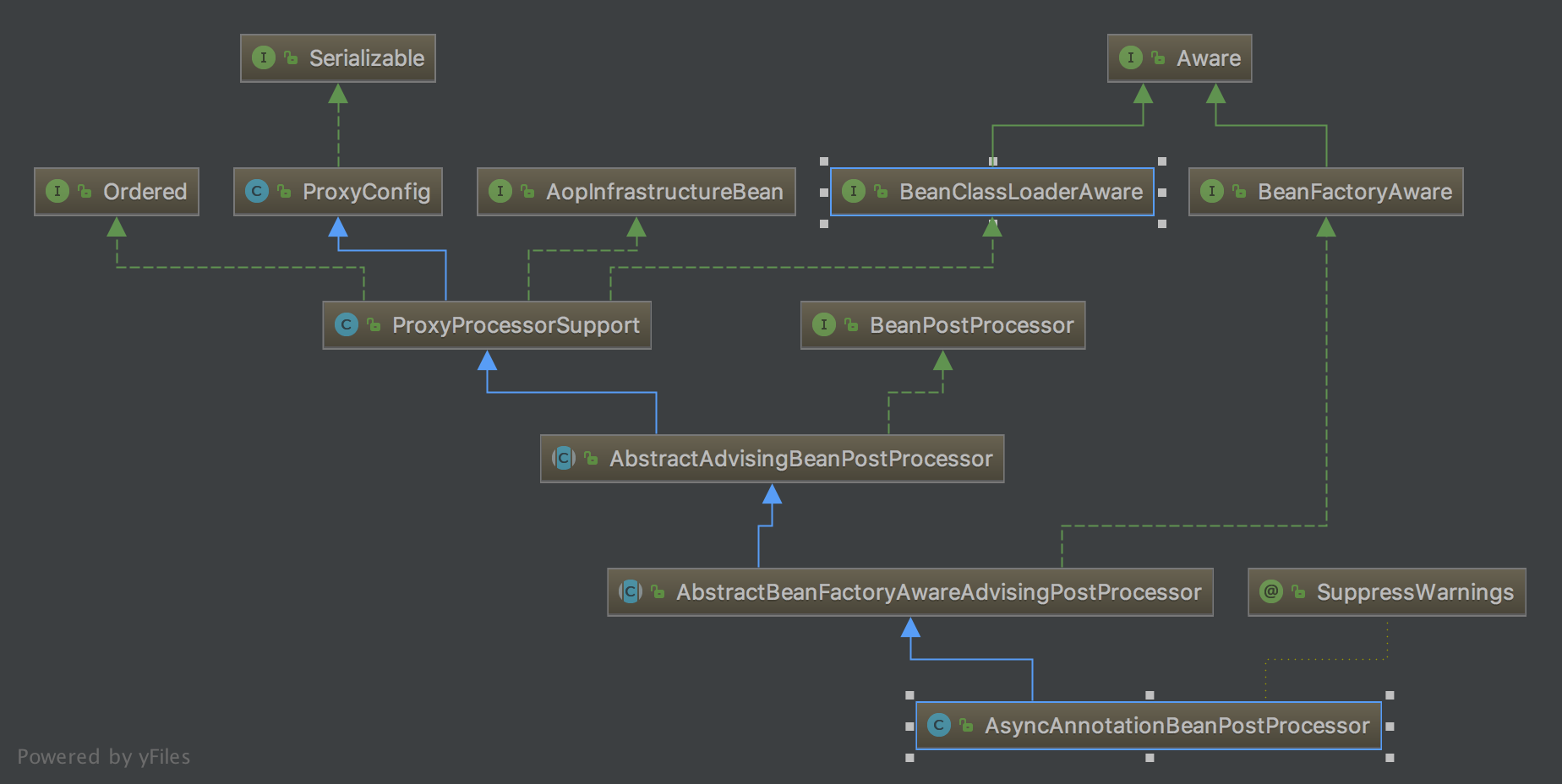
我们先看一下它的父类AbstractAdvisingBeanPostProcessor里重写的方法,在该方法里动态改变Bean的相关属性
@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) { if (bean instanceof AopInfrastructureBean) { // Ignore AOP infrastructure such as scoped proxies. return bean; } // 如果为Advised对象且当前的bean适配当前的Advice,则将advisor添加到Advised里 if (bean instanceof Advised) { Advised advised = (Advised) bean; if (!advised.isFrozen() && isEligible(AopUtils.getTargetClass(bean))) { // Add our local Advisor to the existing proxy's Advisor chain... if (this.beforeExistingAdvisors) { advised.addAdvisor(0, this.advisor); } else { advised.addAdvisor(this.advisor); } return bean; } } // 如果当前的bean复合当前的通知 if (isEligible(bean, beanName)) { ProxyFactory proxyFactory = prepareProxyFactory(bean, beanName); if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { evaluateProxyInterfaces(bean.getClass(), proxyFactory); } proxyFactory.addAdvisor(this.advisor); customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader()); } // No async proxy needed. return bean; }
而AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 重写了BeanFactoryAware接口方法,请大家关注一下属性Executor和setBeanFactory方法:
public class AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends AbstractBeanFactoryAwareAdvisingPostProcessor { /** * The default name of the {@link TaskExecutor} bean to pick up: "taskExecutor". * <p>Note that the initial lookup happens by type; this is just the fallback * in case of multiple executor beans found in the context. * @since 4.2 * @see AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor#DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME */ public static final String DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME = AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor.DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME; protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); private Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType; private Executor executor; private AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler; public AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() { setBeforeExistingAdvisors(true); } /** * Set the 'async' annotation type to be detected at either class or method * level. By default, both the {@link Async} annotation and the EJB 3.1 * {@code javax.ejb.Asynchronous} annotation will be detected. * <p>This setter property exists so that developers can provide their own * (non-Spring-specific) annotation type to indicate that a method (or all * methods of a given class) should be invoked asynchronously. * @param asyncAnnotationType the desired annotation type */ public void setAsyncAnnotationType(Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType) { Assert.notNull(asyncAnnotationType, "'asyncAnnotationType' must not be null"); this.asyncAnnotationType = asyncAnnotationType; } /** * Set the {@link Executor} to use when invoking methods asynchronously. * <p>If not specified, default executor resolution will apply: searching for a * unique {@link TaskExecutor} bean in the context, or for an {@link Executor} * bean named "taskExecutor" otherwise. If neither of the two is resolvable, * a local default executor will be created within the interceptor. * @see AsyncAnnotationAdvisor#AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(Executor, AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler) * @see AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor#getDefaultExecutor(BeanFactory) * @see #DEFAULT_TASK_EXECUTOR_BEAN_NAME */ public void setExecutor(Executor executor) { this.executor = executor; } /** * Set the {@link AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler} to use to handle uncaught * exceptions thrown by asynchronous method executions. * @since 4.1 */ public void setExceptionHandler(AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler) { this.exceptionHandler = exceptionHandler; } @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) { super.setBeanFactory(beanFactory); AsyncAnnotationAdvisor advisor = new AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(this.executor, this.exceptionHandler); if (this.asyncAnnotationType != null) { advisor.setAsyncAnnotationType(this.asyncAnnotationType); } advisor.setBeanFactory(beanFactory); this.advisor = advisor; } }
在这里指定对应的this.advisor为AsyncAnnotationAdvisor。
2.4、AsyncAnnotationAdvisor
在这里我们先看看它的构造函数:
public AsyncAnnotationAdvisor(Executor executor, AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler) { Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<? extends Annotation>>(2); asyncAnnotationTypes.add(Async.class); try { asyncAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.ejb.Asynchronous", AsyncAnnotationAdvisor.class.getClassLoader())); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { // If EJB 3.1 API not present, simply ignore. } if (exceptionHandler != null) { this.exceptionHandler = exceptionHandler; } else { this.exceptionHandler = new SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler(); } this.advice = buildAdvice(executor, this.exceptionHandler); this.pointcut = buildPointcut(asyncAnnotationTypes); }
在这里主要是构建通知和切点,下面我们分别来看看怎么实现的:
buildAdvice:
protected Advice buildAdvice(Executor executor, AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler) { return new AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor(executor, exceptionHandler); }
AnnotationAsyncExecutionInterceptor的父类实现了MethodInterceptor接口,我们来看看它重写的方法:
/** * Intercept the given method invocation, submit the actual calling of the method to * the correct task executor and return immediately to the caller. * @param invocation the method to intercept and make asynchronous * @return {@link Future} if the original method returns {@code Future}; {@code null} * otherwise. */ @Override public Object invoke(final MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable { Class<?> targetClass = (invocation.getThis() != null ? AopUtils.getTargetClass(invocation.getThis()) : null); Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(invocation.getMethod(), targetClass); final Method userDeclaredMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod); //取@Async里的value属性对应Bean,如果没有值取名字为taskExecutor的Bean AsyncTaskExecutor executor = determineAsyncExecutor(userDeclaredMethod); if (executor == null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "No executor specified and no default executor set on AsyncExecutionInterceptor either"); } Callable<Object> task = new Callable<Object>() { @Override public Object call() throws Exception { try { //异步执行本体方法 Object result = invocation.proceed(); if (result instanceof Future) { return ((Future<?>) result).get(); } } catch (ExecutionException ex) { handleError(ex.getCause(), userDeclaredMethod, invocation.getArguments()); } catch (Throwable ex) { handleError(ex, userDeclaredMethod, invocation.getArguments()); } return null; } }; return doSubmit(task, executor, invocation.getMethod().getReturnType()); }
buildPointCut:
/** * Calculate a pointcut for the given async annotation types, if any. * @param asyncAnnotationTypes the async annotation types to introspect * @return the applicable Pointcut object, or {@code null} if none */ protected Pointcut buildPointcut(Set<Class<? extends Annotation>> asyncAnnotationTypes) { ComposablePointcut result = null; for (Class<? extends Annotation> asyncAnnotationType : asyncAnnotationTypes) { Pointcut cpc = new AnnotationMatchingPointcut(asyncAnnotationType, true); Pointcut mpc = AnnotationMatchingPointcut.forMethodAnnotation(asyncAnnotationType); if (result == null) { result = new ComposablePointcut(cpc); } else { result.union(cpc); } result = result.union(mpc); } return result; }
在这里使用AnnotationMatchingPointcut,该切点会在有对应的annotation方法上切入相关的Advice,此处asyncAnnotationTypes对应的就是@Async
三、总结
Spring异步机制用到如下几种方式实现:
1)重写BeanPostProcessor来改变Bean的属性,在这里针对Advised或者ProxyFactory动态添加定义好的通知AsyncAnnotationAdvisor
2) 使用AOP的机制来,异步执行@Async标记的方法